Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Approximately 50% of patients (pts) with chronic diseases are non-adherent to the therapeutic regimen assigned. In pts with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the non-adherence to therapy may impair the efficacy of treatment and is often associated with the disease flare and increased disability; moreover, non-adherence is a dynamic feature, unpredictable, because pts initially compliant to treatment may become non-adherent. The objectives of this survey were to evaluate the presence, to quantify the extent and to identify reasons for non-adherence to treatment with conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs alone (cDMARDs) or with biological DMARDs (bDMARDs) in RA pts in Italy.
Methods
This was a self-reported survey performed in RA pts treated with cDMARDs in Italy. In the hospital waiting room, pts were asked to fill out an anonymous paper based questionnaire, without either nurses or physicians support. Fieldwork: December 3rd 2013 – February 24th 2014.
Results
A total of 1,000 RA pts treated with cDMARDs were recruited from 25 Italian centers (females: 76.3%; mean age: 57 years; mean time since RA diagnosis: 9 years): 360 pts were treated with cDMARDs alone and 640 pts were treated in combination with a biologic drug.
Overall, the proportion of pts reporting non-adherence to cDMARDs was 37.2% (n=372): 28.9% (n=104) treated with cDMARDs alone and 41.9% (n=268) treated in combination cDMARDs + biologic drug. cDMARDs non-adherent pts were asked to report how often they do not take the cDMARDs treatment: the frequency of non-adherence was reported as “sometimes” by 55.38% of pts, “seldom” by 34.14%, “often” by 9.68% and “always” by 0.8%,.
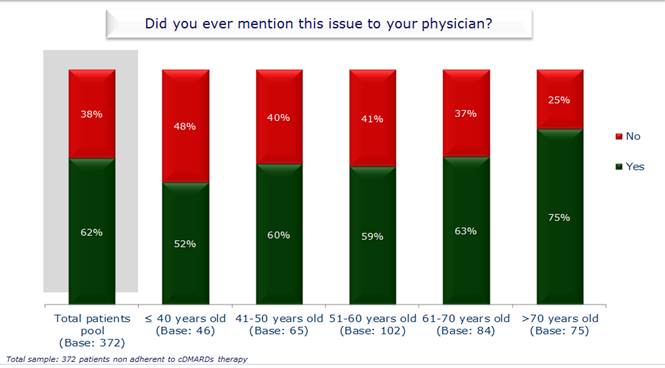
The main reason given for cDMARDs pts non-adherence was forgetfulness (54.8%); other reasons reported were: side effects fear (15.1%), the feeling they were taking too many drugs (14.2%), the thought of feeling better (9.4%) and the difficulty to remember drug dose and frequency of administration (6.5%). Interestingly, pts who did not mention cDMARDs non-adherence to their physician were 37.6% of the total 372 cDMARDs non-adherent pts, particularly younger pts (aged ≤ 40 years). More details are shown in Figures 1 and 2.
Conclusion
This extensive research about non-adherence to cDMARDs treatment, carried out in a large sample of RA pts, allowed to obtain an extensive local real life data set, representing Italian clinical practice. Results show that non-adherence to cDMARDs is fairly widespread (37.2%) among RA pts; furthermore, a considerable proportion of non-adherent pts (37.6%) find difficult to talk to their physician about this issue.
Fig 1
Fig 2
Disclosure:
G. Bianchi,
None;
A. Carletto,
None;
O. M. Epis,
Abbott Laboratories; Pfizer, Roche; BMS; AbbVie; Fidia Farmaceutici,
2,
Fidia farmaceutici, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis; Laborest; BMS;AbbVie, Abbott, Pfizer,
5,
Abbvie, BMS, Pfizer, Roche, Laborest, Sanofi-Aventis, MSD, Fidia Farmaceutici,
8;
C. Scioscia,
None;
A. Semeraro,
None;
L. Bianchino,
Roche Spa,
9;
L. Bazzichi,
None;
G. Lapadula,
None;
L. Sinigaglia,
Amgen,
8,
Abbvie,
8,
Eli Lilly and Company,
8,
MSD,
8;
A. Lo Monaco,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/non-adherence-to-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-italian-survey/