Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation (PASE) Tool is one of the most frequently used tools to screen psoriasis patients for signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). PASE has been used in dermatology outpatient settings, in large-scale epidemiological studies, and in clinical trials and has been translated into more than 20 different languages. The original PASE included 15 questions addressing two separate domains including symptoms (7 questions) and function (8 questions). Given the demonstrated efficacy of the tool for early identification of PsA, we sought to determine the optimal cut off score and generate a shorter version in efforts to improve adoption and implementation in the clinical setting as PASE-2.
Methods: Eligible patients included those adults aged 18-85 with a diagnosis of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, who presented at an academic dermatology clinic. The PASE questionnaire was administered to 190 consecutive patients. From survey responses, we conducted a principal component analysis to guide revision of the tool. Principal component analysis identified a one-factor solution which accounted for 57.5% of total variance. Questions with factor loading below 0.75 were removed. A Youden index was used to guide selection of the appropriate total survey score cutoff for sensitivity and specificity for identifying inflammatory arthritis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated for individual questions and for the revised PASE-2 as a whole.
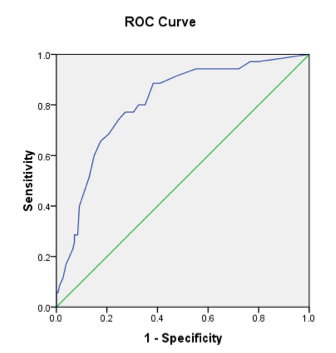
Results: 190 patients with dermatologist-diagnosed psoriasis completed the PASE tool (110 males and 80 females, median age 55). We identified 7 questions for removal, yielding an 8-item questionnaire. Remaining items inquire about joint stiffness, joint function, joint pain and/or swelling, joint warmth/erythema, migratory joint pain, work and activity-related changes. The area under the ROC curve for the 8-item tool was 0.81 (Figure). Selecting a new total score cutoff of 19 or greater provided a sensitivity of 0.84 and specificity of 0.63 for the identification of psoriasis patients at risk for PsA. This is compared to a sensitivity and specificity of 0.82 and 0.73 from the original 15-item PASE tool.
Conclusion: We conducted a principal component analysis to develop an 8-question PASE-2. The improved sensitivity of the PASE-2 highlights the potential for better screening for PsA in the psoriasis population while minimizing survey burden to physicians and patients and thereby increasing adoption of the tool. Further studies will be needed in larger populations to improve the adoption of screening to help improve patient outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thompson J, Darwish M, Paek SY, Merola J, Qureshi A, Husni ME. Optimizing Screening for Psoriatic Arthritis through a Shortened Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation-2 (PASE-2) Tool [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/optimizing-screening-for-psoriatic-arthritis-through-a-shortened-psoriatic-arthritis-screening-and-evaluation-2-pase-2-tool/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/optimizing-screening-for-psoriatic-arthritis-through-a-shortened-psoriatic-arthritis-screening-and-evaluation-2-pase-2-tool/