Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Efficacy, inhibition of structural damage, and safety of tofacitinib versus placebo (PBO) were reported previously from the tofacitinib Phase 3 ORAL Scan trial (NCT00847613) in patients with active RA with an inadequate response (IR) to methotrexate (MTX).1,2 Here we report 24-month patient-reported outcomes (PRO) data from this study.
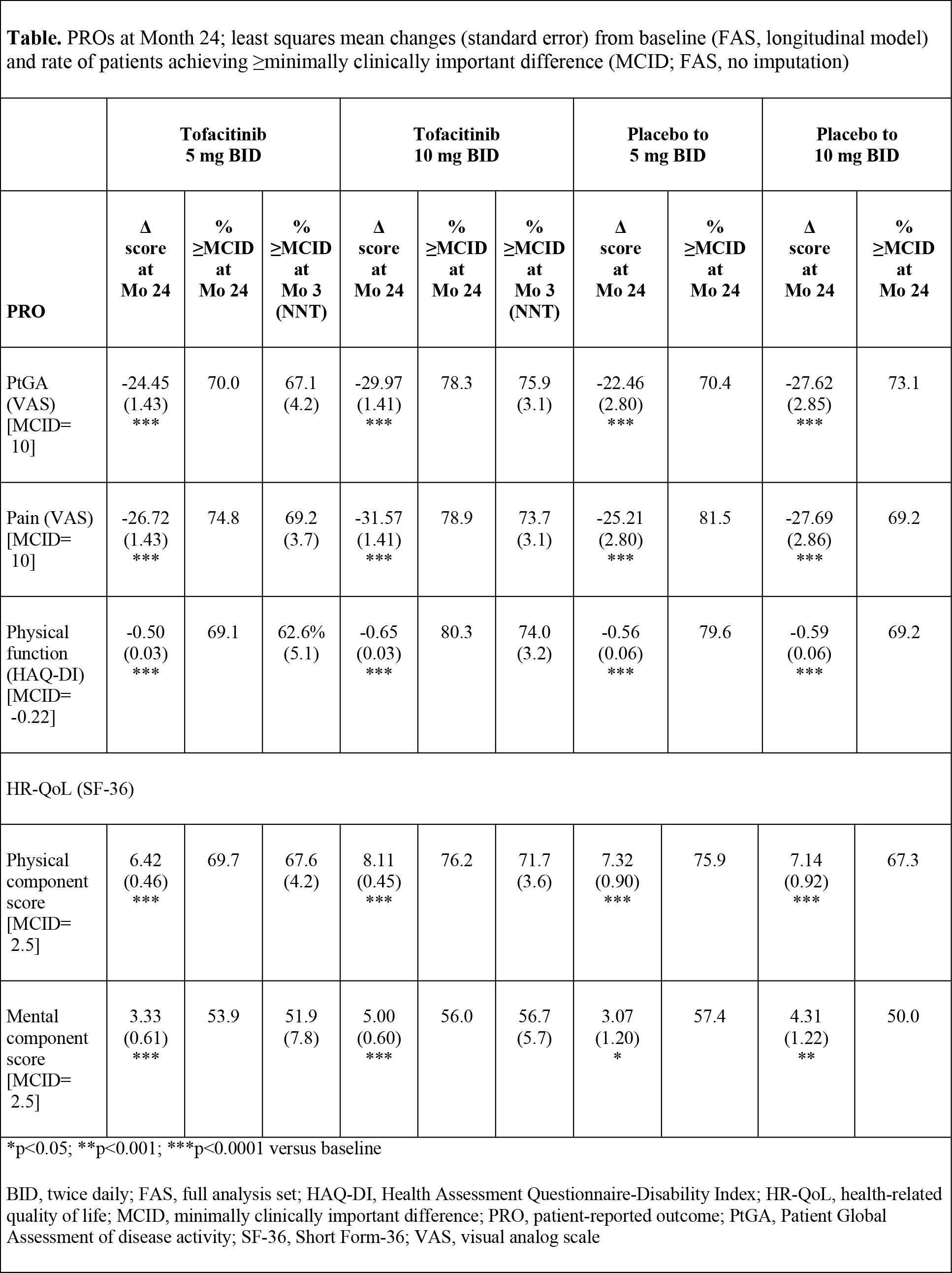
Methods: Patients on stable-dose MTX were randomized 4:4:1:1 to: tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID), 10 mg BID, or PBO advanced to 5 or 10 mg BID. Patients receiving PBO advanced at Month 3 if non-responders (<20% reduction in swollen or tender joint counts) or at Month 6. Mean changes from baseline in PROs were secondary endpoints, including: Patient Global Assessment (PtGA) of disease activity (visual analog scale [VAS]); patient-reported pain (VAS); Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI; mean change from baseline at Month 3 was a co-primary endpoint); and health-related quality of life (HR-QoL; Short Form-36 version 2, acute; SF-36). Analyses used a longitudinal linear mixed-effect model that included all post-baseline visits and accounted for repeated measures on patients, the randomized sequences and baseline values as covariates, on all patients who received ≥1 study drug dose and had both a baseline and ≥1 post-baseline value (full analysis set). Least squares mean changes from baseline at Month 24 are presented. No imputation was used for percentage of patients reporting improvements ≥minimum clinically important differences (MCIDs). Statistical significance at p≤0.05, two-sided testing, no adjustment for multiple testing.
Results: 797 patients were randomized and treated; 535 (67.1%) completed 24-months treatment. Baseline characteristics were similar across groups. At Month 3, patients receiving tofacitinib reported statistically significant mean changes versus placebo in all PROs, exceeding MCID; NNTs ranged from 3.7-7.8 and 3.1-5.7 in 5 and 10 mg BID groups, respectively. At Month 24, tofacitinib treatment resulted in statistically significant improvements versus baseline in all PROs (Table), similar to those reported at Month 3. Mean changes across all PROs were numerically greater in patients receiving tofacitinib 10 mg BID, more of whom reported improvements ≥MCID (Table).
Conclusion: In this Phase 3 trial, MTX-IR patients receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID in combination with MTX reported continued clinically meaningful improvements in PROs from Month 3 to 24, which were statistically significant versus baseline. After rescue at Month 3 or 6, placebo patients reported changes of similar magnitude at Month 24, also significant versus baseline.
References: 1. Burmester G et al. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2012; 64: S10: 549.
2. van der Heijde D et al. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 65: 559-570.
Disclosure:
V. Strand,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
D. van der Heijde,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
4;
C. A. F. Zerbini,
Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol. Lilly, Amgen, MSD,
2,
Pfizer, Bristol, Lilly, MSD,
5,
MSD, Sanofi,
6;
C. A. Connell,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
D. Gruben,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
R. Riese,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
G. Wallenstein,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oral-scan-effects-of-the-oral-jak-inhibitor-tofacitinib-in-combination-with-methotrexate-on-patient-reported-outcomes-in-a-24-month-phase-3-trial-of-active-rheumatoid-arthritis/