Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Adalimumab remains the only biologic approved by the EMA and FDA for the treatment of noninfectious uveitis. There are few reports on the effectiveness of other anti-TNF drugs such as certolizumab pegol (CZP). Our aims were to determine the efficacy and safety of CZP in refractory uveitis secondary to Immune-mediated Inflammatory Diseases (IMIDs).
Methods: national multicenter study of 80 patients with uveitis due to IMID refractory to glucocorticoids and conventional immunosuppressants treated with CZP. Efficacy was assessed with the following ocular parameters: best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), anterior chamber cells, vitritis, macular thickness and presence of retinal vasculitis. The efficacy of CZP was compared between the baseline visit, 1st week, 1st and 6th month, and 1st year. Statistical analysis was performed with IBM SPSS Statistics v.23.
Results: we studied 80 patients/111 affected eyes (33 men/47 women) with a mean age of 41.6±11.7 years. The IMIDs included were: spondyloarthritis (n=43), Behçet’s disease (10), psoriatic arthritis (8), Crohn’s disease (4), sarcoidosis (2), JIA (1), reactive arthritis (1), rheumatoid arthritis (1), relapsing polychondritis (1), TINU (1), pars planitis (1), Birdshot (1) and idiopathic uveitis (6). Anterior was the most frequent uveitis pattern (n=61).
In 20 patients, besides the presence of refractory uveitis, desire of pregnancy was the reason for CZP initiation.
Prior to CZP, patients had received: methotrexate (n=38), sulfasalazine (28), azathioprine (14), cyclosporine (10), leflunomide (3), mycophenolate mofetil (4), and cyclophosphamide (1). Previous biologic therapy was administered in 52 patients (63%), with a median [IQR] of 2 [1-3] drugs per patient. The most used biologic was adalimumab (n=48), followed by infliximab (32), golimumab (15), tocilizumab (5), etanercept (7), rituximab (1), anakinra (1) and secukinumab (1). CZP was administered as monotherapy in 39 patients.
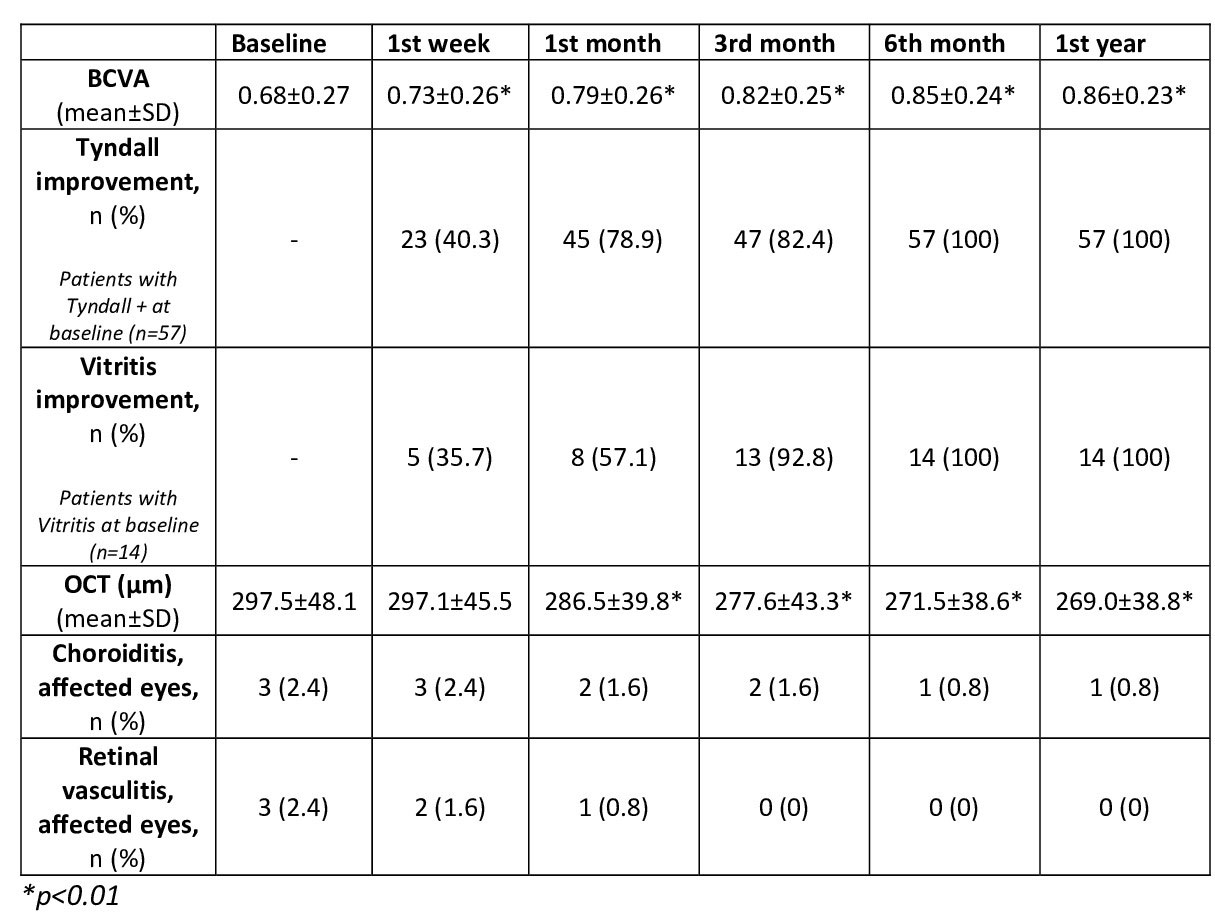
After 24 [12-36] months of follow-up, all parameters analyzed showed a rapid and maintained improvement (TABLE). A decrease in the mean number of uveitis flares was observed before and after CZP, (2.6±2.3 vs. 0.6±0.4, p< 0.001). CZP was discontinued in 16 patients due to: ocular remission (n=3), insufficient ocular response (4) and incomplete response of extraocular manifestations (9). No serious adverse effects were found.
Conclusion: CZP seems to be effective and safe in the control of uveitis associated to different IMIDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martín-Varillas J, Sánchez-Bilbao L, Calvo Río V, Adán A, Hernanz Rodríguez I, Beltrán Catalán E, Castro Oreiro S, Fanlo P, Garcia A, Torre I, Cordero Coma M, de Dios J, Garcia-Aparicio A, Hernandez Garfella M, Sánchez Andrade A, García-valle A, Maiz O, Miguelez Sanchez J, Rodriguez Montero S, Urruticoechea A, Veroz R, Conesa A, Fernández-Carballido C, Jovani Casano V, Martinez O, Moya Alvarado P, Romero Yuste S, Rubio Muñoz P, Peña Sainz-Pardo e, Garijo Bufort M, Hernández J, Blanco R. National Multicenter Study of 80 Patients with Refractory Uveitis Due to Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Treated with Certolizumab Pegol [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/national-multicenter-study-of-80-patients-with-refractory-uveitis-due-to-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-treated-with-certolizumab-pegol/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/national-multicenter-study-of-80-patients-with-refractory-uveitis-due-to-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-treated-with-certolizumab-pegol/