Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Haploinsufficiency of A20 (HA20) is caused by loss-of-function TNFAIP3 variants. Phenotypic and genetic features of HA20 remain uncertain; therefore, clinical distinction between HA20 and Behçet’s disease (BD) requires clarification.
Methods: We have collected twelve Japanese BD-like families. Probands of these families were analyzed by whole exome sequencing (WES) and subsequent Sanger sequencing or quantitative PCR. Copy number variants (CNVs) were examined using WES data with two algorithms: the eXome-Hidden Markov Model (XHMM) and a program based on the relative depth of coverage ratios developed by Nord et al. To observe mutational effects of the nonsense variant, RT-PCR was performed. Clinical features were compared between 54 HA20 patients (including previously reported and new cases) and BD cohorts (520 Japanese BD patients accumulated at our facility and pediatric BD from the Pediatric Behçet’s disease (PEDBD) study by Kone-Paut et al.) Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS version 22 (IBM Japan, Tokyo, Japan). Categorical variables were analyzed using the chi-square test. Continuous variables were examined using Student’s t-test. A p value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
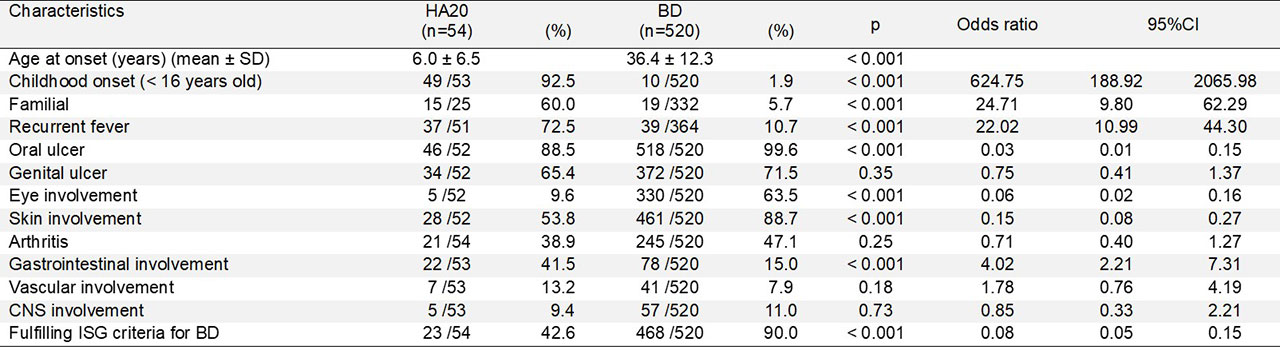
Results: Among Twenty-five patients from twelve families, two novel TNFAIP3 pathogenic changes were found in two families (16.7%, 2 of 12): nonsense variant in one family and a 236 kb deletion at 6q23.3 containing TNFAIP3 in another family. The nonsense variant may be subjected to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). Four HA20 patients in the two families presented with childhood-onset recurrent oral and genital ulcers and were initially diagnosed and treated as BD. Consistent with the clinical features of HA20, recurrent, refractory fever attacks (3/4), and digestive ulcers (2/4) were observed. A comparison of clinical features between HA20 patients and cohorts of BD patients revealed that some features are shared between HA20 and BD as previously reported: recurrent oral and genital ulcers, and skin, eye, musculoskeletal and gastrointestinal involvement. While several critical features were more specific to HA20: early-onset, familial occurrence, recurrent fever attacks, gastrointestinal involvement, and infrequent ocular involvement (Table 1).
Conclusion: We identified a novel nonsense variant and deletion of the entire TNFAIP3 gene in two unrelated Japanese HA20 families. Genetic screening of TNFAIP3 should be considered for familial BD-like patients with early-onset recurrent fevers.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tsuchida N, Kirino Y, Soejima Y, Nakajima H, Miyatake S, Matsumoto N. Novel Nonsense Variant and Entire Deletion of TNFAIP3 Cause Haploinsufficiency of A20 Clinically Distinct from Behçet’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-nonsense-variant-and-entire-deletion-of-tnfaip3-cause-haploinsufficiency-of-a20-clinically-distinct-from-behcets-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-nonsense-variant-and-entire-deletion-of-tnfaip3-cause-haploinsufficiency-of-a20-clinically-distinct-from-behcets-disease/