Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II: Basic and Translational Science
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (CADM) patients are frequently manifested by rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (ILD) and associated with a poor prognosis. Recently cardiac involvement is recognized as a poor prognostic factor in several diseases including inflammatory myositis, however its clinical significance has been rarely investigated in CADM. Here, we determined factors associating with poor prognosis in patients with CADM by focusing on cardiac involvement using cardiac scintigraphy.
Methods: All patients who visited our hospital from 2009 to 2015 and performed cardiac scintigraphy using 99mTl and 123I-BMIPP were retrospectively evaluated. Patients who fulfilled Bohan and Peter’s criteria for DM and Sontheimer ‘s criteria for CADM were selected. We calculated the mismatch score in cardiac scintigraphy by subtracting the uptake of 123I-BMIPP (metabolism) from that of 99mTl (perfusion) on each 17 myocardial segments standardized by American Heart Association. The perfusion-metabolic mismatch indicates an area of hypometabolism without ischemia and a functional abnormality due to myocardial injury. We compared the mismatch scores between patients with classic DM and CADM. Furthermore, independent prognostic factor for poor outcome defined as death or receiving home oxygen therapy was determined in CADM group.
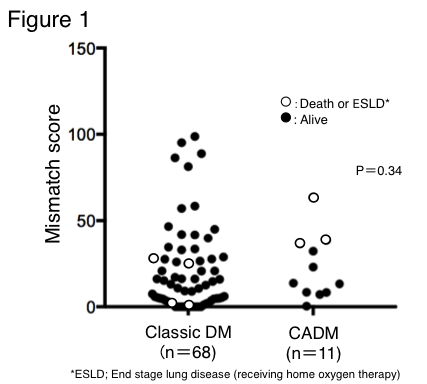
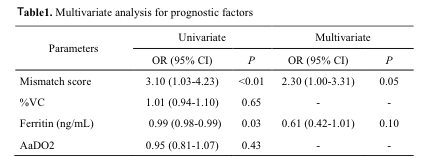
Results: One-hundred and seventy-seven patients were evaluated. We investigated 68 patients with classic DM and 11 patients with CADM. Higher prevalence of poor outcome was seen in CADM patients than classic DM patients (27.2% vs 5.9%, p=0.02), but there was no difference in %VC and level of cardiac enzyme between the groups. We compared the result of cardiac scintigraphy and found the mismatch scores was not different between the 2 groups (p=0.34) (Figure 1). However, a significantly higher level of mismatch score was detected in patients with poor outcome in only CADM group (p=0.02). Multivariate analysis revealed mismatch score was selected as the predictive factor with poor outcome in CADM (odds ratio, 2.30; 95% confidence interval, 1.00–3.31; p=0.04)(Table 1).
Conclusion: High mismatch score in cardiac scintigraphy may predict poor outcome in CADM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Iida H, Hanaoka H, Ishimori K, Kiyokawa T, Takakuwa Y, Kawahata K. Myocardial Fatty Acid Metabolism and Perfusion Mismatch in Scintigraphy Predicts Worse Prognosis in Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myocardial-fatty-acid-metabolism-and-perfusion-mismatch-in-scintigraphy-predicts-worse-prognosis-in-clinically-amyopathic-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myocardial-fatty-acid-metabolism-and-perfusion-mismatch-in-scintigraphy-predicts-worse-prognosis-in-clinically-amyopathic-dermatomyositis/