Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Septic arthritis is known to cause significant morbidity due to joint destruction and mortality if timely and adequate treatment is not given. In this study, we aim to describe outcomes of septic arthritis, focusing on comparison between the patients with and without underlying rheumatic disease.
Methods: Using the National Inpatient Sample database from 2016, we identified patients admitted with a principal diagnosis of septic arthritis based on ICD10 codes. Separate cohort was created for patients with secondary diagnoses of various rheumatic conditions including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteonecrosis, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, polyarteritis nodosa, dermatopolymyositis, scleroderma, and vasculitis. We identified risk factors for development of septic arthritis and compared the outcomes of patients admitted for septic arthritis with and without underlying rheumatic disease. STATA software was used to analyze the data.
Results: Study included 10,808 patients admitted in the year 2016 with septic arthritis, of which 1759 patients had underlying rheumatic disease and 9049 patients did not. For patients who did not have underlying rheumatic disease the mean age was 56.6 years, mean length of stay (LOS) was 5.74 days, and mean charges for hospitalization was $53,683. In comparison, for patients with underlying rheumatic disease, the mean age of patients was 62.6 years, mean LOS was 5.3 days and mean charges of $48,075. Both groups had higher proportion of Caucasians compared to other races (68.3% in those with rheumatic disease vs 69.1% in those without, both p< 0.05). There were no deaths in septic arthritis group with rheumatic disease whereas mortality rate was 0.004% in septic arthritis without rheumatic diseases. The following factors increased the risk of overall septic arthritis with the multivariable regression model: Obesity (OR=1.2), Rheumatoid arthritis (OR=3.7), Psoriatic arthritis (OR=3.13), Osteonecrosis (OR=7.7), Osteoarthritis (OR=2.4), SLE (OR=1.9), Arthroplasty (OR=2.13) with P values < 0.05. Female sex, Asian race and ankylosing spondylitis seemed to lower the risk (OR=0.49, 0.68 and 0.8 respectively) with P values < 0.05. Gout, PAN, Dermatopolymyositis, CKD and smoking were removed in the final analysis as they were found to be collinear variables.
Conclusion: In patients with septic arthritis, those with underlying rheumatic conditions seemed to be older with slightly higher proportion of females compared to those without. People with underlying rheumatic disease are more likely to develop septic arthrits but when they do, they seemed to have lower mortality, LOS and hospitalization charge compared to those without a rheumatic disease. This is likely because of better interdisciplinary care. Further studies are needed to establish various factors resulting in this outcome.

Descriptive data for septic arthritis
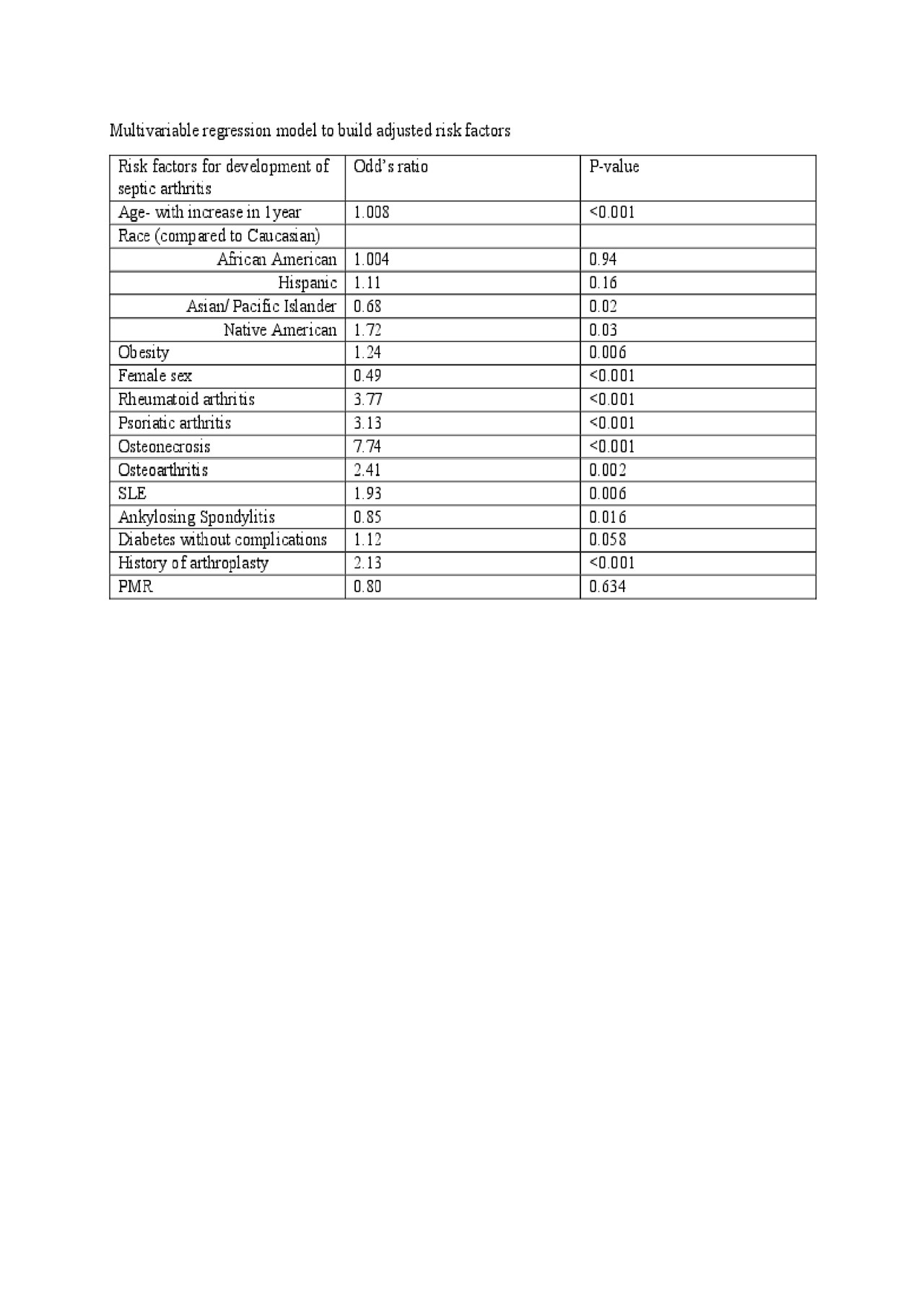
Multivariable regression model
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kambhatla S, Gauto-Mariotti E, Manadan A. Outcomes and Risk Factors in Septic Arthritis with Underlying Rheumatic Conditions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-and-risk-factors-in-septic-arthritis-with-underlying-rheumatic-conditions/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-and-risk-factors-in-septic-arthritis-with-underlying-rheumatic-conditions/
