Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: 4M105 ACR Abstract: RA–DX, Manifestations, & Outcomes III: Diagnosis & Prognosis II (1929–1934)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose:
Patients with RA had increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Interleukin 33 (IL-33) plays an important role in pathogenesis of RA and development of CVD. Plasma IL-33 level was undetectable in most subjects that limits its utility as CVD biomarker. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) function as post transcription regulators of gene expression. This study aimed to ascertain if dysregulated miRNAs targeting IL-33 gene expression were associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in early RA patients
Methods:
76 ERA patients were recruited in this 1 year study. Potential miRNAs binding to 3’UTR of IL-33 gene were predicted by miRanda1. 10 miRNAs with highest possibility targeting functional sites of IL-33 gene were quantified in cell free plasma samples by real time PCR. Carotid IMT and plaque were identified using high-resolution B mode ultrasound annually. Carotid plaque (CP+) was defined as a localized thickening >1.2 mm. Plaque progression (PP+) was defined as increased region harboring plaque
Results:
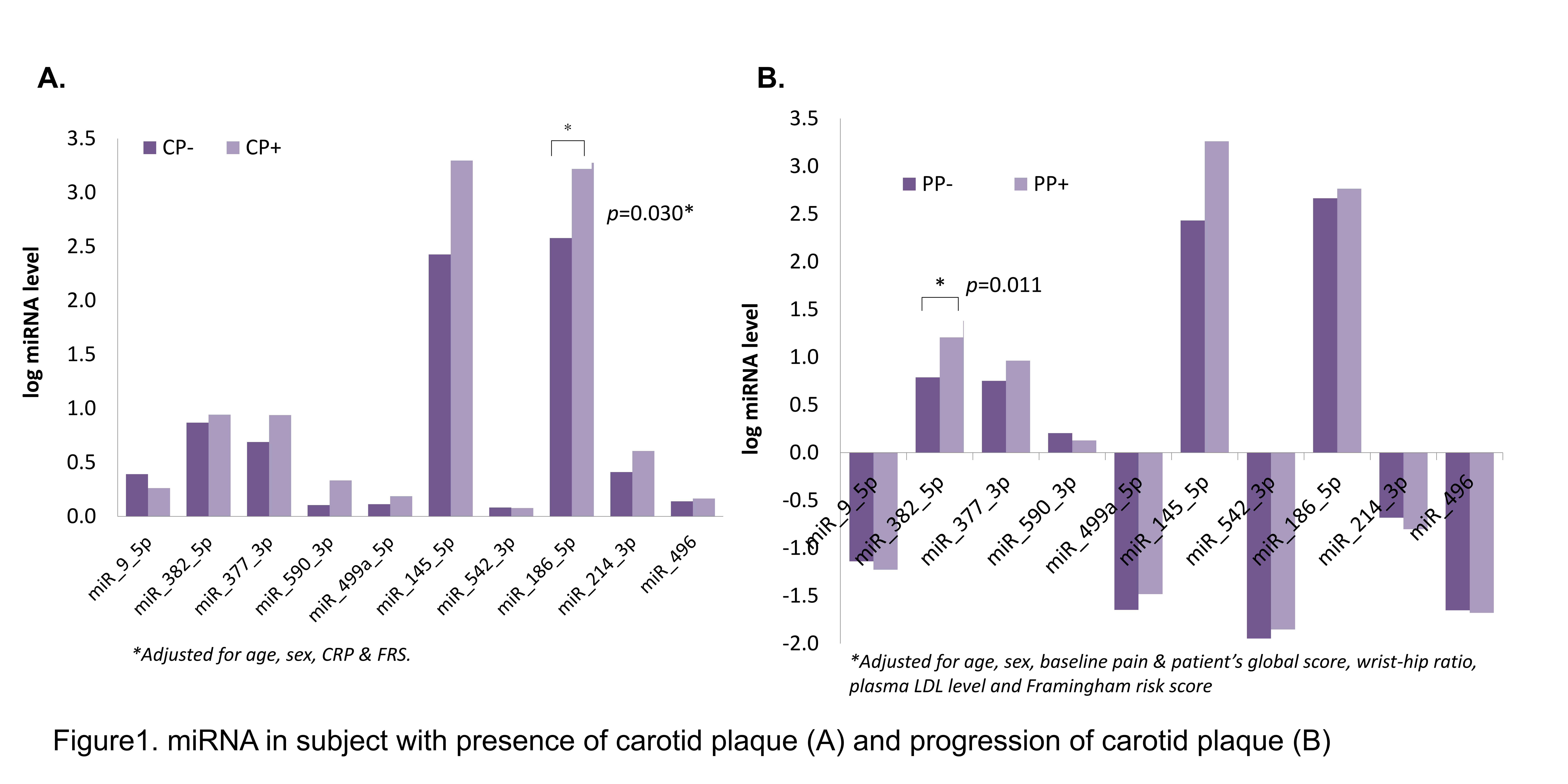
miRNA were detected in >80% of subjects. CP were identified in 26/76 (34%) subjects (CP+ group) at baseline. The CP+ group were predominantly male, older, with a higher CRP level and a prevalence of multiple CV risk factors. Plasma level of miR-186-5p was significantly higher in the CP+ (Fig 1). Using multivariate logistic regression, miRNA-186-5p was independent predictor for presence of CP (Table 1). ROC showed that increased miRNA-186-5p expression level could discriminate patients with and without CP [Area under the ROC (AUC): 0.658, p=0.024]
