Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Epidemiology and Public Health Poster III: Rheumatic Disease Risk and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
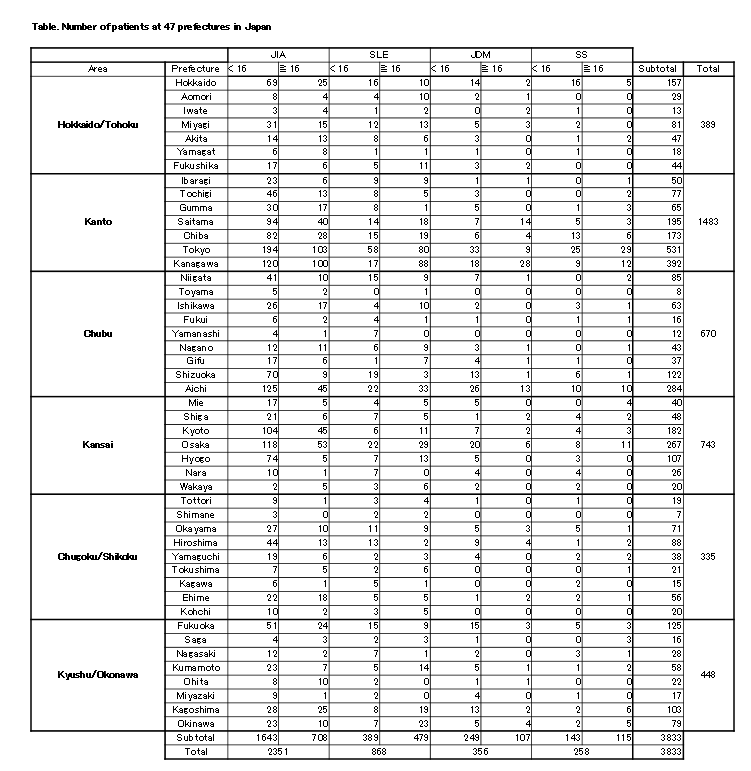
Background/Purpose: We did not grasp how many and where pediatric rheumatic patients exist in Japan quite exactly until now. About juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), child-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM), child-onset Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), we would like to know the actual situation of follow-up in clinical pediatric facilities in Japan.
Methods: For 519 clinical pediatric training institutes in Japan Pediatric Society, we performed the questionary survey for grasping the number of patients < 16 and õ16 years about the above diseases with letter form. The answer period was from May 1 to December 31, 2016.
Results: As for the answer from 474 institutes (91.3%), the number of patients < 16 and †16 years were as follows; JIA: 1,704 vs 750, SLE: 404 vs 525, JDM: 268 vs 113, SS: 148 vs 126, individually. As results of statistical analysis, we could recognize that the number of JIA was approximately 2,700, that of SLE 1,000, that of JDM 400 and that of SS 300 in the whole Japan. Because the population of 2016 of Japan < 16 years was 16,954,000, the prevalence of each disease < 16 years was 11.0, 2.6, 1.7, 1.0 per 100,000 persons. We also reported the detail of the medical actual situation such as the enforcement systems of the transition medicine in the childhood-onset rheumatic diseases, based on 1) number of patients at 47 prefectures in Japan (Table), 2) distribution of pediatric rheumatic specialists, 3) cooperation with the core institutions for pediatric rheumatology in each medical area.
Conclusion: This is the first accurate report about of national survey of childhood-onset rheumatic diseases followed up in the clinical pediatric facilities in Japan. We are convinced that these results build the foundation to plan the cooperation with patient and family society, the choice of the clinical trial facilities of the new medicine, and the construction of both domestic and international pediatric rheumatic disease-registry in future.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mori M, Takei S, Itoh Y, Kobayashi I, Tomiita M, Okamoto N, Yamazaki K. National Survey of Childhood-Onset Rheumatic Diseases Followed up in the Clinical Pediatric Facilities in Japan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/national-survey-of-childhood-onset-rheumatic-diseases-followed-up-in-the-clinical-pediatric-facilities-in-japan/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/national-survey-of-childhood-onset-rheumatic-diseases-followed-up-in-the-clinical-pediatric-facilities-in-japan/