Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is caused by a number of mutations of the MEFV gene, coding for a protein named pyrin that acts as a major regulatory component of the inflammasome. Accumulating evidence has shown the association of microRNAs (miRNAs) with the development of inflammatory disorders (1). However, little is known about the precise role of miRNAs in FMF. Objective: The aim of this study was to identify a serum miRNAs profile and potential biomarkers in FMF and clarify their gene targets for understanding the pathogenesis of autoinflammatory diseases.
Methods: We performed miRNA microarray (Toray 3D-gene miRNA oligo chips) to screen miRNAs in the serum from FMF in attack and in remission. We subsequently examined the effect of candidate miRNAs on cytokine production by using THP-1 cells. Macrophages derived from THP-1 cells were transfected with miRNA mimics or miRNA inhibitor and stimulated with LPS+ATP for 24 hours. We collected the supernatants for the quantification of inflammatory cytokine production. To identify the target genes, we overexpressed its miRNA and performed Agilent expression microarray (SurePrint G3 Human GE 8x60K).
Results: We found that miR-204-3p was greatly decreased in the serum from FMF patients in attack. In vitro study, the expression of miR-204-3p was suppressed by ATP+LPS stimulation in macrophages derived from THP-1 cells. Inhibition of miR-204-3p significantly induced the production of IL-6 whereas overexpression of miR-204-3p inhibited its production. Bioinformatic analysis showed that miR-204-3p is predicted to target genes implicated in Toll like receptor pathway through regulation of PIK3 signaling.
Conclusion: These data suggest that serum miR-204-3p has a potential as a useful biomarker among patients with FMF and that miR-204-3p plays a critical role as a suppressor to regulate the production of IL-6 by targeting PIK3 signaling pathway. References:
1. Singh RP, Massachi I, Manickavel S, et al. The role of miRNA in inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2013 Oct;12(12):1160-5. Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (No. 15657398). 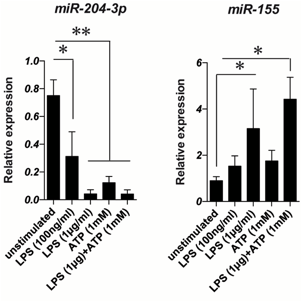
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koga T, Migita K, Yachie A, Ueki Y, Agematsu K, Masumoto J, Yoshiura KI, Eguchi K, Kawakami A. MiR-204-3p Associates with an Increased Level of IL-6 in Familial Mediterranean Fever By Targeting the PIK3 Signaling Pathway [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mir-204-3p-associates-with-an-increased-level-of-il-6-in-familial-mediterranean-fever-by-targeting-the-pik3-signaling-pathway/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mir-204-3p-associates-with-an-increased-level-of-il-6-in-familial-mediterranean-fever-by-targeting-the-pik3-signaling-pathway/