73 subject were followed until year 1. 16/73 (22%) subject had plaque progression. Subjects in the PP+ group were older, had higher prevalence of multiple CV risk factors, with lower pain and patient global score at baseline. A higher proportion of them were on conventional synthetic DMARDs. miR-382-5p expression level was significantly higher in subjects in PP+ group (Fig 1). Using multivariate logistic regression, miRNA-382-5p level was an independent predictor for plaque progression (Table 1). ROC analysis showed that miR-382-5p level could discriminate patients with and without PP (AUC was 0.66, p=0.048)
Conclusion:
Increased expression of miR-186-5p and miR-382-5p was independent predictor for presence & progression of subclinical atherosclerosis. This suggest that circulating miRNA may serve as novel biomarkers for CV risk stratification in ERA patients
Acknowledgement to Hong Kong Society of Rheumatology Project Fund for supporting this project
|
Table 1 – Multivariate analysis on presence and progression of carotid plaque
|
|||
|
OR |
95%CI |
p
|
|
|
Model for determining presence of carotid plaque1 |
|
|
|
|
Framingham Risk Score, baseline |
1.113 |
1.033-1.200 |
0.005 |
|
miR_186_5p |
1.919 |
1.096-3.361 |
0.023 |
|
Model for determining progression of carotid plaque2
|
|
|
|
|
VAS Pain (0-10cm), baseline |
0.513 |
0.318-0.827 |
0.006 |
|
Diastolic Blood Pressure, mmHg, baseline |
1.093 |
1.010-1.183 |
0.028 |
|
Framingham Risk Score, baseline |
1.188 |
1.057-1.336 |
0.004 |
|
miR_382_5p |
2.534 |
1.079-5.952 |
0.033 |
|
1 Adjusted for age, gender, baseline CRP and Framingham risk score; 2Adjusted for age, gender, baseline VAS pain, diastolic blood pressure, Framingham risk score and use of csDMARDs.; CRP:C-reactive protein; csDMARDs: conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; bDMARDs: biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Reference |
|||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheng IT, Shang Q, Shen J, Li M, Mak Q, Kwok KY, Yim IC, Li EKM, Wong P, Yip RM, Pang SH, Tam LS. microRNA Targeting IL-33 Gene As Biomarker to Predict Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microrna-targeting-il-33-gene-as-biomarker-to-predict-subclinical-atherosclerosis-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microrna-targeting-il-33-gene-as-biomarker-to-predict-subclinical-atherosclerosis-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/