Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Patient Reported Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthritis (SpA) are more likely to report depression than the general population, and depression has been associated with poorer outcomes1,2. A multidimensional health-assessment questionnaire (MDHAQ) has been found informative in many rheumatic diseases3, and includes two queries to screen for depression. We compared these 2 MDHAQ depression items to 2 widely-used depression indices: the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), and the Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS).
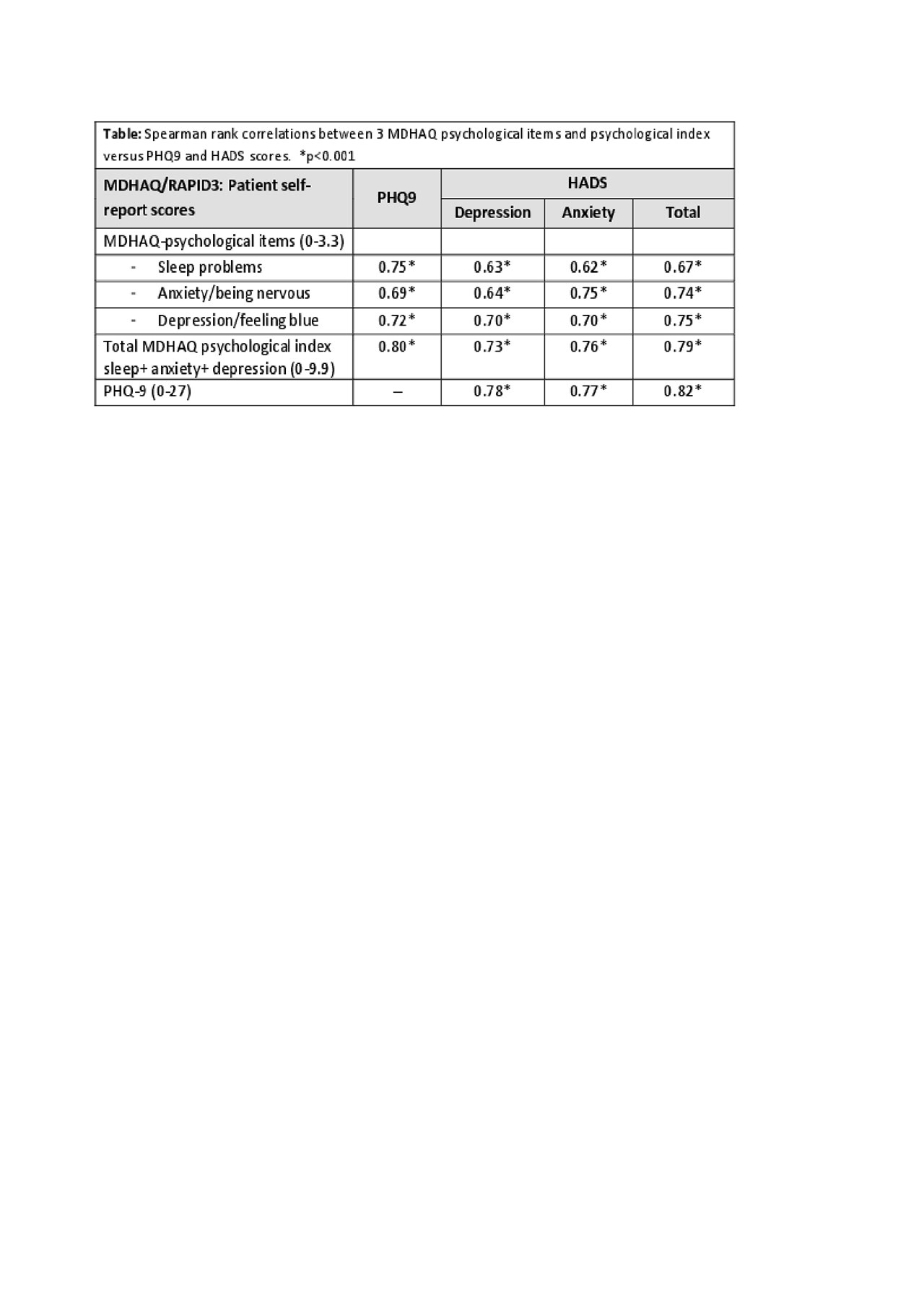
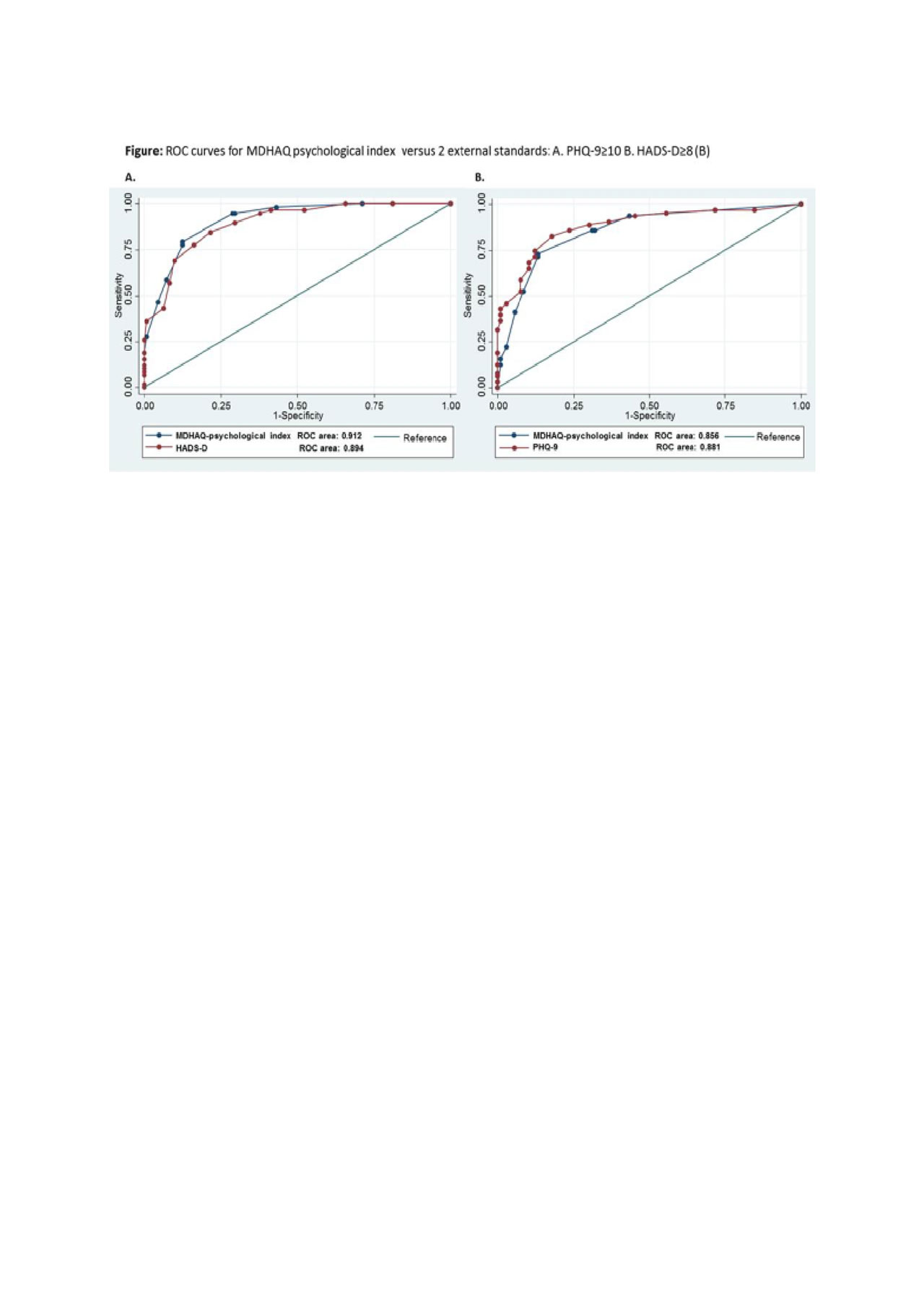
Methods: Consecutive patients attending two rheumatology clinical settings with a primary diagnosis of either RA or SpA completed a MDHAQ, which includes a 60 Yes/No symptom checklist (one symptom is depression), and a psychological index as the sum of 3 queries in the patient-friendly HAQ format (ranging from “without any difficulty” to “unable to do”) concerning dealing with depression, anxiety and sleep quality (each scored 0-3.3 for a total score=0-9.9). Patients also completed the PHQ-9, a depression screening tool (total=0-27, ≥10=depression), and HADS, a 14-item screening tool, 7 for depression (HADS-D) and 7 for anxiety (HADS-A) (total=0-21, ≥8=depression). Spearman correlations between the MDHAQ-psychological index and its 3 individual index items versus PHQ-9 and HADS were computed. Agreement and confidence intervals (CI) between MDHAQ-depression in the symptom checklist versus PHQ-9 ≥10 and HADS-D ≥8 as positive screens for depression was calculated. Receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curves were analysed for the MDHAQ psychological index, using PHQ-9≥10 or HADS-D≥8 as reference standards.
