Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Patients with rheumatoid disease (RD) have an increased mortality risk compared to the normal population, mainly due to cardiovascular (CV) disease. Only a proportion of this risk increase seems explained by traditional cardiovascular risk factors. It is therefore difficult to identify patients with RD at high risk. We identified patients at increased risk for CV diseases and mortality by a screening program that is suitable for clinical practice in rheumatology, and quantified long-term outcome. Patients and Methods:
612 consecutive patients attending the rheumatology outpatient department of the University Hospital underwent a comprehensive CV risk assessment including medical history, patient questionnaires, ECG, and laboratory measurements including natriuretic peptides (NTproBNP). Screening was regarded “positive” if any of the following was present: European CV disease risk assessment Score (SCORE) ≥3% or NTproBNP≥200 pg/ml or any pathological ECG pattern. Patients were followed for a median of 5.5 years. Results:
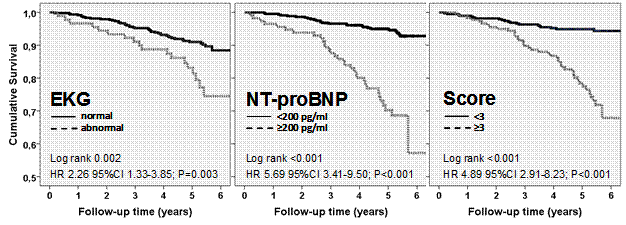
312 subjects suffered from rheumatoid arthritis (RA; 80% female, mean age 54 yrs), and 260 from systemic autoimmune diseases (SAI; 77% female, mean age 51 yrs). Across all subjects, SCORE was ≥3% in 31%, 20% had a NTproBNP level ≥200 pg/ml, and 16% had a pathological ECG. All-cause mortality in RA/SAI was 6.2%/5.6%, respectively; frequency of cardiac events (ie, myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiac decompensation, resuscitation) was 5.8%/7.3%, respectively. The figure shows KM-plots for the 3 screening strategies, and unadjusted hazard ratios with 95%CI. In an age- and sex-adjusted multivariable model, only NTproBNP≥200 pg/ml conferred independent prognostic information with HR 2.8 (1.55-5.03; p<0.001) and an area under the ROC curve of 80%. Conclusion:
RD patients at high risk for death and CV events can be identified using simple screening tools. In patients with a SCORE ≥3% or NTproBNP ≥200 pg/ml are further diagnostics and closer long-term follow-up seem justified.
Disclosure:
S. Kleinert,
None;
M. Breunig,
None;
H. P. Tony,
None;
M. Feuchtenberger,
None;
M. Schmalzing,
None;
C. Kneitz,
None;
S. Lehmann,
None;
C. Angermann,
None;
G. Ertl,
None;
S. Störk,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcome-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-disease-simple-screening-tools-predict-cardiovascular-events-and-death/