Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) have proven efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) however, some patients inadequately response to multiple bDMARDs. This study aims to determine the risk factors for ≥ 2 switches between bDMARDs in RA patients.
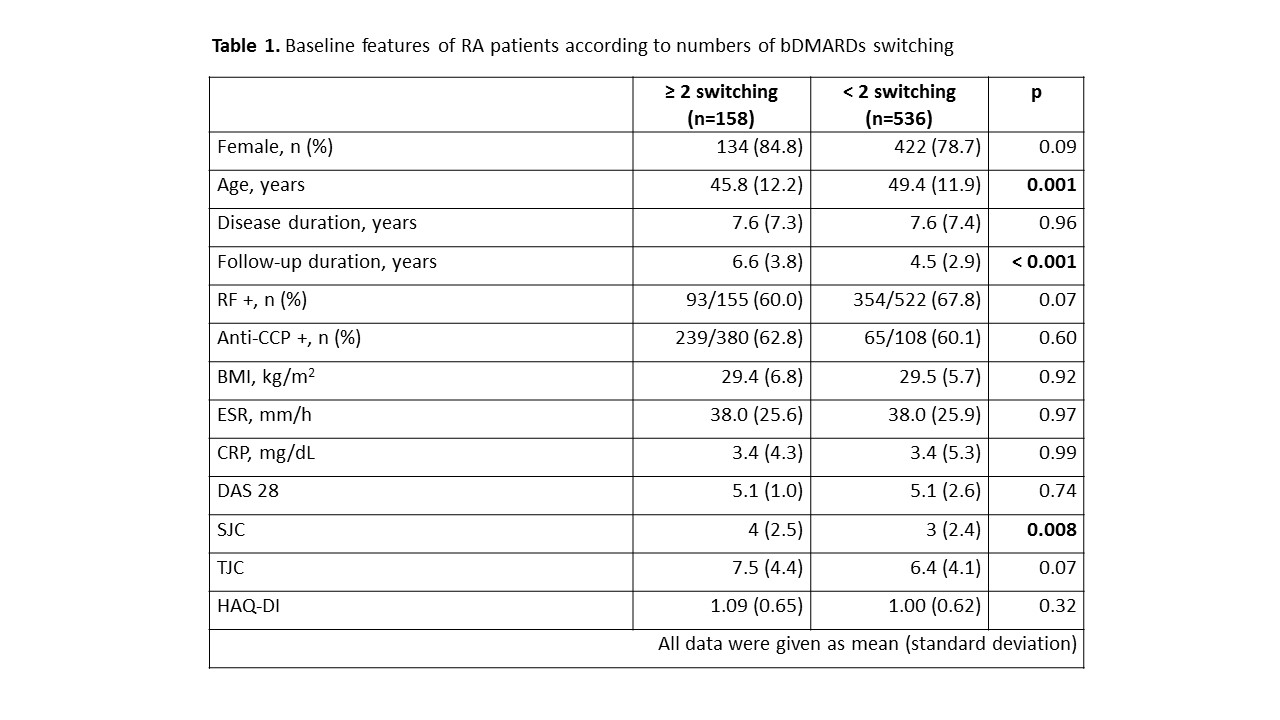
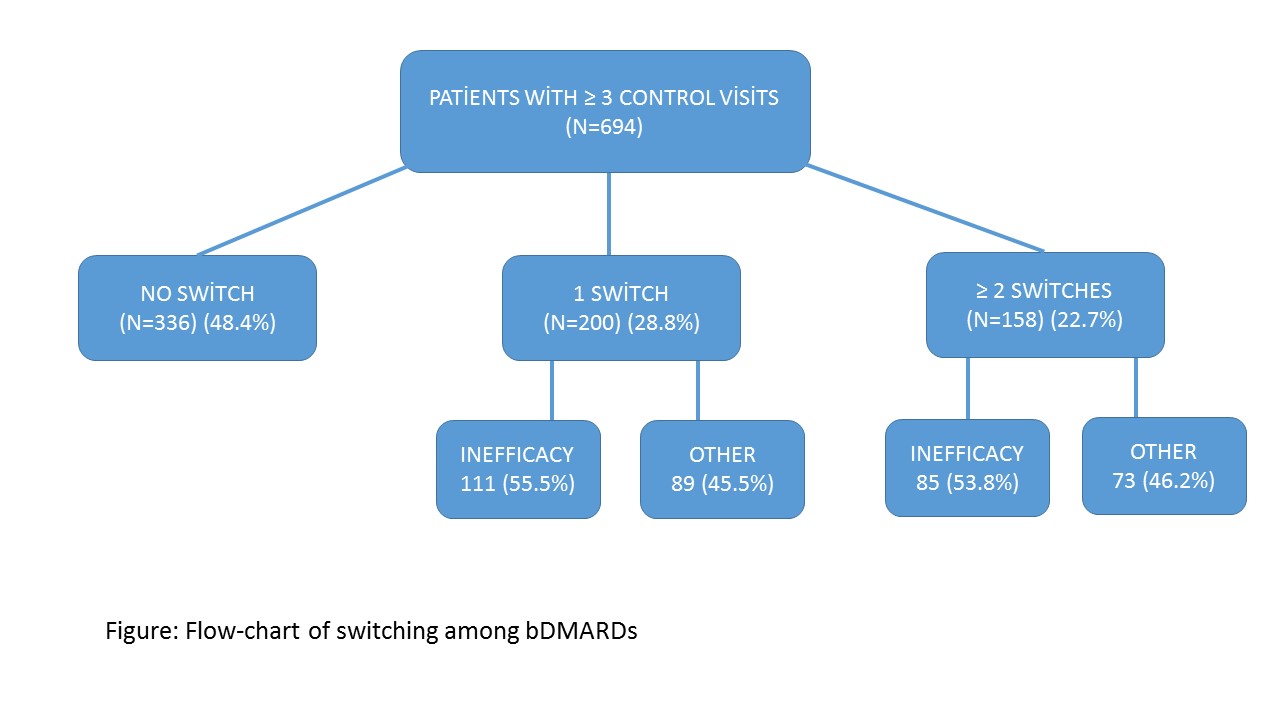
Methods: Hacettepe University Rheumatology Biologic Registry (HUR-BIO) is a monocentric registry of bDMARDs including 1609 RA patients by May 2018. The recorded bDMARDS in HUR-BIO were anti-TNF treatments (adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, golimumab, certalizumab), rituximab, abatacept, tocilizumab, and tofacitinib. Demographic, clinical data and baseline disease activity (DAS-28, swollen and tender joint counts (28 joints)), and functional status were assessed. Six hundred and ninety-four patients with at least 3 control visits were enrolled to analyze. Flow-chart of switching among bDMARDs was shown in Figure. Baseline demographic and clinical risk factors for ≥ 2 switches of bDMARDs were analyzed by using univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results: One hundred and fifty– eight (22.7%) patients had ≥ 2 switches between bDMARDs for any reason. Among this group, 40.5%, 39.2%, 15.1%, 3.8%, 0.6% of patients were treated with 3,4,5,6 and 7 bDMARDs, respectively. Baseline demographic, clinical and laboratory data of patients were shown in Table 1. In multivariate analysis, longer follow-up duration (OR: 1.21, 95% CI: 1.06-1.37) and rheumatoid factor (RF) negativity (OR: 2.10, 95% CI: 1.13-3.89) was found as independent risk factors for ≥ 2 switches of bDMARDs. The analyses were performed again in a subgroup of patients including patients with ≥ 2 switches due to primary or secondary inefficacy (n=85) and patients without any switches (n=336). Patients with ≥ 2 switches were younger (46.2 (11.3) vs 49.5 (11.9), p=0.02), had higher number of swollen joint counts (3.8 (2.5) vs 2.9 (2.5), p=0.04), and longer follow-up duration (6.3 (3.9) vs 4.0 (2.6), p<0.001). Multivariate analysis failed to demonstrate any risk factor in this subgroup.
Conclusion: High prevalence of more than two switches among bDMARDs in our cohort implicates that there is still an unmet need in the treatment of RA patients. Multi-biologic usage of bDMARDs may be related with RF seronegativity.
Figure: Flow-chart of switching among bDMARDs
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sari A, Kilic L, Armagan B, Erden A, Yardımcı G, Akdogan A, Karadag O, Apras Bilgen S, Ertenli I, Kiraz S. Multi-Biologic Usage in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Not Infrequent in the Routine Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multi-biologic-usage-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-not-infrequent-in-the-routine-practice/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multi-biologic-usage-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-not-infrequent-in-the-routine-practice/