Results: Among 170 patients studied, 102 had RA and 68 had SpA, 82% and 47% females, mean age 58.8 and 55.6 years, respectively. In RA, depression screening was positive in 26% of patients by MDHAQ-depression, 28% by PHQ-9 ≥10, and 33% by HADS-D ≥8, versus 35%, 43%, and 45%, respectively in SpA. Agreement between MDHAQ-depression and PHQ-9≥10 was 83% (kappa= 0.60, 95% CI 0.47, 0.73), and with HADS-D≥8 was 79% (kappa= 0.52, 95% CI 0.39, 0.66). Agreement between PHQ-9≥10 and HADS-D≥8 was 82% (kappa= 0.60 95% CI 0.48, 0.72). Correlations between the MDHAQ psychological index and individual items with PHQ-9 and HADS ranged from 0.62 to 0.82 (p< 0.001) (Table). The area under the ROC curve for the total MDHAQ psychological index was 0.91 (95% CI 0.87, 0.95) with PHQ-9≥10 and 0.86 (95% CI 0.79, 0.91) with HADS-D≥8 (Figure).
Conclusion: The prevalence of positive screening for depression was higher in SpA patients versus RA patients according to each screening tools. MDHAQ self-report of depression showed good agreement with PHQ-9 ≥10 and HADS ≥8 to screen for depression. The three psychological queries on the MDHAQ can be combined into a psychological index to provide a useful clue to screen for depression in busy clinical settings.
References: 1.Matcham F. Rheumatology 2013,52:2136-48. 2.Zhao S. Arthritis Res Ther 2018,20:140. 3. Castrejon I. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 2017;75:93-100.
Figure_ACR Abstract_ROC curves be
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Morlà R, Riad M, Ruiz-Esquide V, Espi F, Ramirez J, Del Castillo N, Gomez-Puerta J, Sanmarti R, Pincus T, Castrejon I. Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ) as an Effective Screening Tool to Identify Concomitant Depression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis in Routine Care [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire-mdhaq-as-an-effective-screening-tool-to-identify-concomitant-depression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-spondyloarthritis-in-routine-care/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire-mdhaq-as-an-effective-screening-tool-to-identify-concomitant-depression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-spondyloarthritis-in-routine-care/