Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) experience higher cardiovascular (CV) morbidity compared to controls. Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) accurately detects plaque presence, burden and composition and independently predicts short and long-term incident cardiac events in general patients with unknown coronary artery disease (CAD). We evaluated, for the first time, the long-term prognostic role of CCTA in a cohort of established RA patients without symptoms or known cardiovascular disease.
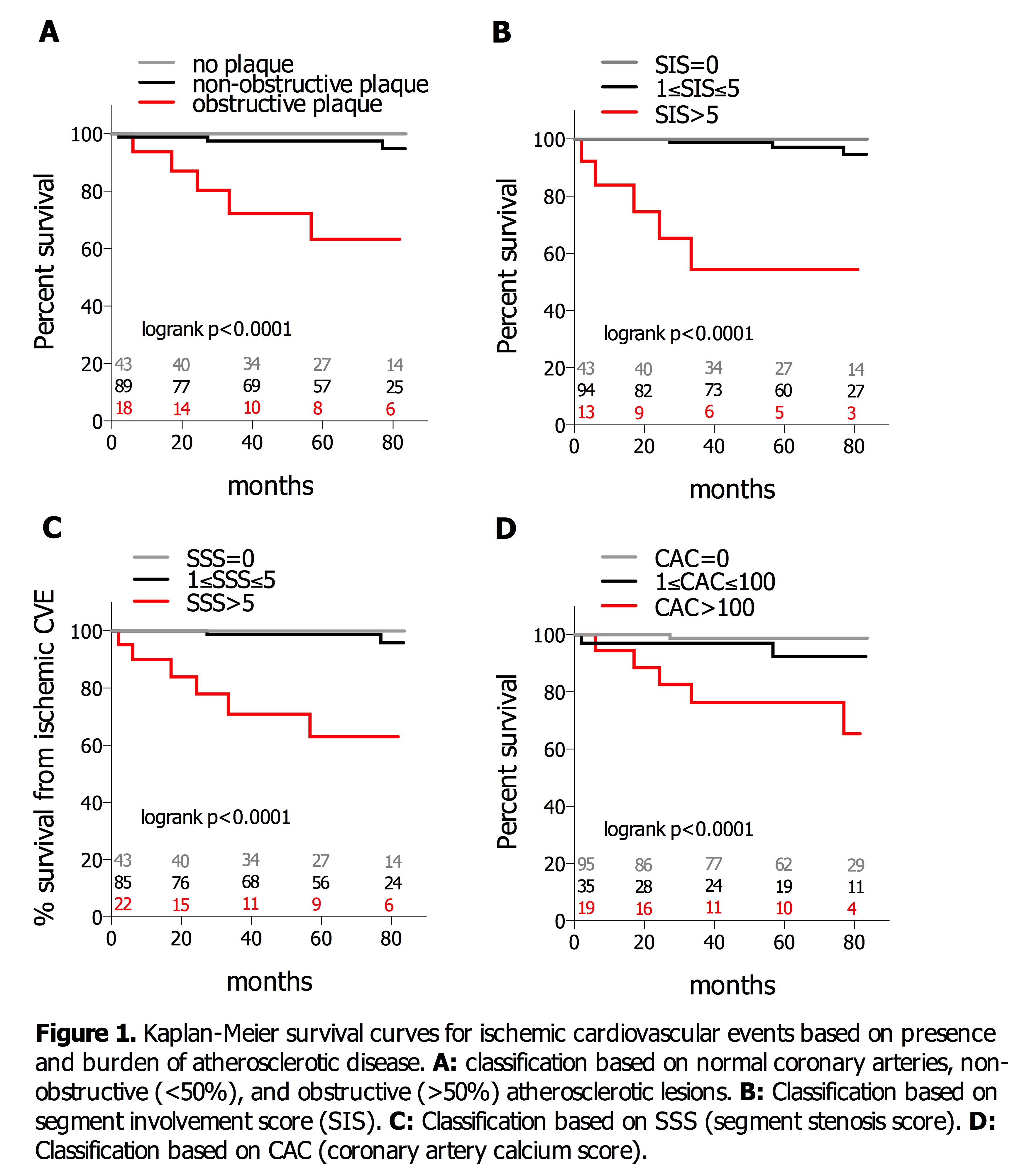
Methods: One hundred and fifty participants from a single center underwent a baseline 64-slice CCTA for plaque evaluation between 3/2010- 3/2011 and followed for a mean of 60±26 months. Patients were classified based on presence of normal coronaries, non-obstructive (<50%) and obstructive (>50%) lesions. Atherosclerosis burden was further evaluated with coronary plaque scores: SIS or segment involvement score, reflected number of segments with at least 1 plaque; SSS or segment stenosis score represented the overall plaque extent. The composite rates of ischemic CV events [cardiac death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial ischemia] were the study end-points. Cox regression analysis evaluated associations between CCTA parameters and outcomes; hazards ratios were generated in both raw and adjusted models. Event-free survival was assessed with Kaplan-Meier analysis and curves were compared using the log-rank test.
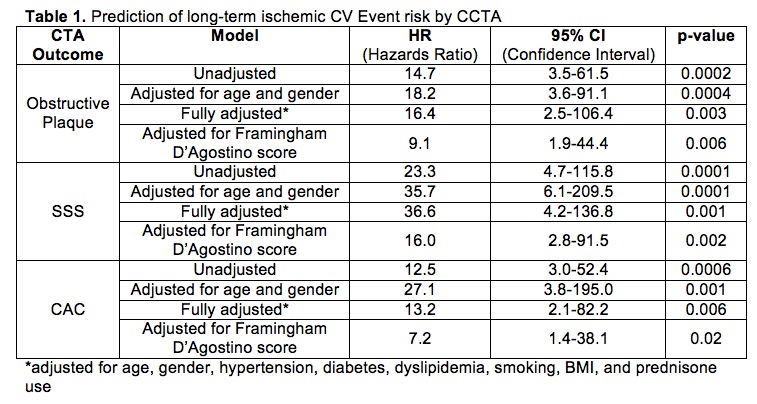
Results: Eleven patients suffered incident CV events (1.54/100PY): 8 were ischemic, including 1 cardiac death, 3 MI, 2 strokes, and 2 peripheral arterial ischemic events requiring emergent revascularizations; the 3 non-ischemic events were new onset, hospitalized, systolic heart failure. No ischemic events occurred in patients with normal coronaries (Figure 1); by contrast event-free survival was 97.5% and 63.3% in patients with non-obstructive and obstructive CAD respectively at 60 months (p<0.0001). Obstructive CAD was an independent predictor of ischemic events (HR=16.4, p=0.003, Table 1). Plaque burden was equally predictive; event-free survival was 97.1% vs. 54.4% in those with SIS=<5 vs. SIS>5 and 98.6% vs. 63% in patients with SSS=<5 vs. SSS>5, (both p<0.0001); 95% with CAC=<100 vs. 76% with CAC>100 experienced no events at 60 months (p<0.0001, Figure 1).
Conclusion: CCTA provided prognostic information in RA patients without symptoms or known CV disease; it showed excellent long-term prognosis when there was no evidence of atherosclerosis, and allowed risk stratification when CAD was present.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Estis J, Todd J, Budoff M. Occult Coronary Plaque Presence and Burden Predict Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/occult-coronary-plaque-presence-and-burden-predict-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/occult-coronary-plaque-presence-and-burden-predict-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/