Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Although the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) is used to assess the activity of axial disease in patients (pts) with PsA, only one of its questions is specific to axial symptoms. Alternatively, the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) excludes assessment of enthesitis, gives less weight to peripheral activity and is considered more objective than the BASDAI. The current post hoc analysis compared the performance of BASDAI and ASDAS in evaluating symptoms of axial involvement in pts with axial PsA (axPsA).
Methods: Pts enrolled in the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 studies (D1+D2) were adults with active PsA despite standard therapies. D1 pts had ≥3 swollen and ≥3 tender joints (SJC; TJC) and CRP ≥0.3 mg/dL; D2 pts had SJC ≥5, TJC ≥5 and CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL. 31% of D1 pts received 1-2 prior tumor necrosis factor inhibitors; D2 pts were biologic-naïve. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO) with crossover to GUS Q4W at W24. axPsA was defined by presence of sacroiliitis based on previous radiograph or MR imaging confirmation. Data were pooled across all treatment groups. In addition to BASDAI and ASDAS, modified versions excluding the peripheral arthritis and enthesitis questions (mBASDAI) and the peripheral arthritis question (mASDAS) were calculated. Normalized (scale of 0-10) versions of ASDAS and mASDAS were calculated based on maximum scores of ≈7 and ≈6.3, respectively. The correlation of BASDAI/mBASDAI and ASDAS/mASDAS with SJC, TJC, enthesitis, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-fatigue, pt pain, pt global, and physician global was assessed with Pearson’s correlation coefficient. The cross-sectional and longitudinal (W52) effects of Leeds enthesitis index (LEI), SJC, and axPsA on BASDAI/mBASDAI and ASDAS/mASDAS were assessed with mixed models.
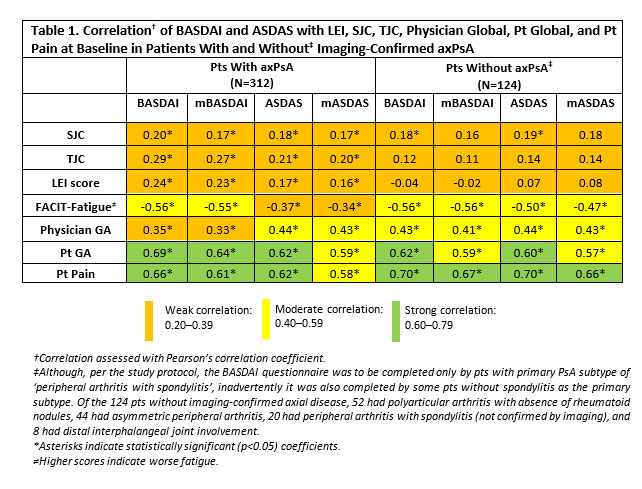
Results: 436 pts with available baseline (BL) BASDAI information were included in the analysis. In pts with axPsA, BASDAI showed weak correlation with SJC, TJC, LEI, and physician global; moderate correlation with fatigue; and strong correlation with pt global and pt pain. Similar results were observed for ASDAS and modified versions. Among pts without axPsA, correlations of BASDAI and ASDAS with SJC, TJC, and LEI remained weak; correlations with pt global and pt pain remained strong. Longitudinally, among pts with and without BL enthesitis, respectively, LEI and SJC showed significant but not clinically important associations with either outcome. Presence of axial disease was associated with significantly greater BASDAI and ASDAS scores, at BL and longitudinally, without differences in the incremental effect on BASDAI, normalized ASDAS, or their modified versions.
Conclusion: In pts with axPsA, the BASDAI and ASDAS performed similarly, with both demonstrating weak correlations with peripheral arthritis and moderate/strong correlations with pt fatigue and pain. The BASDAI and ASDAS also showed similar ability to discern changes in axial disease activity. These results suggest that both BASDAI and ASDAS are valid, and perform comparably, in assessing activity of axial disease in PsA pts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Gladman D, Chakravarty S, Gong C, Shawi M, Rampakakis E, Mitsumasa K, Soriano E, Mease P. Performance of BASDAI vs. ASDAS in Evaluating Axial Involvement in Patients with PsA Treated with Guselkumab: Pooled Analysis of Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-basdai-vs-asdas-in-evaluating-axial-involvement-in-patients-with-psa-treated-with-guselkumab-pooled-analysis-of-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-basdai-vs-asdas-in-evaluating-axial-involvement-in-patients-with-psa-treated-with-guselkumab-pooled-analysis-of-two-phase-3-studies/