Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Checkpoint inhibitors (CI) for cancer therapy are associated with inflammation that can recapitulate features of autoimmunity, including synovitis resembling rheumatoid arthritis (RA). No reports have investigated cellular infiltrates in the synovial tissue (ST) of these patients and no guidelines exist to manage them. Thus, we provide the first report on ST cellular infiltration in PD1 inhibitor-induced rheumatic immune-related adverse-events (irAE).
Methods:
ST biopsies, synovial fluid (SF) and PBMCs from a nivolumab-treated small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patient with severe peripheral inflammatory polyarthritis and inadequate response to DMARDs (negative RF and ACPA); 3 DMARD-naïve patients with seropositive early RA were used as comparators.
Serial sections from fresh-frozen ST blocks were stained with H&E, CD3, CD45RO, CD55 and CD68 and semi-quantitatively scored. ST, SF and PBMC single cell suspensions were stained with Zombie UV®, CD45RO, PD1, CD3, ICOS, CD8, CD4 CD20 prior to flow cytometric acquisition.
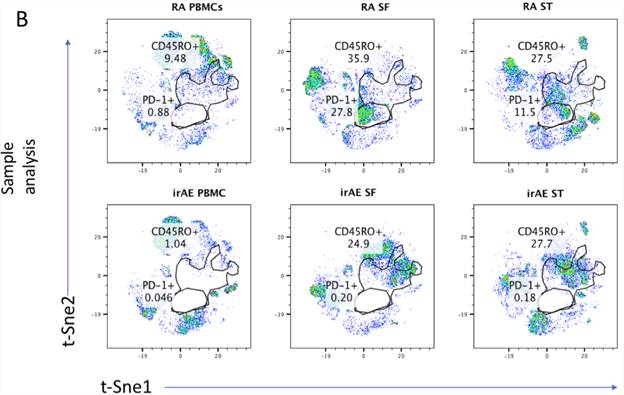
Results: CD68+ macrophage, CD20+ B cell and CD3+ T cell and CD45RO+ memory T cell infiltration in irAE was comparable to RA ST on semi-quantitative scoring, while TNFα staining was markedly elevated in irAE compared to RA (irAE-TNFα; 4, RA-TNFα; 2) (Figure 1). Flow cytometric analysis identified persistent CD45RO_ memory T cell infiltration in the ST and SF compartments (irAE: ST; 27.7, SF; 24.9) compared to RA (RA: ST mean and SEM; 27.5±3.63: SF; 35.9±4.85: n=3 for each), driven by continued occupancy of PD1 by nivolumab even 200-days after cessation of treatment (Figure 2). Finally, treatment with infliximab resulted in partial remission of symptoms and reduced synovitis
Figure 1. A, RA ST sections (images representative of all 3 RA). B, ICI-irAE SCLC ST sections. Images were captured at x10 magnification.
Figure 2. T-Sne global analysis performed on all samples concatenated in a common dimensionally reduced space. Comparable CD45RO+ T cell frequency in ST (irAE; 27.7, RA mean and SEM;26.5±2.3, n=3) and SF (irAE;24.9, RA; 36.6±1.79, n=3), flow cytometry revealed a distinct absence of PD1 staining in irAE (ST: irAE: 0.18, SF; 0.20, PBMCs; 0.46) compared to RA (RA: ST; 12.13±1.63: SF; 25.95±2.85: PBMCs; 0.11±0.13, n=3). RA plots representative of all samples.
Conclusion:
ST infiltration in irAE SCLC recapitulates many features of RA histopathology. The continued persistence of nivolumab occupancy in rheumatic-irAEs provides a mechanism for exacerbated inflammation. Infliximab treatment was shown to lead to remission in irAE demonstrating high levels of ST TNFα.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Murray-Brown W, Weedon H, Wilsdon T, Proudman S, Walker J, Smith MD, Wechalekar MD. Nivolumab-Induced Synovial Tissue T Cell Infiltration, Sustained PD1 Occupancy and Resolution of Severe Synovitis with Infliximab Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nivolumab-induced-synovial-tissue-t-cell-infiltration-sustained-pd1-occupancy-and-resolution-of-severe-synovitis-with-infliximab-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nivolumab-induced-synovial-tissue-t-cell-infiltration-sustained-pd1-occupancy-and-resolution-of-severe-synovitis-with-infliximab-therapy/