Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: NLRP12-associated autoinflammatory disease (NLRP12-AID) is an autosomal dominant autoinflammatory disorder caused by variants of the NLRP12 gene, which lead to a reduction of the inhibitory properties of NLRP12 on NF-κB signaling or an acceleration on the releasing of interleukin (IL)-1β. However, the clinical relevance is sometimes uncertain because of the lack of segregation and incomplete penetrance. NLRP12-AID has been hardly reported especially in Chinese adult population. Herein, we aimed to report a cohort of Chinese adult patients with NLRP12-AID and summarized the phenotypes and genotypes.
Methods: A final diagnosis of NLRP12-AID was reached in 17 patients after performing whole-exome sequencing and included in our cohort at the Department of Rheumatology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital from July 2015 to July 2021. Demographic information, clinical data and genetic analysis were collected and evaluated for each patient.
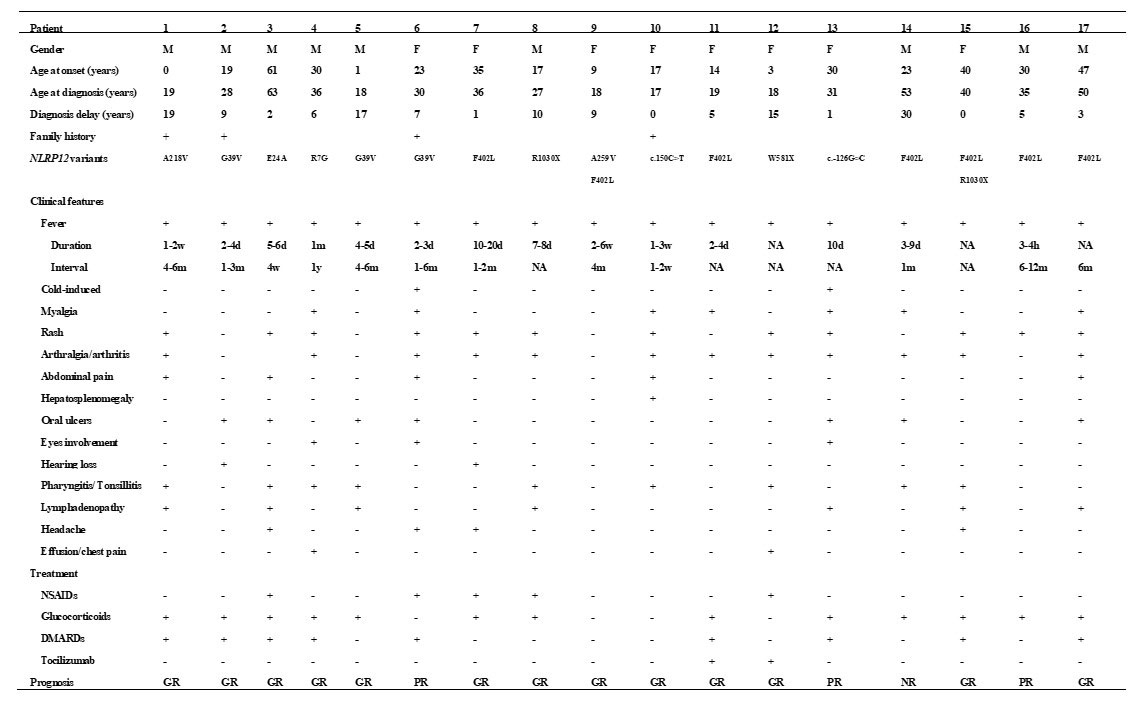
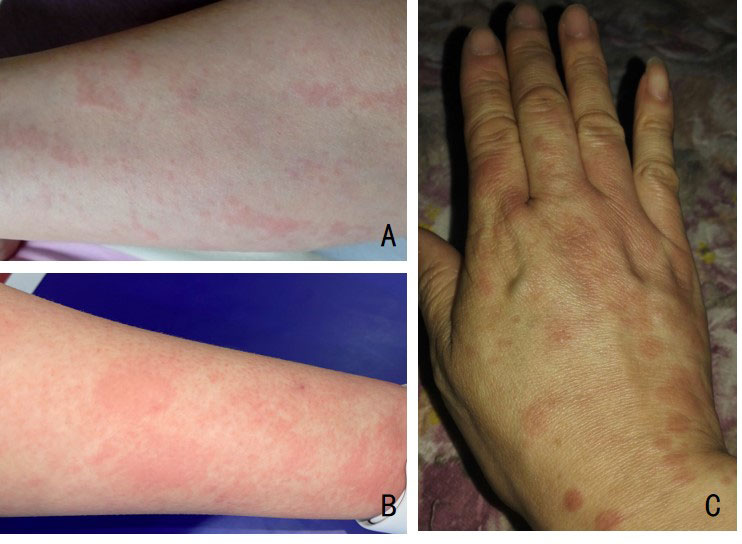
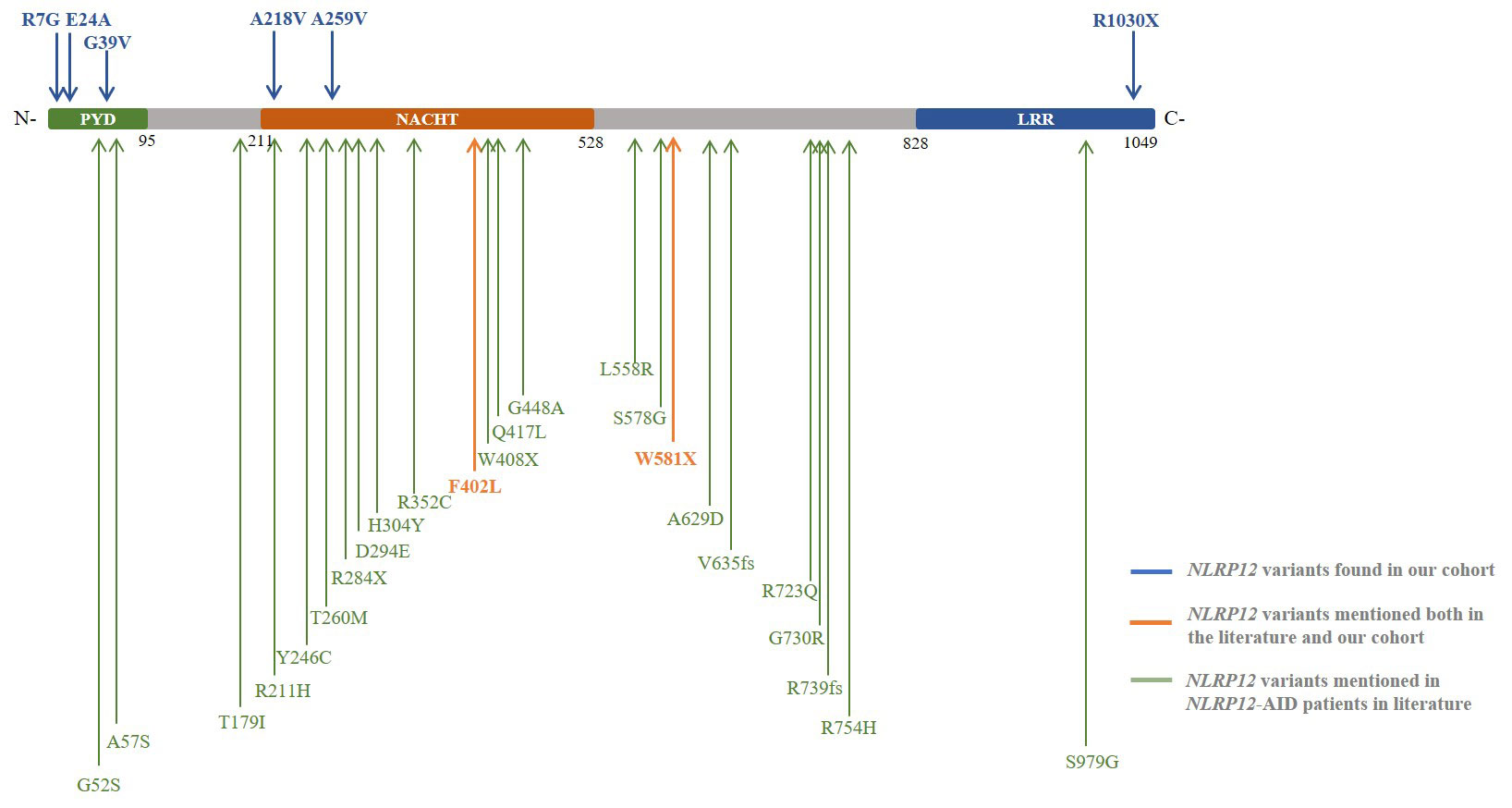
Results: In our cohort, the ratio of male to female was 8:9. The median age of disease onset was 23 (0-61) years old, and 4 patients had disease-onset during childhood. 4 patients were observed with family history of similar manifestations. The most frequent symptoms were fever (17/17, 100%), arthralgia/arthritis (13/17, 76.5%), skin lesions (12/17, 70.6%), pharyngitis/tonsillitis (9/17, 52.9%), myalgia (8/17, 47.1%), lymphadenopathy (7/17, 41.2%), oral ulcer (5/17, 29.4%), abdominal pain (5/17, 29.4%) and headache (5/17, 29.4%). Other symptoms including hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss and effusion/thoracic pain were also seen in several patients (4, 2 and 2 respectively). Thirteen heterozygous NLRP12 variants including two compound heterozygous were detected as F402L (n=7, exon 3), G39V (n=3, exon 1), R1030X (n=2, exon 9), c.