Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Uncontrolled Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) leads to disability, damage, and poor health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Current treatment recommendations emphasize the importance of achieving remission or Low Disease Activity (LDA) (1) to avoid the aforementioned results. In Latin American, RA patients have been shown to achieve low remission but high disability rates. (2-4) and the alternative LDA, could be a reasonable treatment goal. Objective: To explore the impact of not achieving remission over time on the HRQoL in RA patients.
Methods: RA patients from a longitudinal established RA cohort (ACR1987/ACR-EULAR2010 criteria) from a single center were studied. This cohort was established to describe the clinical outcomes of RA Peruvian patients; for this analysis, subjects with at least two evaluations (half-yearly) were included. In each visit clinical remission state was defined if they achieved a 3.3 value in the Simple Disease Activity Index (SDAI). Also, non-remission categories were defining in according to SDAI definition ( >3.3 to ≤11.0; >11.0 to ≤26 and > 26 to low, moderate and high activity disease, respectively). HRQoL was explored with the Short Form 36 Health Survey Questionnaire (SF-36). A generalized estimating equation model was used to explore each SDAI category as a predictor of the summary measures, mental (MCS), and physical (PCS) of the SF-36 obtained on the subsequent visit. The multivariable models were adjusted for other predictors: gender, age at diagnosis, education, socio-economic level (measured by the Graffar scale), disease duration, tobacco use, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies level, disability (MDHAQ), use of conventional (c), and biologic (b) DMARDs, use of corticosteroids (current use, past use or non-use) and the baseline score of the corresponding SF-36 summary measure.
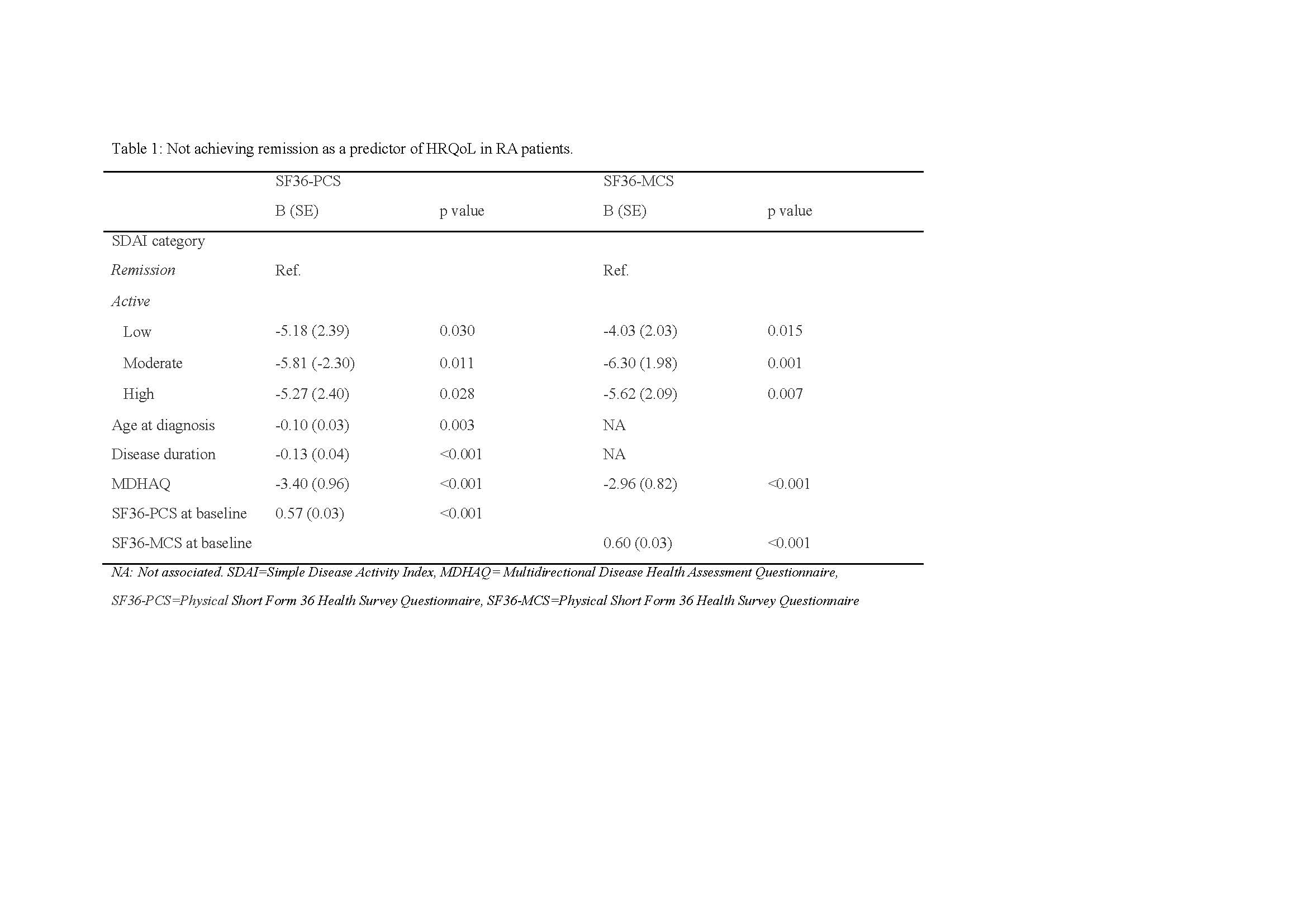
Results: Four hundred thirteen patients were included, 375 (90.8%) were women; age at diagnosis was 43.9 (13.5) years, disease duration was 16.7 (11.4) years. At the baseline visit, the SDAI was 25.6 (22.8); only 4.1% patients were in remission; 14.3%, 41.9% and 39.7 were in low, moderate and high disease activity, respectively; MDHAQ was 0.7 (0.5); current corticosteroid use was 31.6%, cDMARD 59.2% and only 7.8% were in bDMARD treatment. The PCS was 40.5(18.4) and the MCS 45.7 (16.6). One thousand and nineteen visits were analyzed in the follow-up (2.71 per patient). In the multivariable analysis, not achieving remission state was associated with a worse HRQoL; these data are depicted in table 1.
Conclusion: Not achieving remission states predicted a worse HRQoL in the follow-up of RA patients, in our real world cohort. These results reinforced the importance of remission as a goal of RA management in clinical practice in our region.
(1). Smolen. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:3-15. (2) Gamboa. Clin Rheum 2019 doi 10.1007/s10067-019-04618-x (3) Cardiel J Clin Rheumatol. 2012; 18:327-35. (4) Massardo Arthritis Care Res 2012; 64:1135-1143
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gamboa-Cárdenas R, Ugarte-Gil M, Reátegui-S C, Pimentel-Quiroz V, Medina M, Rodríguez-Bellido Z, Garcia-H S, Zeña-Huancas P, Gil L, Noriega E, Zevallos-M F, Alfaro-Lozano J, Perich-Campos R, Pastor-A C, Alarcón G. Not Achieving Clinical Remission Predicts a Poor Health-Related Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Results of a Latin American Real World Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/not-achieving-clinical-remission-predicts-a-poor-health-related-quality-of-life-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-of-a-latin-american-real-world-database/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/not-achieving-clinical-remission-predicts-a-poor-health-related-quality-of-life-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-of-a-latin-american-real-world-database/