Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis is known to be associated with increased mortality over the years when compared to the general population. In the BeSt study, 508 patients were treated to target (Disease Activity Score ≤2.4) for 10 years between April 2000 and August 2012. At the end of the initial study follow-up observed mortality in the BeSt cohort was similar to mortality in the general population. In the current study we evaluated the mortality in the BeSt cohort after 17 years follow-up and compared it to the general Dutch population.
Methods: In the BeSt study 508 patients diagnosed with early RA were randomized to four initial treatment strategies: 1. Sequential monotherapy; 2. Step-up combination therapy; 3. Initial combination therapy with prednisone; or 4. Initial combination therapy with infliximab. During the 10-year follow-up period treatment was aimed at low disease activity (DAS ≤2.4) and adjusted every three months if necessary. After 10-years patients were treated and followed-up according to regular care. We explored mortality through the Dutch state registry for mortality (Centrum voor Familiegeschiedenis) and treating rheumatologist. Mortality in the BeSt cohort was compared to the general Dutch population (Statistics Netherlands) matched by gender, age, and calendar year using the standardized mortality ratio (SMR). Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank test were used to compare survival among the initial treatment strategies.
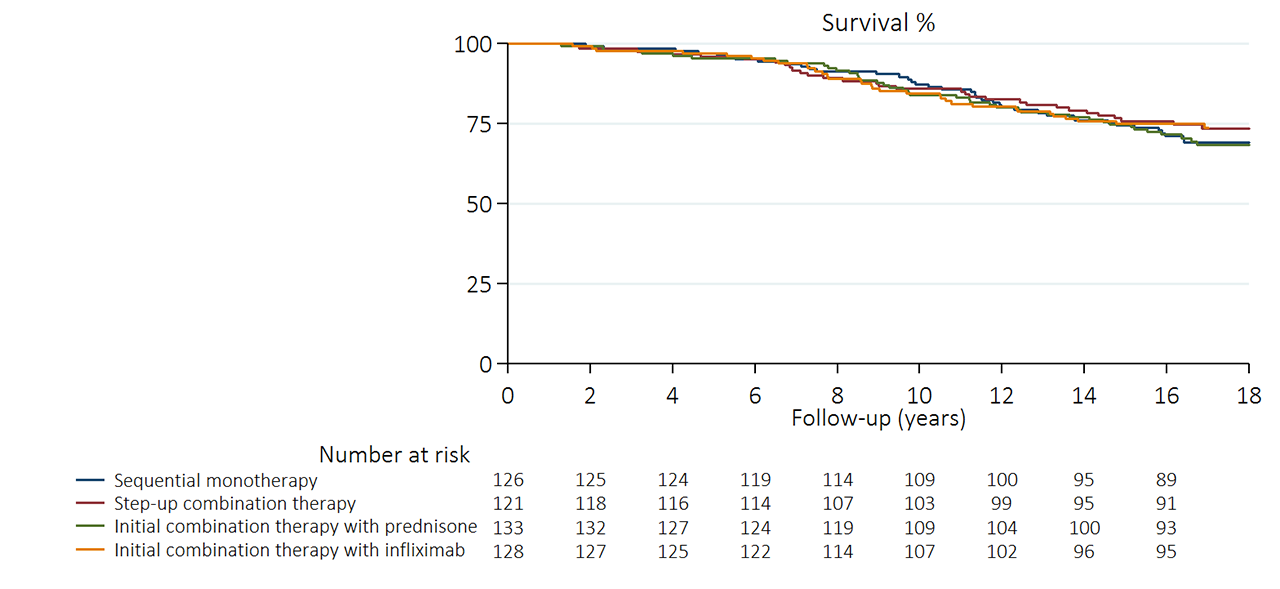
Results: The mean duration of follow-up in alive patients was 17 years (range 16-18). In total, 143 patients died (28%) compared to a total of 105 (21%) expected deaths in the reference population. The overall SMR after 17 years was 1.37 (95% CI: 1.16-1.61). Within the study population, no statistically significant difference in survival-curves was observed between the four initial treatment strategies (log-rank p=0.76) (table 1, and figure 1).
Conclusion: After (mean) 17 years of follow-up there was increased mortality in the BeSt study cohort compared to the general Dutch population. We observed no difference in survival among the four treatment strategies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maassen J, Goekoop Y, van Groenendael J, Lems W, Kerstens P, Huizinga T, Allaart C. Mortality of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Treated to Target at Low Disease Activity: 17-years Follow-up of the BeSt Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-to-target-at-low-disease-activity-17-years-follow-up-of-the-best-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-to-target-at-low-disease-activity-17-years-follow-up-of-the-best-cohort/