Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2195–2226) Reproductive Issues in Rheumatic Disorders Posters
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Women with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) are frequently diagnosed during their childbearing years. While studies have reported on pregnancy complications in this population, deriving generalizable prevalence estimates has been hampered by smaller study cohorts. Where reported, there is a concerning trend toward increased pregnancy complications in axSpA compared to the general population. Severe maternal morbidity (SMM) is a serious adverse physical or psychological event related to pregnancy which negatively impacts maternal health. Clinically recognized in the general population, SMM has not been studied in women with rheumatic diseases, including axSpA. The aim of this study was to determine if there is a higher prevalence of pregnancy and neonatal complications, including SMM, in women with axSpA compared to women in the general population.
Methods: This was a population-based cohort study of administrative healthcare data from Ontario, Canada. Primary data source was the Mombaby Database, allowing near-complete capture of all hospital-based livebirths and stillbirths. The study included all women aged 10 to 55 years with a livebirth recorded between April 1st, 2002 and March 31st, 2020. Diagnosis of axSpA was based on the presence of an axSpA diagnosis code on at least two healthcare claims within a two-year period with at least one made by a Rheumatologist. Pregnancies in axSpA women were matched in a 1:5 ratio with pregnancies of women without axSpA (controls) according to maternal age, year of first pregnancy, and geographic location. Prevalence of pregnancy and neonatal outcomes were compared between axSpA women and controls. Multivariable logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with SMM in axSpA pregnancies.
Results: In total, 3,010 women with axSpA were matched with 15,050 non-axSpA controls, each contributing 5,176 and 26,350 study pregnancies, respectively. Most of axSpA and control women were nulliparous (70.9% vs 72.7%, p=0.72), and median age was 31 years. For pregnancy complications, gestational diabetes (7.5% vs 6.6%, p=0.03), antepartum haemorrhage (0.9% vs 0.6%, p=0.03), and SMM (4.4% vs 3.7%, p=0.02) were significantly more prevalent in axSpA pregnancies (Table 1). For neonatal complications, preterm birth was more prevalent in axSpA pregnancies (9.7% vs 8.1%, p< 0.01) (Table 2). In multivariable analyses, factors associated with SMM in axSpA women were maternal age (aOR 1.03, 95% CI 1.00-1.06), comorbidity burden (defined by the Elixhauser Comorbidity Index; aOR 1.27, 95% CI 1.16-1.38), and gestational age at delivery (aOR 0.76, 95% CI 0.73-0.78) (Table 3).
Conclusion: In this large, population-based cohort study, women with axSpA were more likely to experience SMM, preterm birth, gestational diabetes and antepartum haemorrhage compared to controls. Furthermore, experiencing SMM was associated with increasing maternal age, lower gestational age and increasing comorbidity burden. These results are concerning and call for further studies to identify and develop strategies to limit SMM in women with axSpA. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest population-based study of pregnancy in axSpA women and the first study of SMM in axSpA.
