Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Patients with RA and longer disease duration generally do not
respond as well to treatment with DMARDs as patients with a shorter duration of
disease. Earlier use of biologic DMARDs can improve disease control.1,2
The AVERT trial provides the opportunity to examine outcomes in patients with
varying degrees of early disease duration in which the definition for disease
duration is well defined across groups.
with early active RA (clinical synovitis in ≥2 joints for ≥8 weeks,
persistent symptoms for ≤2 years and DAS28 [CRP] ≥3.2),
and who were anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-2 positive, were randomized to
SC abatacept (ABA) 125 mg/week + MTX, SC ABA 125 mg/week alone or MTX alone for
12 months. All RA treatment was removed after 12 months in patients with DAS28 (CRP) <3.2.3 In this post
hoc analysis, proportions of patients achieving protocol-defined remission
(DAS28 [CRP] <2.6) or improvement in HAQ-DI (≥0.3 units from baseline)
were assessed by ≤3 months’, >3 to ≤6 months’ or >6 months’
disease duration (defined as the duration of persistent symptoms at baseline) and
treatment group. Adjusted mean changes from baseline in HAQ-DI were also
evaluated by disease duration.
were randomized and treated with ABA+MTX (n=119) or MTX (n=116): 36 and 48 with
≤3 months’; 34 and 29 with >3 to ≤6 months’; 49 and 39 with
>6 months’ disease duration, respectively. No systematic differences were
seen in baseline demographics and clinical characteristics for patients grouped
by disease duration. Irrespective of baseline disease
duration, a higher proportion of ABA+MTX-treated patients achieved Month 12 and
sustained (Month 18) remission, compared with MTX alone. A higher
proportion of ABA+MTX-treated patients with disease duration ≤3
months maintained remission following all treatment
withdrawal compared with longer disease durations and MTX alone (Figure). ABA+MTX-treated patients with ≤3 months’ disease
duration also had the fastest onset of response (Figure). Results for HAQ-DI were
similar to the overall population, regardless of baseline disease duration.
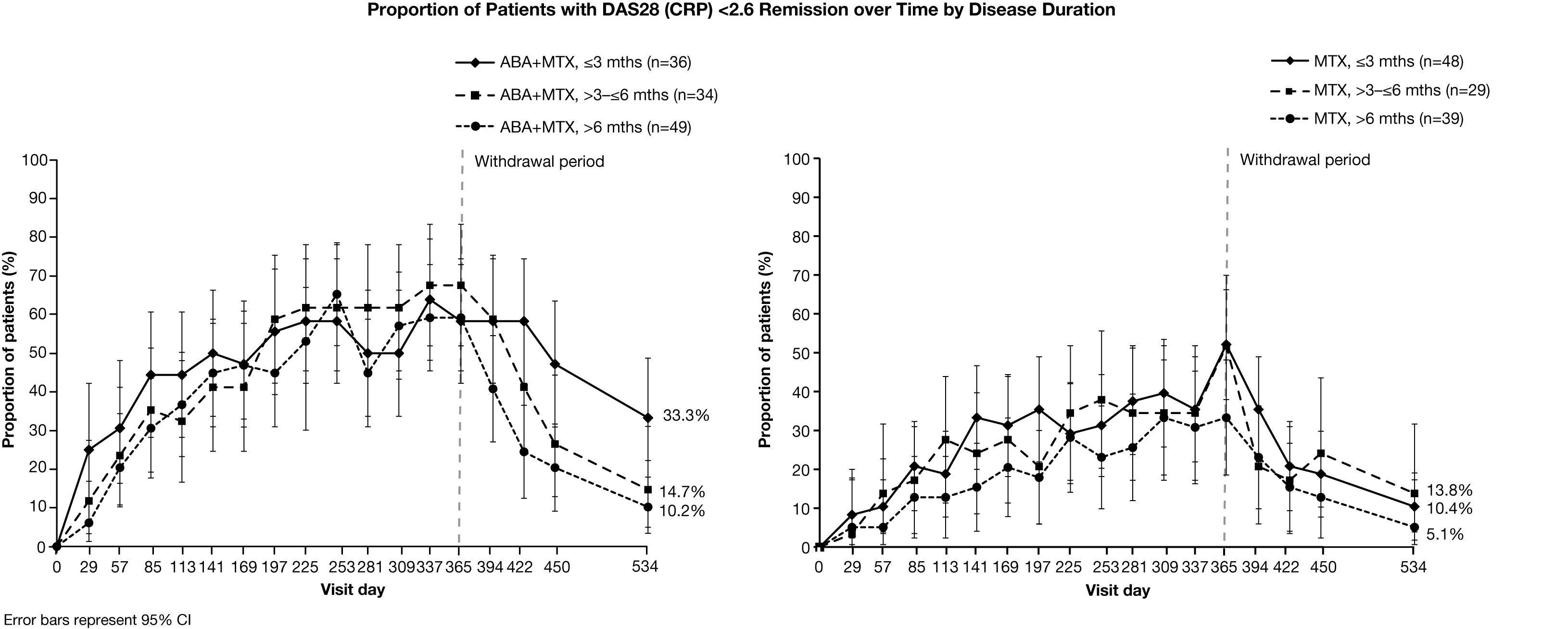
Conclusion: Disease duration
of ≤3 months was associated with faster onset of clinical response and
the ability to achieve higher rates of drug-free remission following treatment
with abatacept+MTX in AVERT.4
1. Westhovens
R, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:1870–7.
2. Emery P, et
al. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:510–6.
3. Emery P, et
al. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73(Suppl 2):69.
4. This abstract was first presented at the
EULAR Congress, 10–13 June 2015, Rome, Italy (FRI0152) and published in the
corresponding supplement of Ann Rheum Dis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bykerk V, Burmester G, Combe B, Furst DE, Huizinga TWJ, Wong D, Emery P. On Drug and Drug-Free Remission By Baseline Disease Duration: Abatacept Versus Methotrexate Comparison in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/on-drug-and-drug-free-remission-by-baseline-disease-duration-abatacept-versus-methotrexate-comparison-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/on-drug-and-drug-free-remission-by-baseline-disease-duration-abatacept-versus-methotrexate-comparison-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/
