Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) comprise a group of autoimmune diseases associated to different myositis related antibodies (MRA), that determine distinct phenotypes but share some symptoms, including myositis, skin rash and high prevalence of interstitial lung disease (ILD), the latter being particularly associated with some MRA. Some patients with MRA and ILD will fulfill IIM classification criteria, but others will not and may be classified as ILD with autoimmune features (IPAF). The aim of our study is to describe the clinical and radiological features of a group of patients with ILD and MRA, and their association with baseline and longitudinal pulmonary function (PF).
Methods: Descriptive study of a multicentric cohort of 211 patients evaluated between 2016-2018 in 3 multidisciplinary ILD clinics in Argentina, Chile and México. Every patient was confirmed to have ILD by thoracic high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Descriptive statistics, univariate and multivariate analysis were performed.
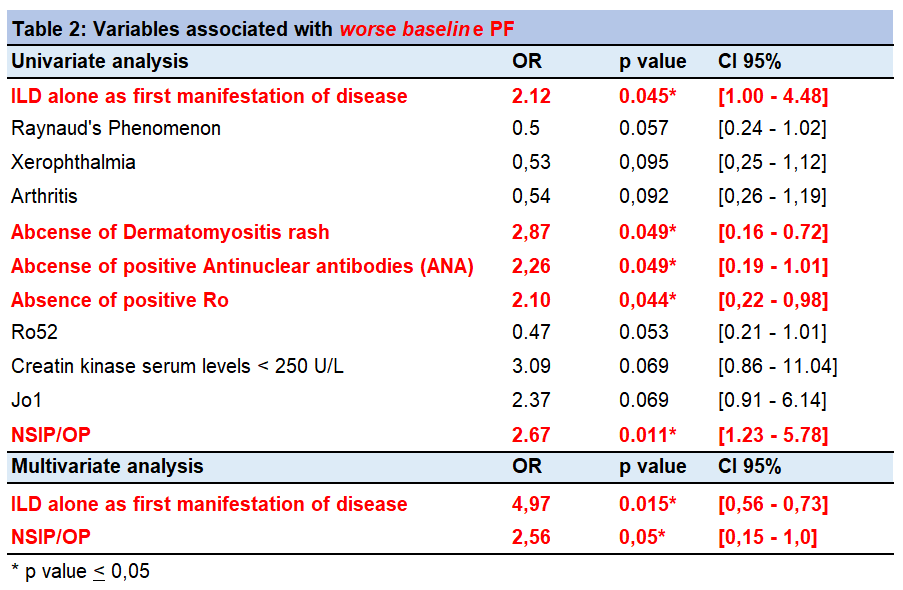
Results: 211 patients were included, (Chile = 119, México = 50 and Argentina = 42). Most patients were women (77,4%), mean age of 57 +-12 years. In 146 patients (70%) ILD was diagnosed first, in 43 patients (18%) ILD and connective tissue disease (CTD) were diagnosed simultaneously, and CTD was diagnosed first in 25 patients (12%). Mean interval between ILD and CTD diagnosis was 7.6 months (Table 1). Anti-Synthetase (AS) antibodies were the most frequent (Jo-1, PL12, PL-7), followed by Ro-52, PM-Scl 75-100 and Ku. Most frequent CTD diagnoses were AS syndrome and IPAF. Most prevalent HRCT patterns were non-specific interstitial pneumonia /organizing pneumonia overlap (NSIP/OP) and NSIP (Table 1). Worse baseline PF was defined as forced vital capacity (FVC) < 70% and/or diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide (DLCO) < 60% at debut. Worse baseline PF was associated to ILD alone as initial diagnosis, NSIP/OP HRCT pattern, absence of dermatomyositis rash and absence of positive ANA and Ro (uni/multivariate analysis, Table 2). Functional improvement was defined as an increase of FVC greater than 10% in follow up. 121 patients with > 3 months of follow-up were included. Functional improvement was associated with absence of ILD as the first manifestation of disease and absence of sclerodactily, presence of OP HRCT pattern and mechanic´s hands (uni/mulitvariate analysis, Table 3). First line immunosuppressive treatments consisted in corticosteroids (CS) associated with a CS sparing agent like mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, leflunomide, tacrolimus or rituximab (Table 1).
Conclusion: In our MRA-ILD cohort, AS antibodies and AS Syndrome were the most common findings, followed by IPAF. NSIP and NSIP/OP were the most prevalent HRCT patterns. Worse baseline PF could be related to the absence of extra-thoracic symptoms and “classic” antibodies of CTD (e.g ANA, Ro), causing delay in diagnosis and treatment. On the contrary, better functional improvement could be related to the presence of extra-thoracic signs that allow an opportune diagnosis and therapy, and more acute-subacute forms of ILD, as OP HRCT pattern.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
WOLFF V, ALBERTI M, REYES F, JUAREZ E, ROJAS-SERRANO J, CARO F, BUENDIA I, MEJIA M, FLORENZANO M, PAULIN F. Myositis Related Antibodies and Interstitial Lung Disease: Variables Associated with Baseline Lung Function and Functional Improvement: Results from a Multicentric Latin-american Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myositis-related-antibodies-and-interstitial-lung-disease-variables-associated-with-baseline-lung-function-and-functional-improvement-results-from-a-multicentric-latin-american-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myositis-related-antibodies-and-interstitial-lung-disease-variables-associated-with-baseline-lung-function-and-functional-improvement-results-from-a-multicentric-latin-american-cohort/