Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) is a heterogeneous auto-inflammatory skin disease, that is driven to a great extent by interferon (IFN) type I1, and is characterized by superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal infiltration of lymphocytes as well as interface dermatitis. Unfortunately, no specific histological marker for CLE is currently available.
Methods: 163 skin biopsy specimens were collected from the local pathology database. Various conditions (eg. CLE, dermatomyositis, rosacea, psoriasis, graft versus host disease, scleroderma) were selected, provided that clinical diagnosis matched with histological diagnosis. Herpes simplex lesions were used as positive controls. Skin sections were incubated with anti-MxA (R&D systems, AF7946). Consecutively, rabbit anti goat-HRP conjugate (Dako, 0449) was added and sections were stained with diaminobenzidine.
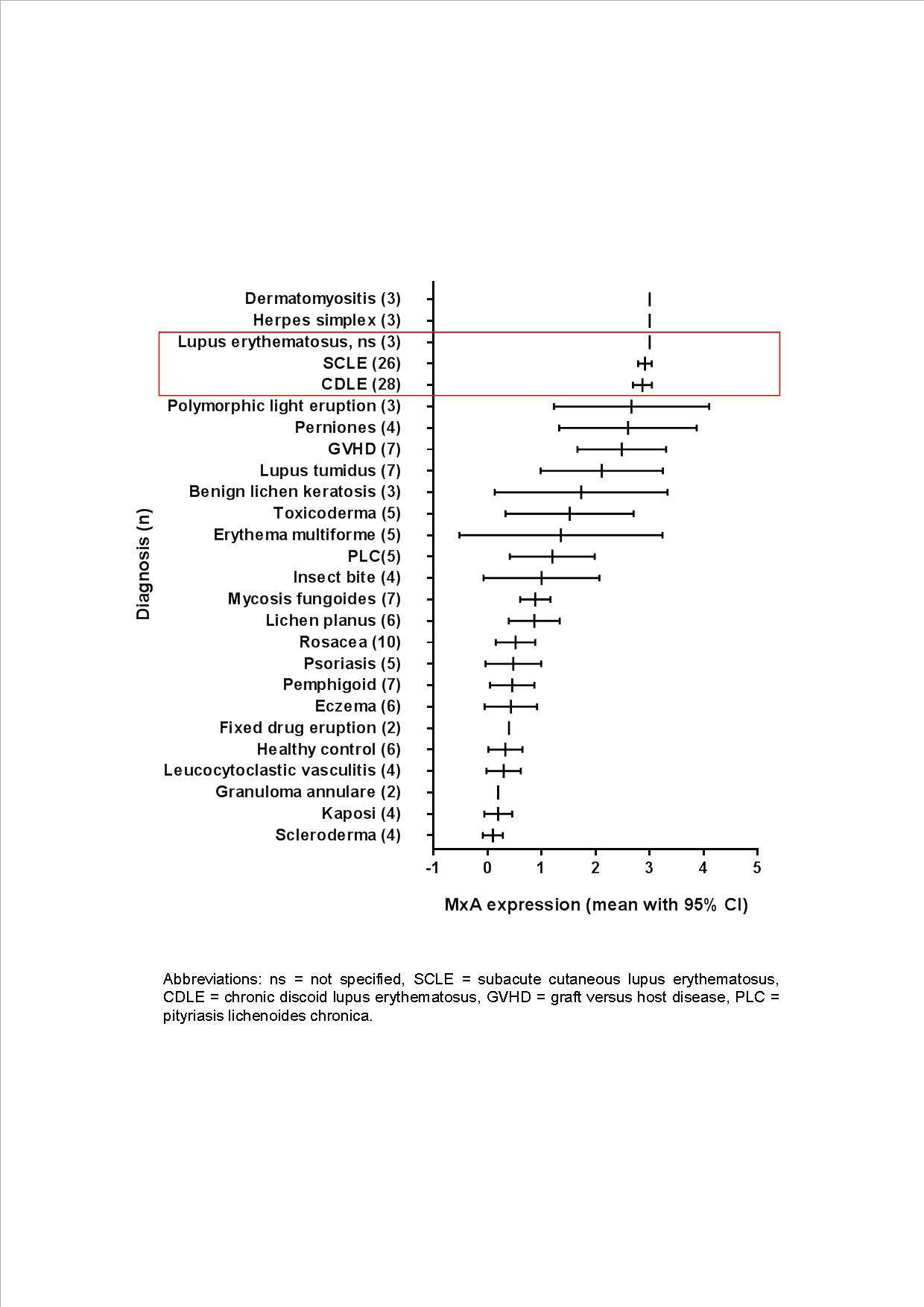
The expression of MxA was scored semi-quantitatively by 2 researchers in respectively epidermis, dermal structures, fibroblasts, infiltrates, and endothelium (0 for no expression, 1 for moderate expression, 2 for mediate expression, and 3 for strong expression). Mean scores were calculated based on cumulative expression divided by the number of assessable skin parts.
