Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: With multiple targeted immunomodulators (TIMs) approved by the FDA for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA), the relative efficacy and cost-effectiveness of these TIMs remains uncertain, particularly for the newly introduced agents. In the absence of head-to-head trials, indirect comparison provides valuable informative evidence for decision makers. This study compared the clinical (ACR 20/50/70; PASI 75/90) and cost-effectiveness outcomes of TIMs among PsA patients without prior biologic treatment.
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted to identify Phase 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for TIMs approved for the treatment of active PsA in the US, including tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors (adalimumab [ADA], certolizumab pegol [CZP], etanercept [ETN], golimumab [GOL], and infliximab [INF]), interleukin-17 inhibitors (secukinumab [SEC] and ixekizumab [IXE]), an interleukin-12/23 inhibitor (ustekinumab [UST]), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor (apremilast [APR]), a selective T cell costimulation modulator (abatacept [ABA]), and a janus kinase inhibitor (tofacitinib [TOF]) in active PsA. Joint (ACR 20/50/70) and skin (PASI 75/90) responses at Week 24 were estimated via a Bayesian network meta-analysis (NMA) among biologic-naïve patients. Treatment costs were based on Wholesale Acquisition Cost as of April 18, 2018 and included drug acquisition and administration costs. Incremental costs per responder relative to placebo were calculated as incremental treatment costs during 24 weeks divided by response rate difference vs. placebo.
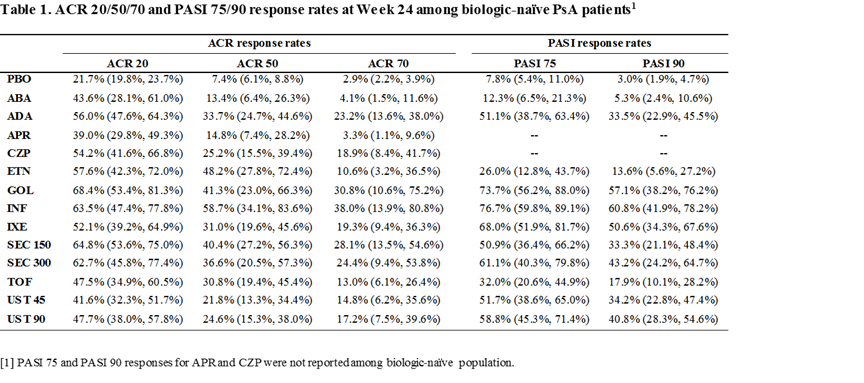
Results: Fourteen RCTs that reported ACR and/or PASI responses at Week 24 among biologic-naïve PsA patients were included. INF, ETN, and GOL had higher ACR 50 response compared with other TIMs (Table 1). In terms of ACR 20 and ACR 70, GOL, INF, and SEC 150 mg had higher efficacy than other TIMs. With respect to PASI responses, INF, GOL, and IXE had higher efficacy than other TIMs. In terms of cost-effectiveness, when considering skin and joint responses together, INF ($47,899 for ACR 50/$42,522 for PASI 90), GOL ($79,982 /$50,238), and ADA ($111,259 /$96,149) were associated with lower incremental costs per additional ACR 50 or PASI 90 responder than other TIMs (Figure 1).
Conclusion: At Week 24, INF, GOL, and ADA had the lowest incremental cost per responder for joint and skin outcomes among all TIMs approved for PsA in biologic-naïve patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Husni ME, Griffith J, Song Y, Singh R, Zhao J, Betts KA. Network Meta-Analysis of Targeted Immunomodulators in the Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients without Prior Biologic Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/network-meta-analysis-of-targeted-immunomodulators-in-the-treatment-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-without-prior-biologic-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/network-meta-analysis-of-targeted-immunomodulators-in-the-treatment-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-without-prior-biologic-treatment/