Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treat-to-Target (T2T), achieving a DAS28 lower than 2.6 (remission) or below 3.2 (low disease activity), is the main management strategy. The Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM) is an interactive mobile disease management tool, including the doctors¡¯ and patients¡¯ application system. The patients can perform self-evaluation, including DAS28, morning stiffness time (MST) and HAQ, and enter medical records (including medication and laboratory test results) through the mobile application. The data synchronizes to the mobiles of authorized rheumatologists through cloud data base and advices could be delivered. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the patterns of T2T and related influential factors among RA patients after applying SSDM in real world.
Methods: Patients were registered through downloading the SSDM application, then were trained to master SSDM by health professionals in clinics. The first assessment for DAS28 were performed as baseline. The patients were required to perform repeated assessments once a month after leaving hospital.
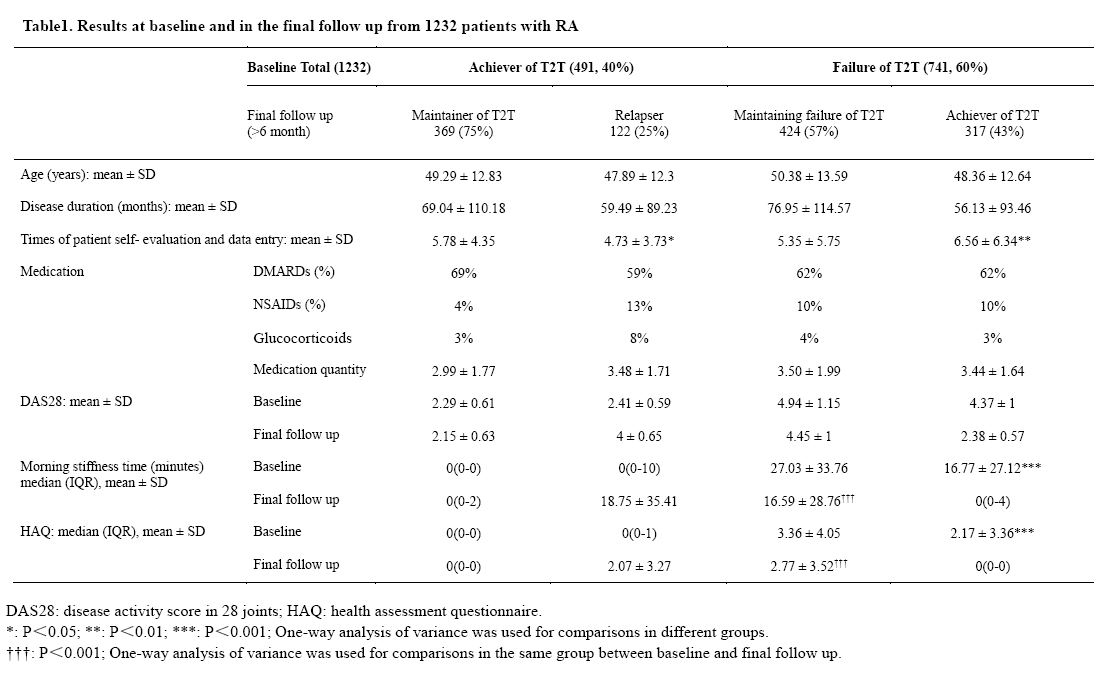
Results: From June 2014 to June 2017, 1,232 RA patients from 145 hospitals across China were followed up for more than 6 months through SSDM, and the results at baseline and in final follow up were shown in table 1. The rate of T2T achievers were 40% (491/1,232) at baseline, and improved significantly to 64% (793/1,232) after 6 month follow up. Among T2T achievers at baseline, 75% (369/491) maintained T2T, 25% (122/491) relapsed. Compared with relapsers, T2T maintainers performed more self-evaluation (5.78 vs 4.73, P=0.017), took medications at higher ratio on DEMARDs (69% vs 59%), lower ratio on NSAIDs (4% vs 13%, p<0.01) or glucocorticoid (3% vs 8%, p<0.01). Among patients failed to reach T2T at baseline, 57% (424/741) achieved T2T after 6 months. Comparing with 6 month failure (317/741), new T2T achievers got shorter the MST (16.77¡À27.12 vs 27.03¡À33.76, p£¼0.001), lower HAQ score (2.17 ¡À 3.36 vs 3.36 ¡À 4.05, p£¼0.001) at baseline, performed more times of self-evaluation (6.56 vs 5.35, P=0.007). However, even in patients of 6 month failure, the MST and HAQ score improved significantly in final follow up comparing with those at baseline (16.59¡À28.76 vs 27.03¡À33.76, p£¼0.001; 2.77¡À3.52 vs 3.36¡À4.05, p£¼0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: After interactive disease management via SSDM for more than 6 months, the rate of T2T in RA patients increased significantly. More NSAIDs and glucocorticoid but less DMARDs were associated with higher probability of relapse. The patients perform more self-evaluations through SSDM had lower probability of relapse and higher T2T maintaining and achievement. SSDM is a valuable tool for long term RA follow-up through empowering patients. Future RCT of improvingT2T outcome through intervention of above influential factors with SSDM is warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mu R, Yang J, Wei H, Fan W, Huang J, Wang H, Ru J, Wang Y, Zou J, Dong J, Duan X, He F, Shi X, Xin X, Xiao F, Xiao H, Jia Y, Wang M, He L, Bai R, Huang X, Wu B, Li Z. Pattern and Influential Factors in Promoting Treat-to-Target (T2T) for Follow-up RA Patients with a Rheumatologist-Patient Interactive Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM): A Cohort Study from China [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pattern-and-influential-factors-in-promoting-treat-to-target-t2t-for-follow-up-ra-patients-with-a-rheumatologist-patient-interactive-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm-a-cohort-study-from-ch/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pattern-and-influential-factors-in-promoting-treat-to-target-t2t-for-follow-up-ra-patients-with-a-rheumatologist-patient-interactive-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm-a-cohort-study-from-ch/