Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Fostamatinib (Fosta) is an oral SYK inhibitor. This 52-wk study (NCT01197521) compared Fosta vs placebo (PBO) + methotrexate (MTX) in patients (pts) with active RA despite MTX.
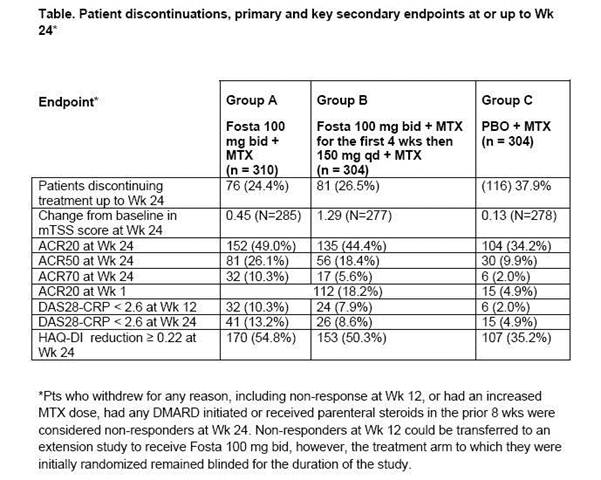
Methods: Adult pts on MTX were randomized (1:1:1) to Fosta (100 mg bid for 52 wks [Group A, n = 310] or 100 mg bid for 4 wks then 150 mg qd [Group B, n = 304]) or to PBO for 24 wks then Fosta 100 mg bid (Group C, n = 304). Non-responders at Wk 12 could leave the study and enter an active extension study. Co-primary endpoints were the proportion of pts achieving ACR20 response at Wk 24 and the change from baseline to Wk 24 in modified total Sharp score (mTSS). Secondary endpoints evaluated efficacy, safety and tolerability up to 52 wks.
Results: Demographic and baseline characteristics were well balanced across groups. Fosta Groups A and B had significantly more pts achieving ACR20 at Wk 24 vs PBO (Table, p < 0.001; p = 0.006, respectively), with 18.2% of Fosta pts achieving ACR20 as early as Wk 1 (vs 4.9% PBO). Fosta Groups A and B did not show a significant difference in mTSS at Wk 24 (p = 0.25; p = 0.17, respectively [Table]) vs PBO. The percentages of pts who did not progress (mTSS change ≤ 0.5) in Groups A, B and C were 80.7%, 77.6% and 79.5%. Key secondary efficacy endpoints were consistently favorable for Fosta Groups A and B vs PBO (Table), with better results at the higher dose, but were not tested statistically due to failure of the mTSS co-primary endpoint.
In the 24-wk PBO-controlled period, the most frequently reported AEs in pts in Groups A, B and C were hypertension (15.9%, 15.1%, 3.9%), diarrhea (13.9%, 15.1%, 3.9%) and nausea (4.2%, 6.9%, 3.6%). Serious AEs occurred in 2.9%, 4.9% and 1.6% of pts. AEs leading to discontinuation occurred in 5.2%, 9.2% and 2.6% of pts, the most frequent being diarrhea, hepatic enzyme increase, hypertension and ALT increase. Elevated BP (≥ 140/90 mmHg) was observed in 44.2%, 41.6% and 19.3% of pts at ≥ 1 visit.
Overall exposure up to 52 wks was 111 patient-years (PY) for PBO and 569 PY for Fosta. There were 9 adjudicated CV events: 2 on PBO, and 7 on Fosta (5 in Group B, 2 in Group C). One pt on PBO died (0.9/100 PY; pulmonary embolism) and 5 died while on Fosta (0.9/100 PY; 2 in Group B [sepsis/renal failure; gastroenteritis/hypovolemic shock/cardiorespiratory failure] and 3 in Group C [septic shock/interstitial lung disease; circulatory collapse; acute renal failure/cardiorespiratory arrest]). There were 5 malignancies, all on Fosta (0.9/100 PY; 2 × non-melanoma skin cancer; 1 × gastric, renal or thyroid cancer), over 52 wks.
Conclusion: In this phase III study both Fosta regimens achieved statistical improvements in ACR20 response rate at 24 wks vs PBO in pts treated with MTX but did not show a significant difference in mTSS. The overall level of response with Fosta was not as large as observed in the phase ll (TASKi) program. Safety and tolerability findings were consistent with the profile observed in earlier studies.
Disclosure:
M. Weinblatt,
Rigel Pharma,
5,
AstraZeneca,
5;
M. C. Genovese,
Rigel Pharma,
2,
Rigel Pharma,
5,
AstraZeneca,
2,
AstraZeneca,
5;
M. Ho,
AstraZeneca,
3;
S. Hollis,
AstraZeneca,
3,
AstraZeneca,
1;
K. Rosiak-Jedrychowicz,
None;
A. Kavanaugh,
None;
D. Millson,
AstraZeneca,
1,
AstraZeneca,
3;
G. Leon,
None;
M. Wang,
AstraZeneca,
3;
D. van der Heijde,
AstraZeneca,
5,
AbbVie,
5,
Amgen,
5,
Augurex,
5,
BMS,
5,
Celgene,
5,
Centocor,
5,
Chugai,
5,
Covagen,
5,
Daiichi Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Eli Lilly and Company,
5,
GlaxoSmithKline,
5,
Janssen Biologics,
5,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Novo-Nordisk,
5,
Otsuka,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
5,
Schering-Plough,
5,
UCB,
5,
Vertex,
5,
Imaging Rheumatology BV,
9.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oskira-1-a-phase-iii-multicenter-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-parallel-group-study-of-2-dosing-regimens-of-fostamatinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-an-inadequate-response/