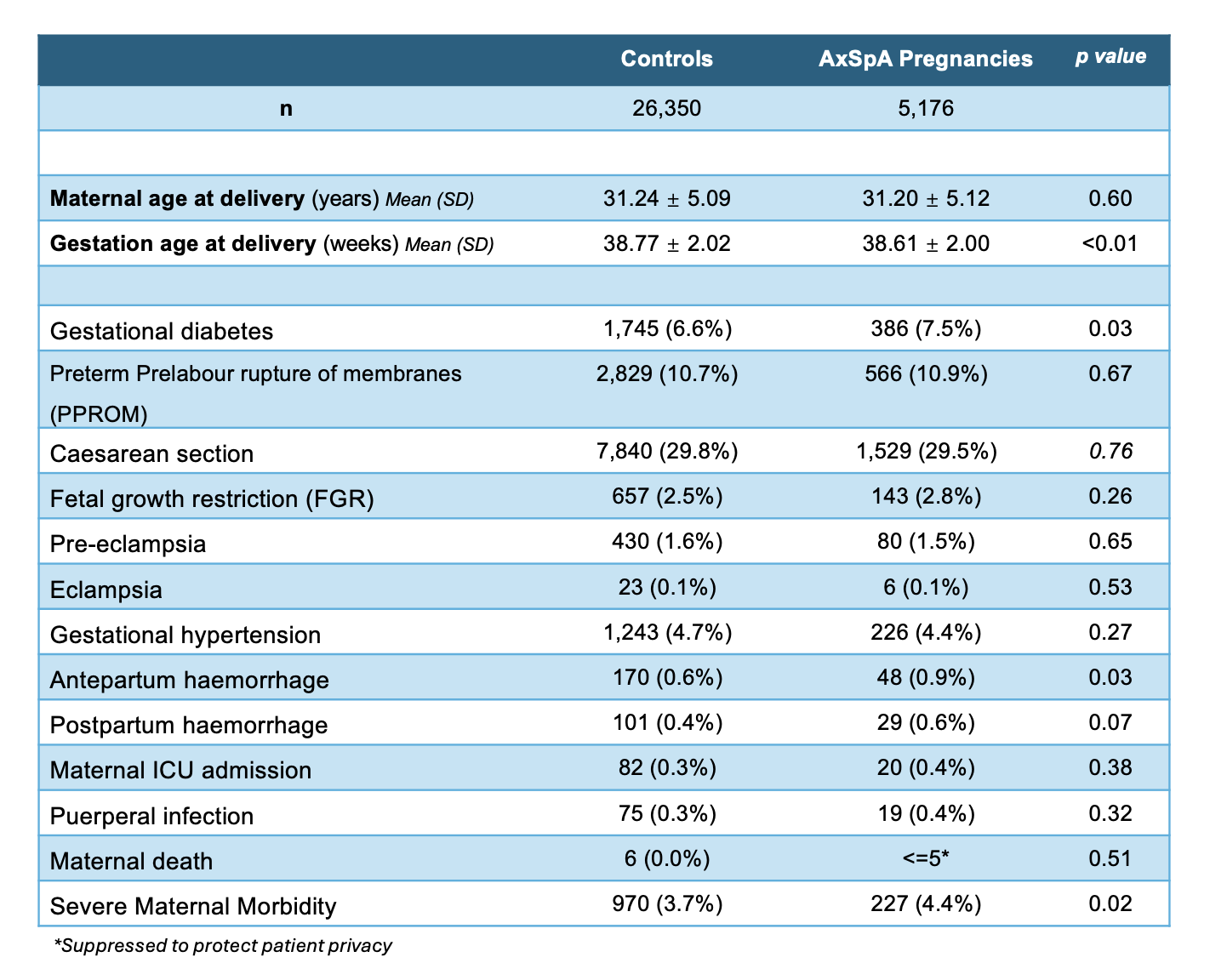 Table 1: Pregnancy characteristics & maternal outcomes among women with axSpA and matched controls
Table 1: Pregnancy characteristics & maternal outcomes among women with axSpA and matched controls
.jpg) Table 2: Neonatal Outcomes in axSpA and non-axSpA (control) pregnancies
Table 2: Neonatal Outcomes in axSpA and non-axSpA (control) pregnancies
.jpg) Table 3: Factors associated with Severe Maternal Morbidity (SMM) in AxSpA Pregnancies
Table 3: Factors associated with Severe Maternal Morbidity (SMM) in AxSpA Pregnancies
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maguire S, Snelgrove J, Pequeno P, Paterson M, Wu F, Passalent L, Perruccio A, Mahendira D, Karam E, Inman R, Haroon N. Obstetric and Neonatal Complications in Women living with Axial Spondyloarthritis: a population-based, matched cohort study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obstetric-and-neonatal-complications-in-women-living-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-population-based-matched-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obstetric-and-neonatal-complications-in-women-living-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-population-based-matched-cohort-study/
