Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: 4M125: Pediatric Rheumatology: Outcomes & Quality of Life (1920–1925)
Session Type: ACR/ARP Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is the most common rheumatic disease in children and many medications are available to control the disease. While physician-reported adverse events (AE) are captured in clinical trials and registries, perceptions of parents about side-effects (SE) of anti-rheumatic medications are not well studied.
Using data from the Canadian Alliance of Pediatric Rheumatology Investigators (CAPRI) JIA registry, we describe the frequency and incidence of parent-reported medication SE in children with JIA, compare them to physician-reported AE, and assess their impact on health-related quality of life.
Methods: All children with JIA enrolled within 3 months of diagnosis who had at least one visit documented in the Registry as of May 9, 2019 were included in this analysis. At every clinic visit parents were asked “Is your child having any side effects from medications taken for his/her arthritis?” They selected SE from a 17-item list, added any not listed, and rated their overall severity on a 21-point numerical rating scale from 0=no problem, to 10=very severe. Physicians reported AE that required additional visits, tests or treatments (irrespective of their cause) and used a standard 18-item list, similar to other registries. Health-related quality of life was assessed using the parent’s global assessment from Singh’s Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire (CHAQ) “Considering all the ways that arthritis affects your child rate how your child is doing”, from 0=very well, to 10=very poor; and the child’s answer to Feldman’s Quality of My Life questionnaire (QoML) “Considering my HEALTH my life is” from 0=the WORST, to 10=the BEST (if the parent felt the child could answer the question).
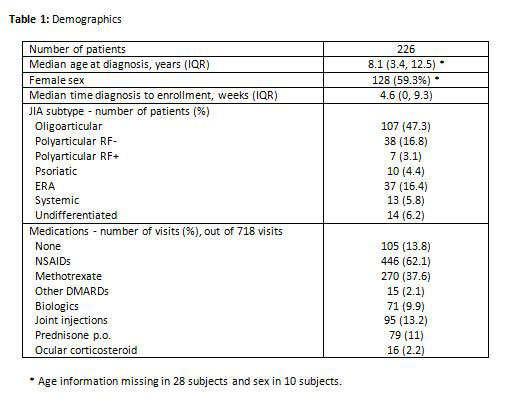
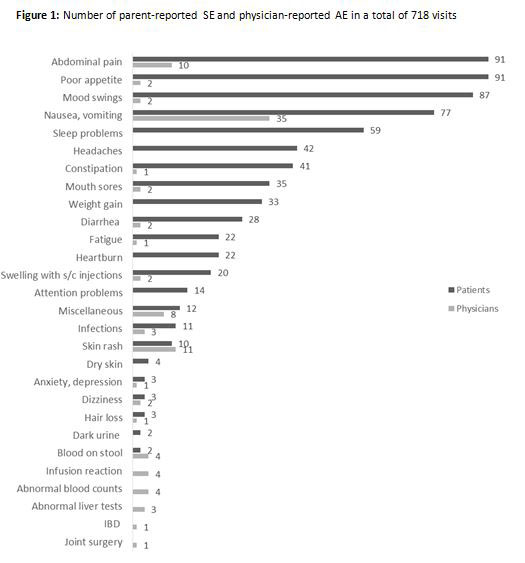
Results: The 226 included patients were typical of western JIA inception cohorts (Table 1). Parent reports were available for 718 of 760 visits (94.5%). Patients were receiving medications at 613 (85.4%) of those visits. Parents reported SE at 294 of 613 visits (48%) with a median of 2 SE per visit (IQR 1, 3). The corresponding incidence rate was 76 SE per hundred patient-years of follow-up with a 54% (CI 48-59) probability of experiencing at least one SE by 1 year after diagnosis. For physician-reported AE it was 25 events per 100 patient-years with a 24% (CI 19-30) probability of at least one AE by 1 year after diagnosis. The reported SE and AE are shown in Figure 1. The most common SE were gastro-intestinal. The severity of SE was a median of 3 out of 10 (IQR 1.5, 5) and 82% were mild with a score ≤ 5. The parent’s global assessment was a median of 2 (IQR 0.5, 5.5) when SE were present, and a median of 0.5 (0, 2) when absent (p< 0.0001, median test). The patient’s rating of their health-related quality of life was a median of 7 (5, 8.5) when SE were present, and a median of 8 (6.5, 9.5) when absent (p< 0.0001).
Conclusion: Parents of children with JIA report a very high frequency of medication SE, significantly higher than physician reported AE. SE have a measurable effect on the parent’s global assessment and on the patient’s assessment of health-related quality of life. Better addressing these SE may improve quality of life and adherence with medication regimens in children with JIA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chédeville G, Batthish M, Berard R, Bolaria R, Bruns A, Cabral D, Duffy C, Gerhold K, Gerschman T, Proulx-Gauthier J, Rosenberg A, Rumsey D, Schmeling H, Shiff N, Soon G, Tucker L, Guzman J. Parent-Reported Medication Side-Effects and Their Impact on Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Results from the CAPRI Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/parent-reported-medication-side-effects-and-their-impact-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-children-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-results-from-the-capri-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/parent-reported-medication-side-effects-and-their-impact-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-children-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-results-from-the-capri-registry/