Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Fluorescence optical imaging (FOI) has been used for assessment of inflammation in the hands and has in several cross sectional studies been compared with US and MRI, but no validated scoring systems exist.
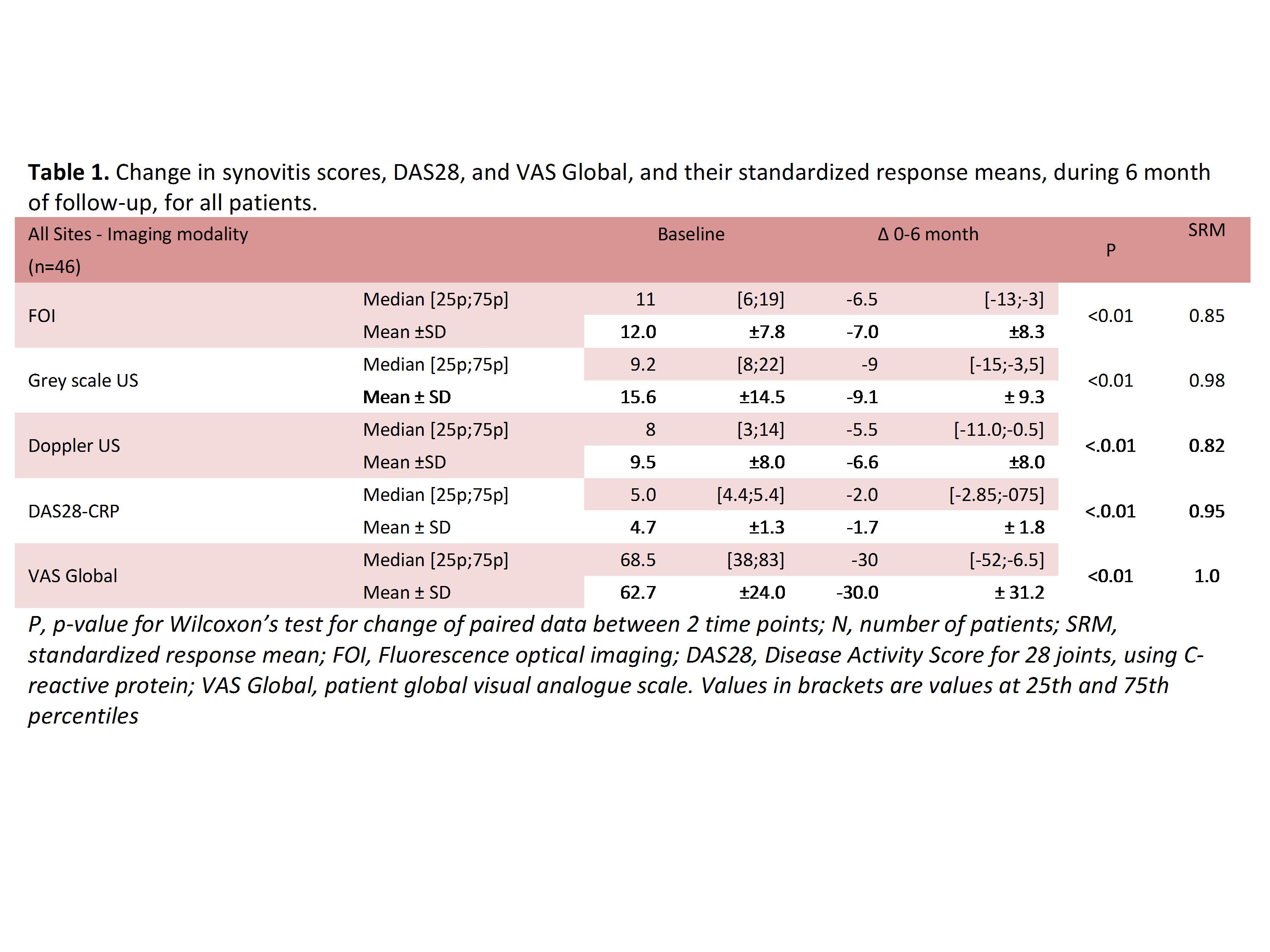
The aim was in a longitudinal study to validate a new and clinically feasible FOI scoring system for assessments of synovitis in RA hands by comparison with US and determining its sensitivity to change.
Methods:
46 RA patients eligible for initiation or intensification of disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and with ≥1 clinically swollen joint in the hand, were included and assessed by FOI, US and clinical assessment at baseline and 6 months. FOI image-sets of both wrists and hands were obtained using a Xiralite system unit. The patients received a bolus of i.v. indocyanine green (ICG) 10 seconds after starting the examination, which obtained 1 image/second for 6 minutes.
All FOI images were scored by two readers for synovitis at the wrist, MCP and PIP joint levels in both hands. The novel synovitis scoring is based on the assumption that inflamed tissue would demonstrate a more rapid enhancement than surrounding tissues. For each joint, the images were assessed sequentially from start to peak enhancement. Synovitis was defined as a sharply marginated enhancement with clear delineation from surrounding tissues and correct anatomical location, lasting ≥3 seconds. The width of the pathology fulfilling these criteria was compared to the width of the joint at the 3rd second of enhancement of that particular joint, and scored 0-3 for synovitis (total range 0–66) The readers were blinded to patient data, but not chronology, and had previously showed a high intra- and inter-reader agreement (ICC:0.70-0.92).
For US assessment, a GE Logiq E9 US unit with a high frequency linear 6-15 ML probe and with Doppler settings optimised for slow flow. Synovitis was scored from 0-3 for grey scale (GS) and Doppler using the OMERACT US synovitis scoring system by two trained assessors with a previously documented high intra- and inter-reader agreement (wKappa:0.88-0.95).
Agreement for status and change scores was assessed using single measure intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and Spearman correlation coefficients (rho). Responsiveness was assessed using standardized response mean (SRM)
Results:
Baseline scores, change scores and their respective SRMs are presented in table. 1. The mean SRM was good for all parameters
ICC and rho between FOI and US total scores were low for both readers at baseline (range 0.3-0-4) (p<0.05), and low to moderate (range 0.31-0.54) (p<0.01) for change scores.
Conclusion:
A moderate correlation with US for change over time, and good responsiveness, were found for a new FOI scoring system. FOI may potentially prove useful for monitoring RA patients in clinical trials and practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ammitzbøll-Danielsen M, Glinatsi D, Terslev L, Østergaard M. Novel Fluorescence Optical Imaging Scoring System of Inflammation in the Hand and Wrist Is in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis – Agreement with Ultrasonography and Sensitivity to Change [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-fluorescence-optical-imaging-scoring-system-of-inflammation-in-the-hand-and-wrist-is-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-agreement-with-ultrasonography-and-sensitivity-to-change/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-fluorescence-optical-imaging-scoring-system-of-inflammation-in-the-hand-and-wrist-is-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-agreement-with-ultrasonography-and-sensitivity-to-change/