Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) have demonstrated large clinical improvements in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA), with patients naïve to bDMARDs experiencing substantial benefits; additional treatments are also becoming available. The aim of this network meta-analysis (NMA) was to compare efficacy of various bDMARDs in bDMARD-naïve adult patients with nr-axSpA.
Methods: A systematic literature review (SLR) identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published on bDMARDs in adult patients with axSpA who failed at least one non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. RAPID-axSpA (NCT01087762) and C-axSpAnd (NCT02552212) clinical study reports informed clinical efficacy of certolizumab pegol (CZP). After evaluation of the evidence, trials assessing the efficacy of bDMARDs in initially bDMARD-naïve nr-axSpA populations/subpopulations were analyzed. Fixed-effects Bayesian NMAs were conducted to compare treatments of interest; fixed-effects models were employed due to limited data. At 12–16 and 52 weeks, the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society 40% response (ASAS40) was evaluated with odds ratios (ORs) and 95% credible intervals (CrIs).
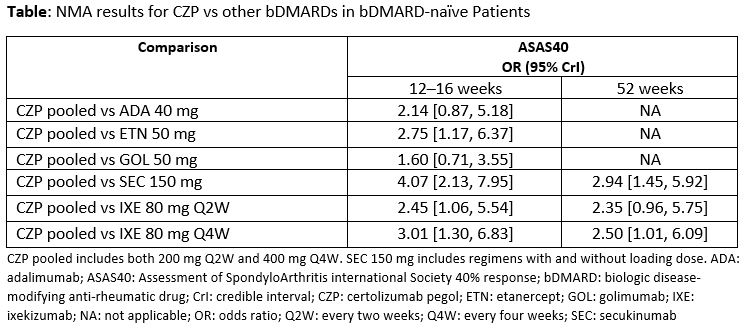
Results: The SLR identified 10 trials evaluating nr-axSpA patients, of which seven were considered comparable for the NMA. Trials primarily evaluated bDMARD-naïve patients, while others reported data for bDMARD-naïve subgroups. Identified bDMARDs included adalimumab (ADA), CZP, etanercept (ETN), golimumab (GOL), ixekizumab (IXE), and secukinumab (SEC), encompassing tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) and anti-interleukin (anti-IL) agents. From these trials, RAPID-axSpA (CZP), ABILITY-1 (ADA), EMBARK (ETN), and GO-AHEAD (GOL) reported data only at 12–16 weeks; C-axSpAnd (CZP), PREVENT (SEC), and COAST-X (IXE) reported data at both 12–16 and 52 weeks. At 12–16 weeks (Table), CZP demonstrated the greatest odds of ASAS40 compared with SEC (OR [95% CrI]: 4.07 [2.13, 7.95]), with significantly greater odds of response vs ETN or IXE every two weeks (Q2W), and IXE every four weeks (Q4W). Treatment advantage for CZP vs ADA and GOL in ASAS40, while numerically greater, did not reach statistical significance. At 52 weeks (Table), CZP demonstrated significantly greater odds of ASAS40 response compared to SEC (2.94 [1.45, 5.92]) and IXE Q4W (2.50 [1.01, 6.09]); advantages for CZP compared to IXE Q2W for ASAS40 did not reach statistical significance. Exploration of statistical heterogeneity was limited by the fact that only one study per treatment was identified for all treatments but CZP.
Conclusion: In bDMARD-naïve patients with nr-axSpA, CZP showed increased odds of an ASAS40 response vs most bDMARDS investigated at 12–16 weeks, and vs anti-IL agents investigated at 52 weeks.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiri S, Kim M, Betts M, Chitnis M, Fahrbach K, Tarpey J, Turner M. Network Meta-Analysis of Long-Term Efficacy (ASAS40) of Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (bDMARDs) in bDMARD-Naïve Patients with Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/network-meta-analysis-of-long-term-efficacy-asas40-of-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-bdmards-in-bdmard-naive-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/network-meta-analysis-of-long-term-efficacy-asas40-of-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-bdmards-in-bdmard-naive-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/