Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The laboratory criteria used in the 2006 Sydney Classification criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) which is widely used in clinical practice, includes IgG/IgM isotypes of anti-cardiolipin antibodies (aCL), IgG/IgM isotypes of anti β2-glycoprotein I antibodies (aβ2GPI) and lupus anticoagulant (LAC), but there stands a group of patients tagged as seronegative-APS (SNAPS) with clinical manifestation prompting APS but persistent negative criteria antiphospholipid antibodies. Since these patients are at risk of developing recurrent thrombosis and pregnancy morbidities as the APS patients are, it is of great importance to distinguish these patients, meanwhile necessary clinical intervention or preventive measures should be carried out to minimize losses due to the disease. This study aims to assess the value of non-criteria antiphospholipid antibodies in SNAPS patients.
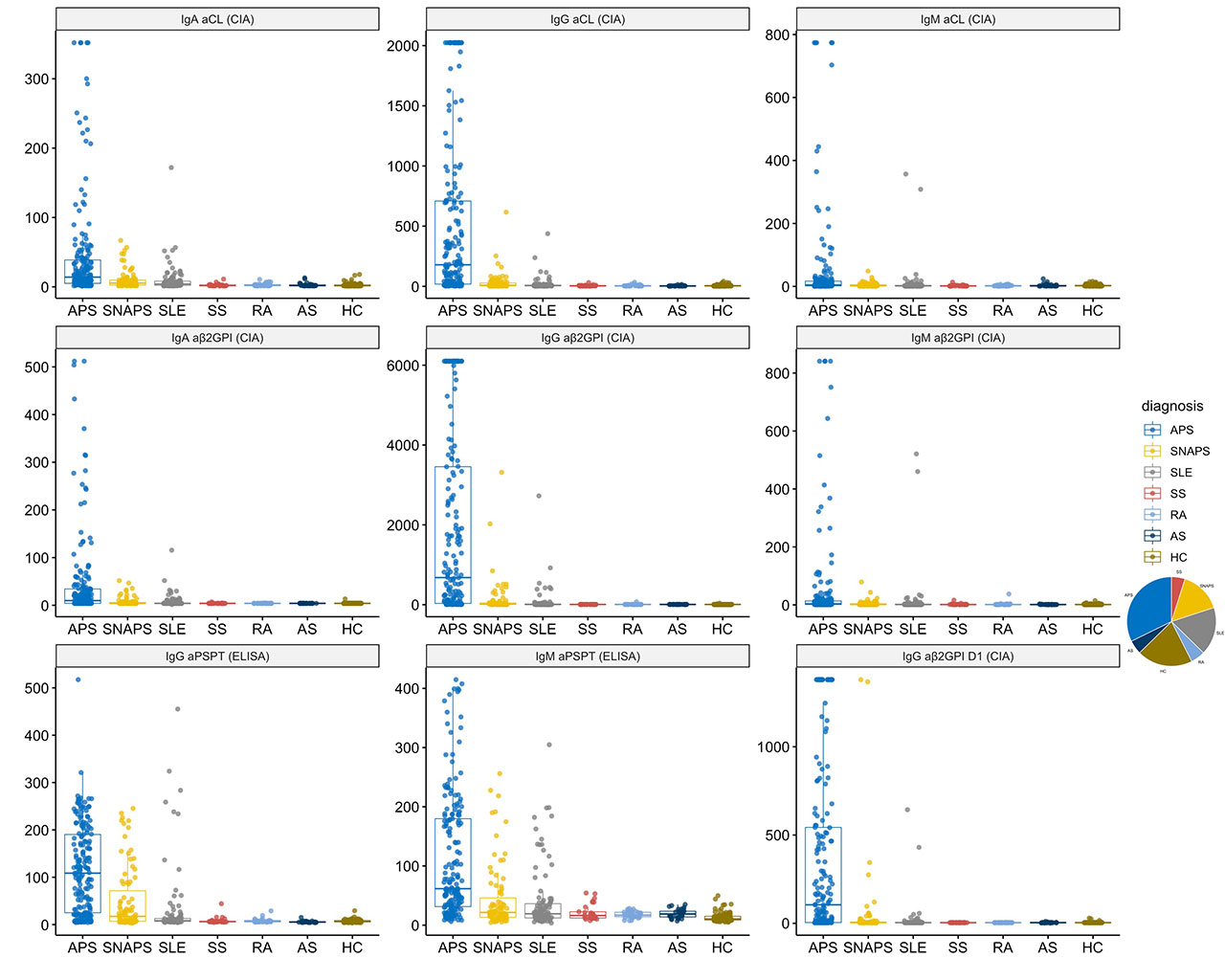
Methods: 192 APS patients fulfilling the 2006 Sydney classification criteria, 90 SNAPS patients, 193 disease control with other autoimmune diseases and 120 healthy controls were included in the survey. A total of 10 different aPLs were tested in the cohort using commercial kits, including 5 non-criteria aPLs: IgG/IgM anti-phosphatidylserine/prothrombin antibodies (aPS/PT), IgA aCL, IgA aβ2GPI, IgG anti-β2GPI Domain 1 (aβ2GPI D1).
