Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Miscellanous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Disease Poster III: Autoimmune Conditions and Therapies
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) enhance anti-tumor immunity by stimulating a patient’s immune system to fight cancer. ICIs have demonstrated unprecedented response rates in a wide array of cancers, but have a unique side effect profile known as immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that can result in significant morbidity and mortality. Inflammatory arthritis (IA) is one of the most commonly encountered rheumatic irAEs and can persist after ICI cessation. Early recognition and appropriate treatment is critical to avoid erosive joint damage. Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) is a commonly used scale for disease severity and guides therapeutic strategy in rheumatoid arthritis, which can also be utilized in ICI-induced IA to inform clinical approach. Additionally, other patient-reported outcome measures (PROs) are used to evaluate pain, physical function, and quality of life in rheumatic diseases. In this study, we evaluate PROs and disease activity to establish the impact of ICI-induced IA. We also evaluate the factors correlating with CDAI, so that management can be optimized to facilitate the goal of achieving remission.
Methods: Patients evaluated at an academic Rheumatology clinic with confirmed ICI-induced IA who were enrolled in our prospective cohort study of rheumatic irAEs were included. Patient and physician data from questionnaires at the baseline visit were analyzed to obtain median and interquartile range (IQR) values. CDAI and Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (mHAQ) scores were calculated. Univariate analysis was completed to assess factors that impacted CDAI score. Multivariate linear regression analysis was performed with variables that were significant in univariate analysis to identify the factors that yielded the greatest impact upon CDAI.
Results: Sixty patients were included in the analysis. 33 patients (55%) were female. Clinical characteristics and PROs are summarized in Table 1.
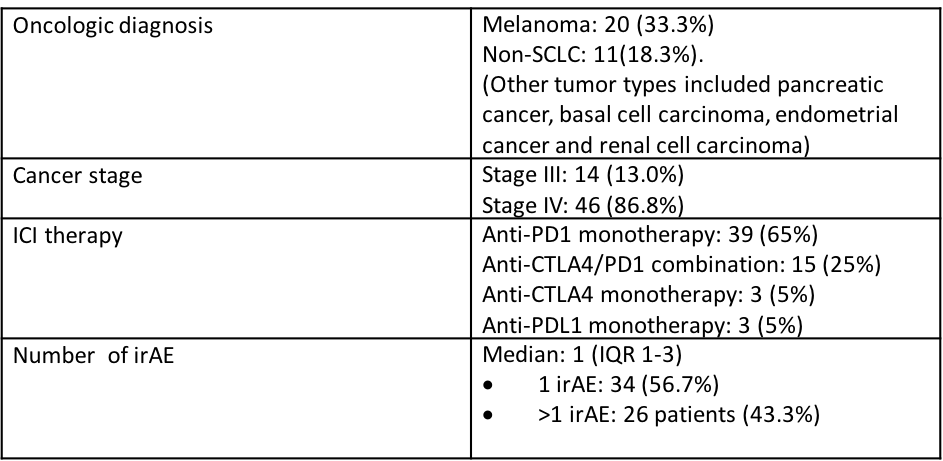
Oncologic history, immunotherapy regimen, and irAE are detailed in Table 2.
Univariate analysis revealed a significant relationship between CDAI and patient stiffness (p 0.001), patient fatigue (p 0.019), mHAQ score (p 0.03) and patient pain (p 0.0001), while age (p 0.212), cancer stage (p 0.9), number of irAEs (p 0.575) were not significant. In multivariate analysis, pain exerted a significant influence on CDAI (0.001).
Conclusion: Patients with ICI-induced IA have high levels of disease activity and experience significant impairment. The majority of patients have moderate or high disease activity. This is significant given the increasing incidence and prevalence of this disease entity. Furthermore, patient-reported pain, fatigue, and stiffness correlated with CDAI in these patients. Physicians should recognize and address these primary symptoms in order to optimize management. Assessment of a wider range of PROs may provide additional insight into the factors that could be modified to maximize health-related quality of life, enhance physical function, and reduce disease activity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Connolly C, Braaten T, Shah A, Bingham C, Cappelli L. Patient Reported Outcomes and Factors Predicting Clinical Disease Activity in Patients with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Inflammatory Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-and-factors-predicting-clinical-disease-activity-in-patients-with-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-inflammatory-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-and-factors-predicting-clinical-disease-activity-in-patients-with-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-inflammatory-arthritis/