Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Due to lack of validated outcome measures in non-psoriatic peripheral spondyloarthritis (pSpA), recent studies in this patient (pt) population have used varying endpoints [1]. Thus, developing new pSpA-specific indices may be worthwhile. Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) has been validated in psoriatic arthritis but not in pSpA. The objective of this study is to evaluate the performance of a modification of the MDA criteria (excluding psoriasis) in pSpA patients (pts) from the ABILITY-2 study [2].
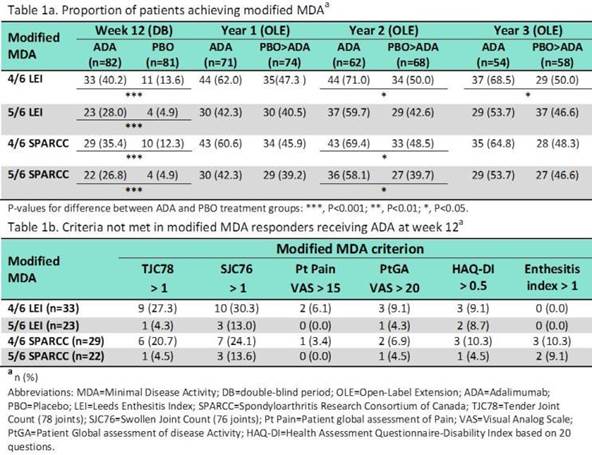
Methods: This post-hoc analysis evaluated the validity of a modified MDA (mMDA) in pSpA. ABILITY-2 was a 12-week trial comparing adalimumab (ADA) with placebo (PBO) in pSpA followed by a 144 week extension. The mMDA for pSpA was defined as achieving at least 4 or 5 out of the following 6 criteria: (1) tender joint count (TJC, 78 joints) ≤ 1; (2) swollen joint count (SJC, 76 joints) ≤ 1; (3) pt pain visual analog scale (VAS) ≤ 15 of 100 mm; (4) pt global activity (PtGA) VAS ≤ 20 of 100 mm; (5) health assessment questionnaire–disability index (HAQ-DI)≤ 0.5; and (6) tender entheseal points ≤ 1. Enthesitis was assessed by the Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) or the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) Enthesitis Index for this analysis. The proportion of pts achieving the 4 different versions of mMDA were evaluated (either 4 or 5 of 6 using LEI and either 4 or 5 of 6 using SPARCC). The correlations between mMDA and the novel pSpA response criteria [PSpARC] remission from ABILITY-2 and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score Inactive Disease [ASDAS ID] were evaluated by tetrachoric correlation (rtet).
Results: Of the 163 pts (82 ADA, 81 PBO) who completed wk 12, significantly greater proportion of pts receiving ADA achieved mMDA (regardless of the definition) compared with PBO (P<0.001 for all comparisons, Table 1a). The proportion of mMDA responders at yrs 1, 2, and 3 was numerically higher in pts initially randomized to ADA. The mMDA response showed a stronger positive correlation with PSpARC remission (rtet > 0.9) than ASDAS ID (rtet > 0.75) at wk 12, and yrs 1-3. Among pts who fulfilled the 4/6 criteria (LEI or SPARCC), approximately 20-30% of pts did not meet TJC and SJC criterion (Table 1b). However, the 5/6 criteria (LEI or SPARCC) were more stringent with approximately 5% and 13% not meeting the TJC and SJC criterion, respectively.
Conclusion: All 4 versions of mMDA discriminated between ADA and PBO treatment groups; both entheseal indices performed similarly. The mMDA (particularly the 5/6 versions which closely represents the concept of MDA) could be an appropriate treatment target in pSpA pts. References:
1. Turina, M.C., et al., Ann Rheum Dis, 2015. (doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-207235).
2. Mease, P., et al., Arthritis Rheumatol, 2015. 67(4): p. 914-23.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates LC, Abraham S, Tillett W, Mease PJ, Ramiro S, Xia Y, Wang X, Pangan AL, Song IH. Performance of Modified Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) in Patients with Peripheral Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-modified-minimal-disease-activity-mda-in-patients-with-peripheral-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-modified-minimal-disease-activity-mda-in-patients-with-peripheral-spondyloarthritis/