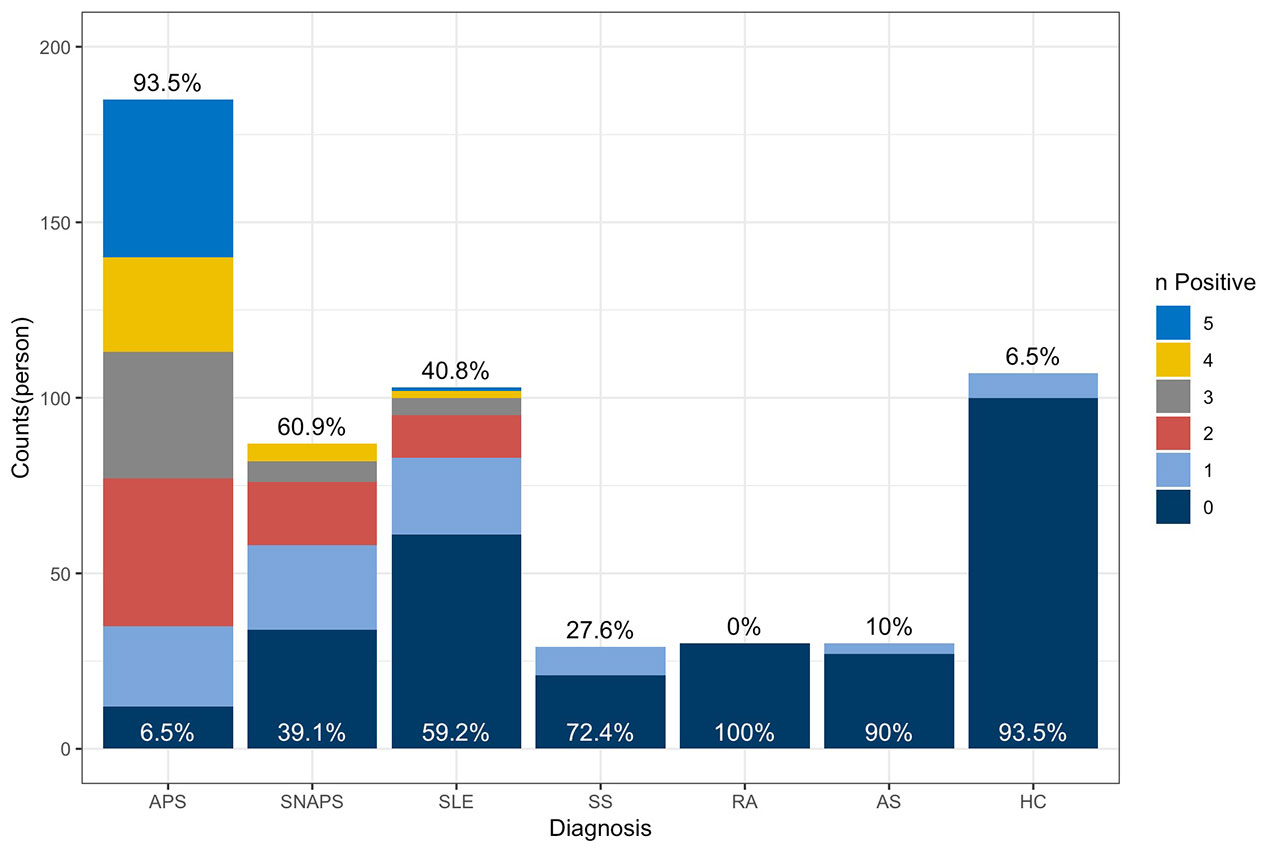
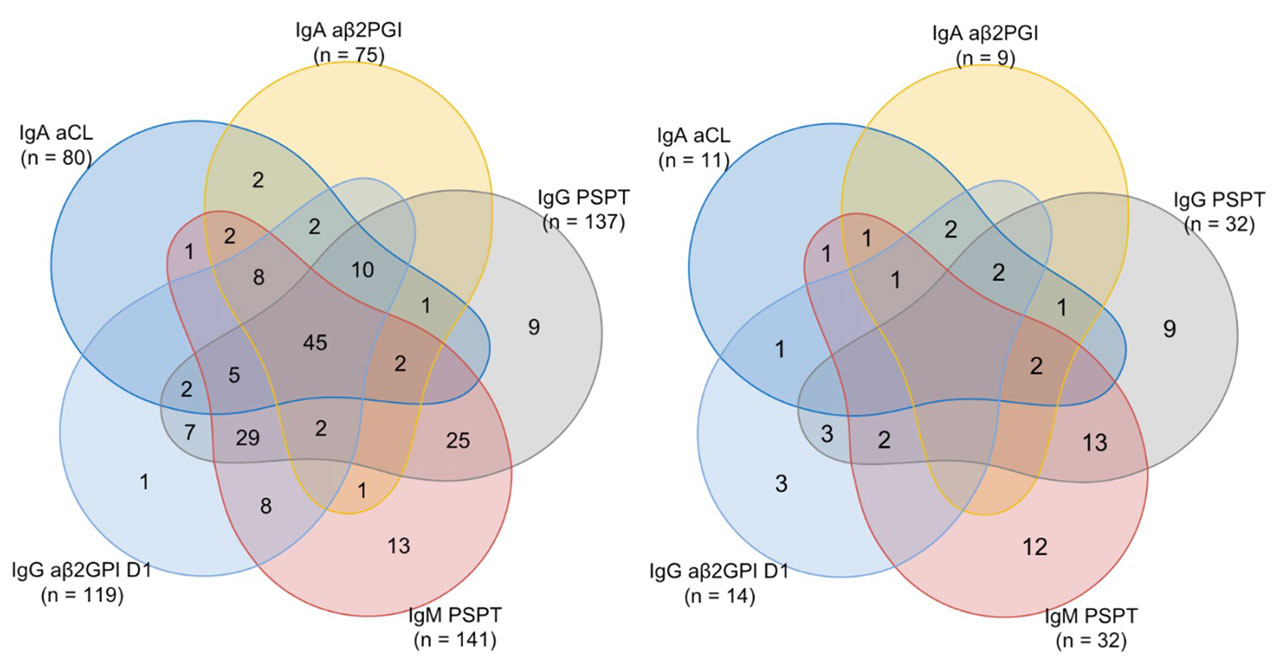
Results: Up to 60.9% SNAPS patients were detected by at least one kind of non-criteria aPLs, and the percentage reaches 93.5% in the APS group. IgG aPS/PT has the biggest Youden Index in classifying APS and SNAPS from the control group, while IgM aPS/PT is a little bit better in sensitivity, just secondary to IgG aβ2GPI. Besides, IgG β2GPI Domain1 is best related with pregnancy morbidities among all the markers. All of the three aforementioned markers can be separately detected in some of the SNAPS patients, while the IgA isotypes of aCL/aβ2GPI tend to appear together with other biomarkers, but they show better diagnostic and prognostic value compared with the IgM isotypes of the same aPL. Combined analysis showed better performance of the antibodies profiles with the help of non-criteria aPLs.
Conclusion: SNAPS patients account for a noticeable cohort in the clinical management of thrombotic and obstetric adverse events, and the non-criteria antiphospholipid antibodies help to distinguish a considerable part (40.8%) of these patients in clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gu J, Liu T, Wan L, Norman G, Yang C, Shi H. ‘Non-criteria’ Antiphospholipid Antibodies Add Value to Antiphospholipid Syndrome Diagnoses in a Large Chinese Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/non-criteria-antiphospholipid-antibodies-add-value-to-antiphospholipid-syndrome-diagnoses-in-a-large-chinese-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/non-criteria-antiphospholipid-antibodies-add-value-to-antiphospholipid-syndrome-diagnoses-in-a-large-chinese-cohort/