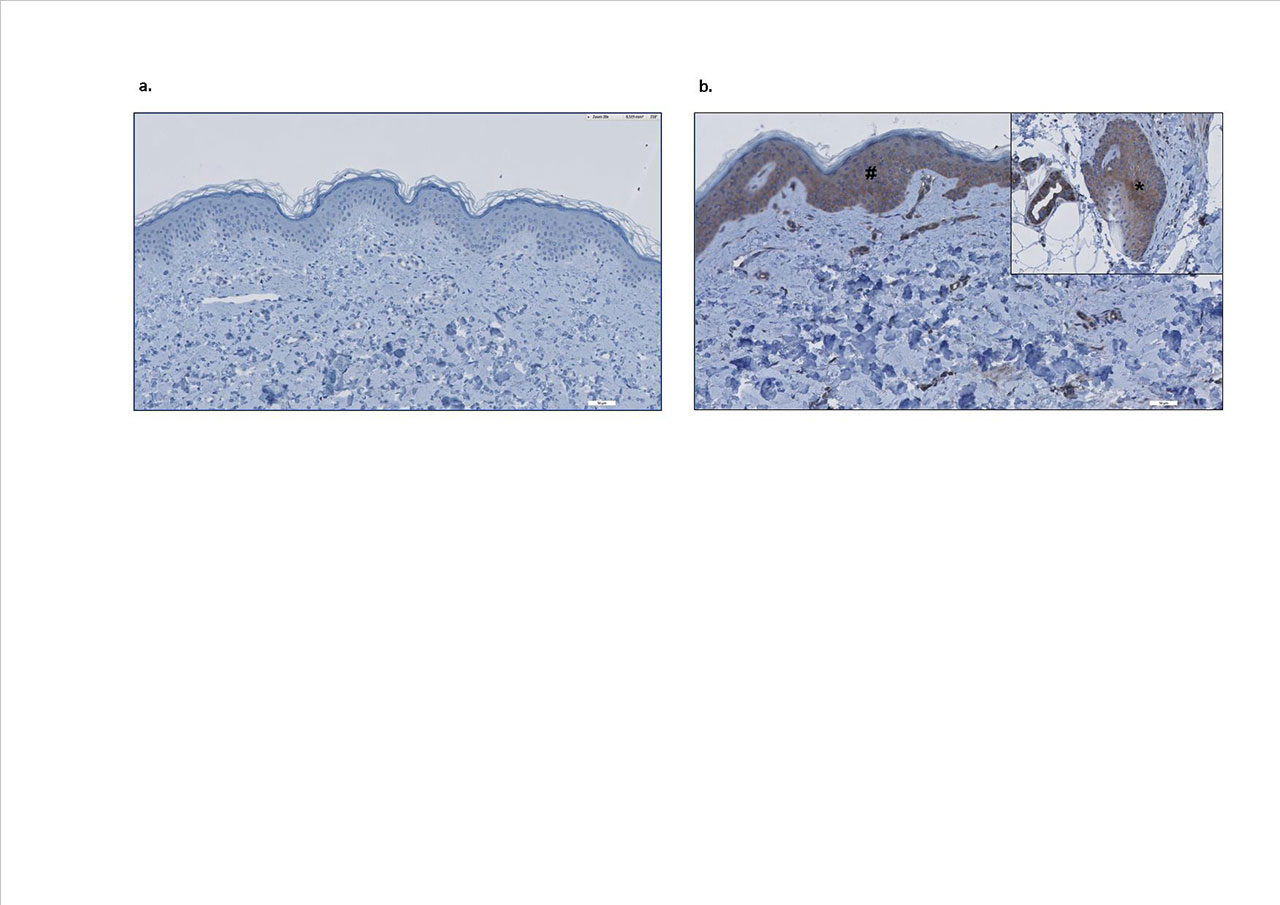
Results: MxA staining was strongly positive in both epidermis, dermal structures, infiltrate, and endothelium in nearly all lesional CLE skin sections (except lupus tumidus), as well as in dermatomyositis (see figure 1), which is also an IFN-driven autoimmune disease. Although most other inflammatory skin diseases did show no or a low expression of MxA. In some conditions, like perniones and graft versus host disease, high expression could be found, but this was less consistent compared to CLE.
Conclusion: MxA is strongly expressed in CLE skin, and therefore is useful as additional diagnostic histological marker, expectedly resulting in restriction of misdiagnosis and treatment delay. The high expression found in skin biopsies from graft versus host disease and perniones, suggests that IFN type I plays a role in the pathogenesis of these conditions.
Abbreviations: ns = not specified, SCLE = subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, CDLE = chronic discoid lupus erythematosus, GVHD = graft versus host disease, PLC = pityriasis lichenoides chronica.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lambers W, de Leeuw K, Homan F, Doornbos-van der Meer B, Bootsma H, Westra J, Diercks G. Myxovirus Resistance Protein a Is a Useful Additional Histological Marker for Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myxovirus-resistance-protein-a-is-a-useful-additional-histological-marker-for-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myxovirus-resistance-protein-a-is-a-useful-additional-histological-marker-for-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus/