Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is a metabolic disease caused by deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) monohydrate crystals in different tissues. Imaging may be useful to evaluate the extent of MSU deposition, the presence of acute and chronic inflammation, and tissue structural damage. The aim of the current study was to develop evidence-based and expert opinion recommendations for the use of imaging techniques in the diagnosis, monitoring, prognosis and treatment of patients with gout.
Methods: A selected group of experts (rheumatologists, radiologists, rheumatologist sonographers, methodologists and statisticians) from different PANLAR countries were included in the gout imaging task force. Imaging modalities evaluated were: conventional radiography (CR), ultrasound (US), computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and dual-energy computed tomography (DECT). Seven clinical questions were selected using the Delphi technique with RAND/UCLA modified methodology. Each question was scored in a visual analogue scale from 1 to 9 (1: complete disagreement; 9: complete agreement). With the information obtained, questions were reformulated and re-evaluated using the same scoring system. One question did not reach agreement. Finally, six questions were selected. A systematic literature review was performed using Medline, LILACs, Embase and Cochrane databases from January 1966 to February 2018. The search resulted in a total of 8657 articles, of which 1957 were duplicated. Of the 6700 remaining, 6020 were excluded based on the title and/or summary, leaving 680 for full text review. After that, 639 were excluded, leaving a total of 41 articles as supporting evidence, by two independent reviewers (agreement 97%, kappa 0.91). Recommendations were developed by consensus following similar methodology utilized for clinical question selection. Such recommendations were graded according to levels of evidence from the Oxford Center of Medicine in 2011. Final recommendations were eventually presented to an independent committee including representatives from several PANLAR rheumatologist societies.
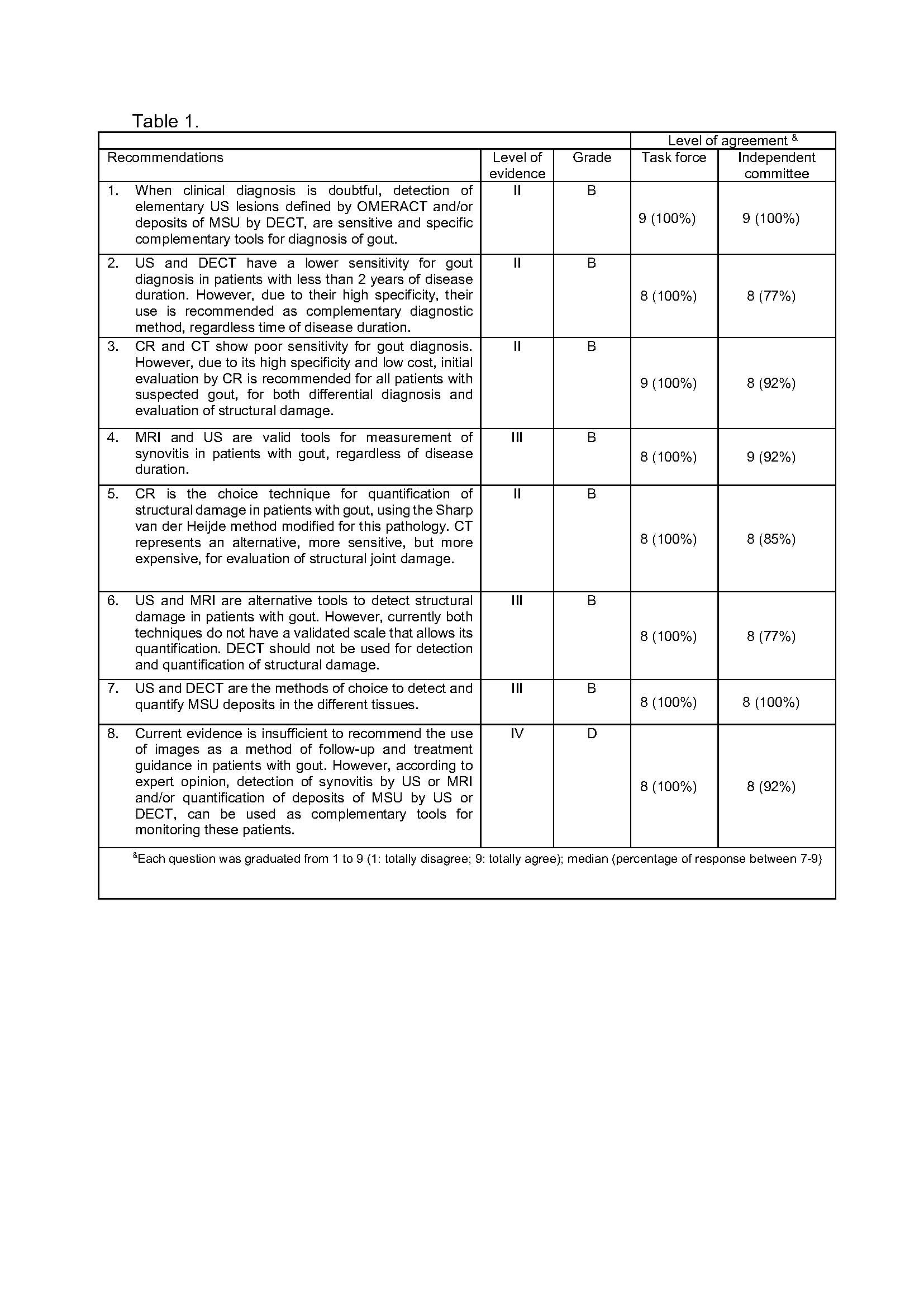
Results: Eight recommendations were developed for the use of imaging techniques in the diagnosis, monitoring, prognosis and treatment of patients with gout. The strength of each recommendation was established based on the evidence level as well as rate of agreement. Both gout imaging task force and independent committee agreed with the final recommendations (Table 1).
Conclusion: To the best of our knowledge, these are the first evidence-based and expert opinion recommendations for the use of imaging in patients with gout, providing some guidelines for their use in daily clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gutierrez M, Pineda C, Vazquez-Mellado J, Moreno Alvarez M, Rosa J, Reginato A, Chavez M, Alva Linares M, Audisio M, Mendonca J, Cazenave T, Sedano O, Ventura Ríos L, de Miguel E, Kaeley G, Scheines E, Hofmann F, Aguilar G, Waimann C, Marengo F, Ruta S. PANLAR Ultrasound Study Group Recommendations for the Use of Imaging in the Management of Patients with Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/panlar-ultrasound-study-group-recommendations-for-the-use-of-imaging-in-the-management-of-patients-with-gout/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/panlar-ultrasound-study-group-recommendations-for-the-use-of-imaging-in-the-management-of-patients-with-gout/