-150C >T (exon 1), R7G (exon 1), E24A (exon 1), A218V (exon 3), A259V (exon 3), W581X (exon 3), and c.*126G >C (exon 10) (n=1, respectively). The patients with variants in exon 1 were prone to be suffered from oral ulcers compared with those carried variants in other exons (4/6 vs 1/11, p=0.028). Glucocorticoids was given to 13 patients, DMARDs given to 9 patients, NSAIDs to 5 patients, and tocilizumab to 2 patients, among whom 13 had good responses with no episodes now, 3 had partial responses and 1 had no response.
Conclusion: This is the largest cohort of adult NLRP12-AID patients in the world. Distinct clinical features with the same variants suggested the heterogeneity of NLRP12-AID and the modifying roles that the NLRP12 gene might played in the pathogenesis. R7G, E24A, G39V, A218V, A259V, R1030X,c.-150C >T and c.*126G >C were the variants identified in our cohort only. Further exploration is needed to explain the relationship between the phenotypes and genotypes of NLRP12-AID.
NA: not available; GR: good response; PR: partial response; NR: no response;
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Miao J, Shen M. NLRP12-associated Autoinflammatory Disease in Chinese Adult Patients: A Single-center Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nlrp12-associated-autoinflammatory-disease-in-chinese-adult-patients-a-single-center-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nlrp12-associated-autoinflammatory-disease-in-chinese-adult-patients-a-single-center-study/