Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Treat-to-target guidelines for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) suggest adjusting therapy every 3-6 months for pts who fail to achieve a disease activity target. However, pts treated with adalimumab (ADA) plus methotrexate (MTX) can exhibit a delayed clinical response without radiographic damage.1 Data from the Optimal Protocol for Treatment Initiation with MTX and ADA (OPTIMA) trial were used to evaluate differences in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) between pts maintained on ADA+MTX after failing to achieve a stable treatment target on that regimen compared to those treated with ADA+MTX after failing to respond to MTX monotherapy.
Methods: MTX-naïve pts ≥18 years of age with RA <1 year and active disease were randomized to ADA+MTX (N=515) or placebo (PBO) plus MTX (N=517) for 26 wks (Period 1). Those who failed to achieve stable low disease activity (LDA) (DAS28CRP <3.2 at wks 22 and 26) were offered open-label (OL) ADA+MTX for an additional 52 wks (Period 2). Pts completed the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) questionnaire, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy Fatigue (FACIT-F) subscale, Patient Acceptable Symptom State (PASS) classifier, and other PRO measures at wk 0 (baseline) and subsequent time points.
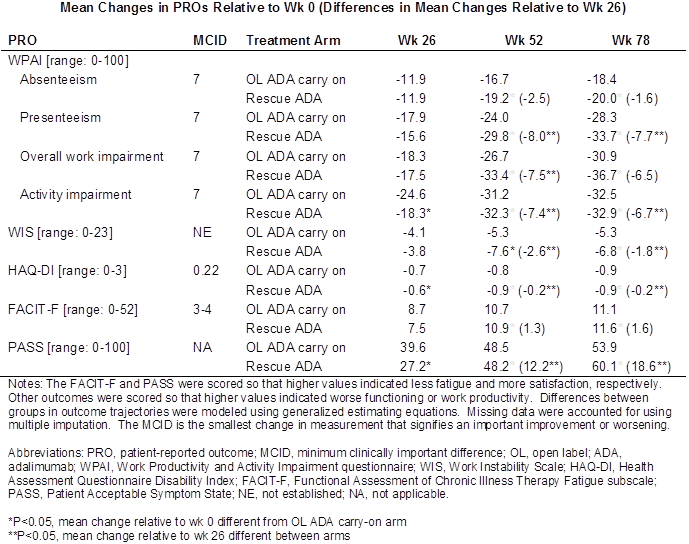
Results: At the end of Period 1, 259/466 (56%) ADA+MTX pts failed to achieve stable LDA (OL ADA carry-on arm) compared with 348/460 (76%) PBO+MTX pts (rescue ADA arm). Baseline characteristics for the OL ADA carry-on arm and rescue ADA arm were comparable, though pts in the former were less likely to be employed (46.8% vs. 55.7%, P=0.029) and were more fatigued (mean FACIT-F score: 23.6 vs. 25.8, P=0.022) than pts in the latter. Between wks 0 and 26, pts in the OL ADA carry-on arm had significantly greater improvements in physical functioning (mean HAQ-DI score change: -0.7 vs. -0.6, P=0.001), activity impairment (mean WPAI activity impairment score change: -24.6% vs. -18.3%, P=0.002), and health satisfaction (change in percent in PASS: 39.6% vs. 27.2%, P<0.001) than pts in the rescue ADA arm. Compared with pts in the OL ADA carry-on arm, pts in the rescue ADA arm experienced significantly greater improvements in most PROs throughout Period 2. However, differences between the groups in improvements at wk 78 relative to wk 0 were statistically non-significant.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that sustained treatment with ADA+MTX in the absence of an initial clinical response can yield substantial benefits beyond the inhibition of radiographic progression. In addition, for patients not achieving stable LDA with MTX alone, the introduction of ADA after six months of treatment allows for significant improvements in work productivity and other PROs.
Reference:
1Keystone E et al. ACR/AHRP Scientific Meeting, Atlanta, GA, November 7-11, 2010. P1102.
Disclosure:
A. Kavanaugh,
Abbott Laboratories,
5;
R. F. van Vollenhoven,
Abbott Laboratories,
5,
Abbott Laboratories,
2;
P. Emery,
Abbott Laboratories,
5;
J. W. Shaw,
Abbott Laboratories,
3;
M. A. Cifaldi,
Abbott Laboratories,
3,
Abbott Laboratories,
1;
S. Florentinus,
Abbott Laboratories,
1,
Abbott Laboratories,
3;
J. S. Smolen,
Abbott Laboratories,
5,
Abbott Laboratories,
2.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-failing-to-achieve-stable-low-disease-activity-comparing-addition-of-adalimumab-to-methotrexate-monotherapy-with-maintenance-on-adalim/
