Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: 5T090 ACR Abstract: SLE–Clinical III: Translational Aspects (2832–2837)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disorder characterized by disturbed cellular and humoral immune responses. Dysregulations of intrinsic or adaptive immune system as well as immunosuppressive medications predispose SLE patients to infection. This study aimed to investigate the alterations and their clinical significance of the absolute numbers of lymphocyte subpopulations in SLE patients with different infection and to restore the immunologic balances by low-dose IL-2.
Methods: Total 333 patients with SLE without recent infection, 163 patients suffering infection, and age- and sex-matched 132 healthy individuals were recruited. Of these patients, 54 were received a five-day course of low-dose IL-2 administration at a dose of 0.5 million IU per day. Lymphocyte subpopulations were analyzed by flow cytometry before and after the treatment.
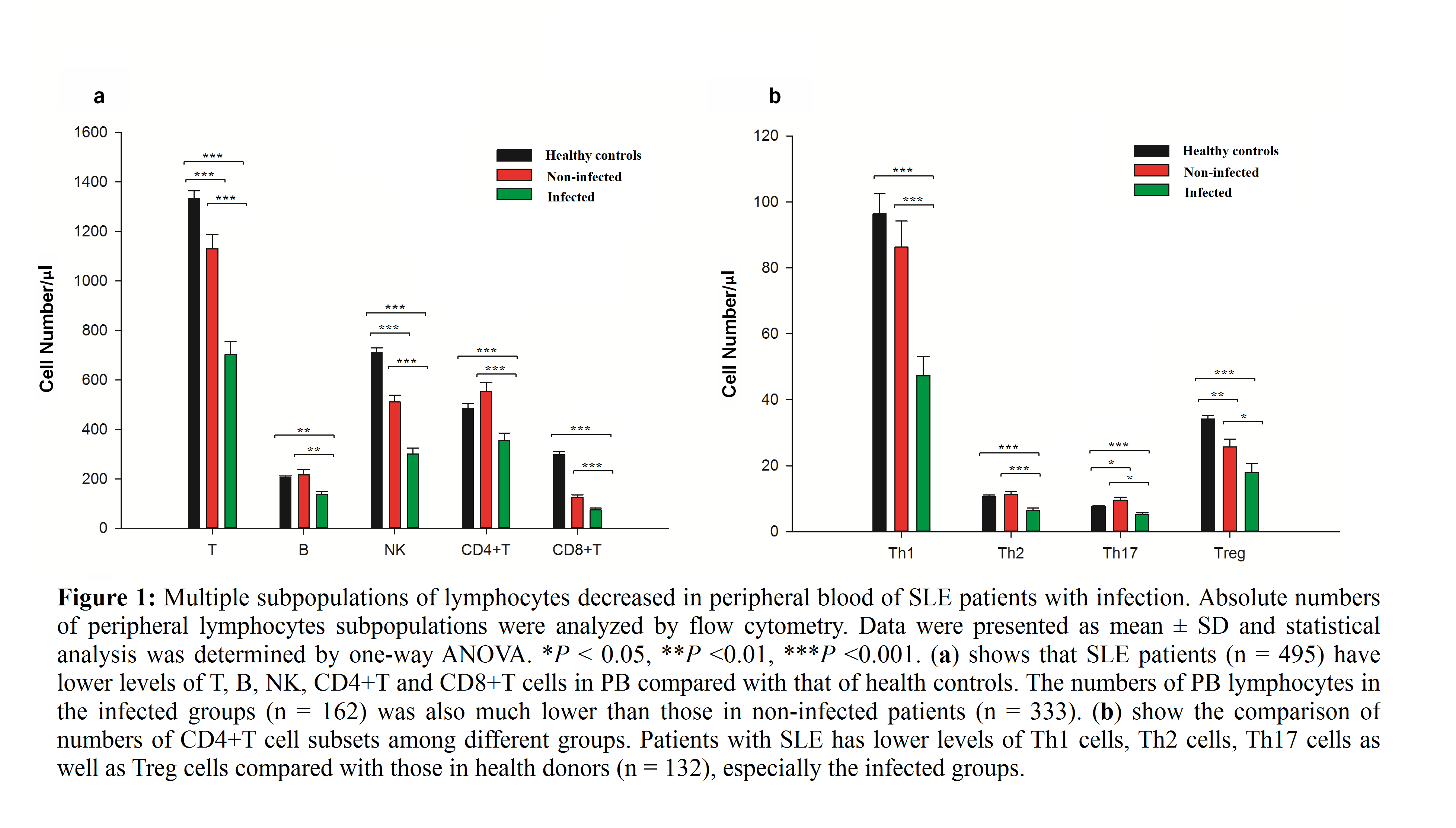
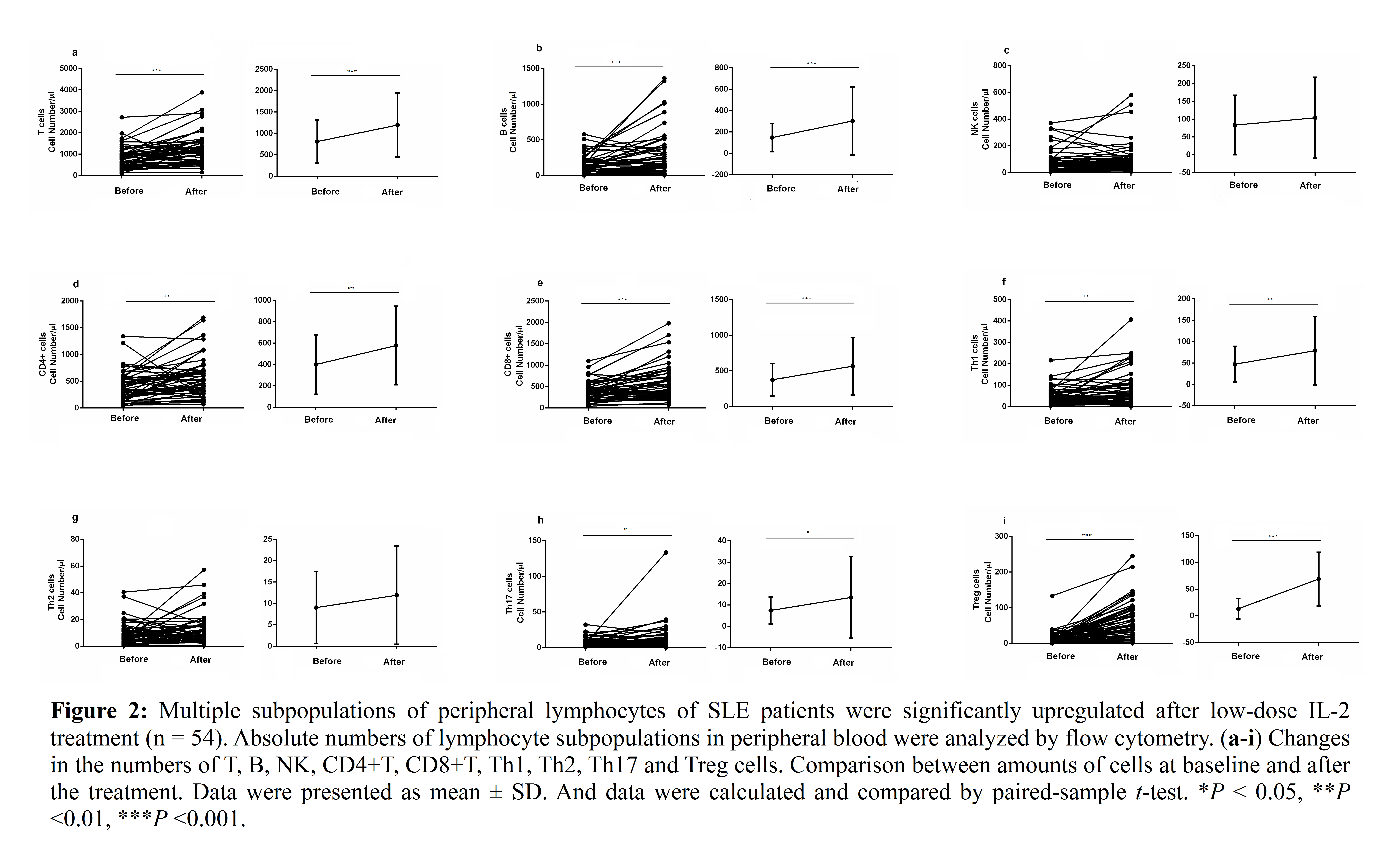
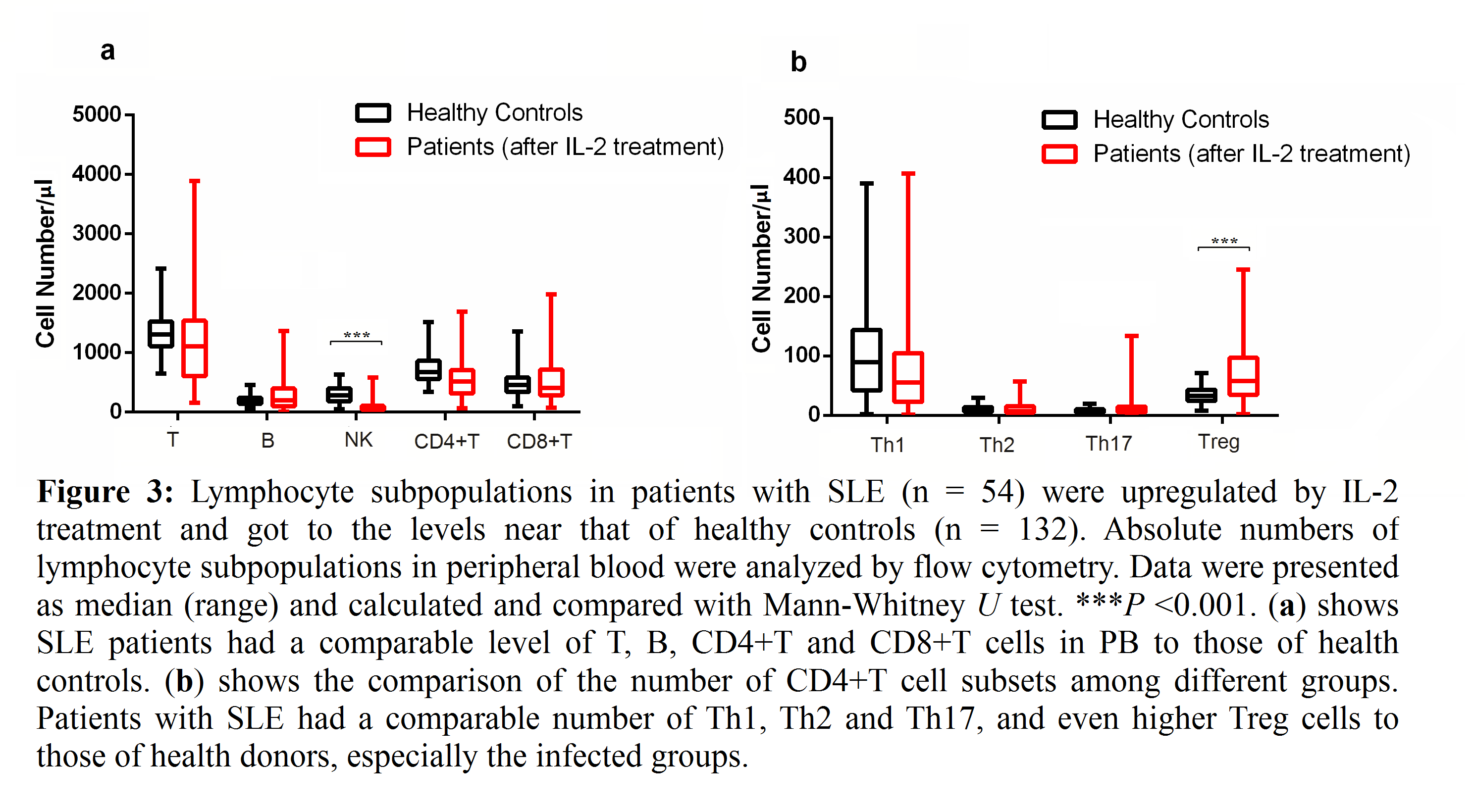
Results: Patients with SLE had a lower level of lymphocyte subpopulations in peripheral blood such as T, B, NK, CD4+T, CD8+ T, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells, and the reduction in these cells was more obvious in SLE patients with infection (P< 0. 05 to P< 0.01). Low-dose IL-2 effectively expanded T (P < 0. 001), B (P < 0. 001), CD4+T (P < 0. 01), CD8+T (P < 0. 001), Th1 (P < 0. 01), Th17 (P < 0. 1) and Treg cells (P < 0. 01) of SLE patients, these cells were comparable to that of health controls after the IL-2 treatment.
Conclusion: Patients with SLE had fewer cells in various lymphocyte subsets than healthy controls. The absolute cell numbers in these subsets were reduced more dramatically in SLE patients with infection than those without infection, suggesting that the low absolute numbers of these cells may be used as indicators of high infection risk in SLE patients and low-dose IL-2 may enhance the ability to resistant infection in SLE patients by restoring the decreased number of lymphocyte subpopulations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang SX, Wu XY, Luo J, Liu GY, Gao C, Wang CH, Li XF. Multiple Subpopulations of Peripheral Lymphocytes Were Absolutely Decreased in SLE Patients with Infection and Restored By Low-Dose IL-2 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multiple-subpopulations-of-peripheral-lymphocytes-were-absolutely-decreased-in-sle-patients-with-infection-and-restored-by-low-dose-il-2/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multiple-subpopulations-of-peripheral-lymphocytes-were-absolutely-decreased-in-sle-patients-with-infection-and-restored-by-low-dose-il-2/