Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : SB5 is a biologic agent developed as a biosimilar of the reference adalimumab (ADL). One year results including radiographic progression from the phase III equivalence study have been previously presented. This study further evaluates radiographic progression by different disease activity states by disease activity score by 28 joint count (DAS28) based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), simplified disease activity index (SDAI) and clinical disease activity index (CDAI).
Methods : Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were randomized to receive 40 mg of either SB5 or ADL every other week. At week 24, patients receiving ADL were re-randomised to either switch to SB5 (ADL/SB5) or continue on ADL (ADL/ADL) up to 52 weeks. Patients receiving SB5 continued to receive SB5 (SB5/SB5). The proportion of patients achieving remission, low disease activity (LDA), moderate disease activity (MDA), or high disease activity (HDA) in terms of DAS28, SDAI, and CDAI was compared at weeks 12, 24, and 52. Radiographic progression was measured using the modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) at weeks 0 and 52 and patients with mTSS ¡Â 0 at week 52 were regarded as radiographic non-progressors.
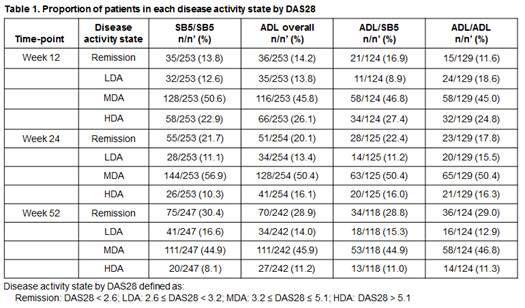
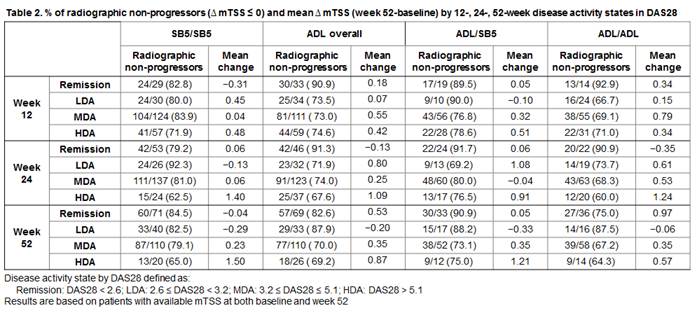
Results : The proportion of patients with remission, LDA, MDA, or HDA was comparable across all treatment groups (SB5/SB5 vs. ADL overall vs. ADL/SB5 vs. ADL/ADL) in terms of DAS28 (Table 1) and also SDAI and CDAI (data not shown). The proportions of radiographic non-progressors by disease activity were comparable across treatment groups at week 12, 24 and 52 (Table 2). There was a general trend of higher radiographic progression (decreasing number of radiographic non-progressors and increasing change in mTSS) as disease activity worsened, but the overall radiographic progression was very low across all disease states in SB5 or ADL maintenance groups as well as in the ADL/SB5 switch group.
Conclusion : The proportion of patients in each disease state was comparable upon treatment with SB5 or ADL. The overall radiographic progression was very low across all treatment groups with the lowest progression generally seen in patients with remission and higher scores seen with increasing disease activity. These data further confirm similar effects on clinical and radiographic status with SB5 and ADL, even after switching occurs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weinblatt M, Baranauskaite A, Ghil J, Cheong SY, Hong E. Minimal and Comparable Radiographic Progression By Disease Activity States in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Continued SB5 or Reference Adalimumab and Who Switched to SB5 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/minimal-and-comparable-radiographic-progression-by-disease-activity-states-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-continued-sb5-or-reference-adalimumab-and-who-switched-to-sb5/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/minimal-and-comparable-radiographic-progression-by-disease-activity-states-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-continued-sb5-or-reference-adalimumab-and-who-switched-to-sb5/