Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: In RA-BEAM (NCT01710358), baricitinib (BARI), an oral selective inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK 2, yielded significant improvements in patients (pts) with active RA who had an inadequate response to methotrexate compared to placebo (PBO) or adalimumab (ADA).1 We analyzed molecular pathways modulated by BARI compared with ADA after 4 and 12 weeks (wks) of treatment relative to PBO.
Methods: Pts (N=1307) were randomized 3:3:2 (PBO [switched to BARI after 24 wks], BARI 4 mg once daily, ADA 40 mg every other week) for 52 wks. Total RNA extracted from whole blood collected at baseline (BL), wk 4, and wk 12 was analyzed using the GeneChip Human Transcriptome Array 2.0 (Affymetrix). Probeset level data were summarized to a data-driven transcript level and analyzed using a mixed effects model on a log2 transformed response. Multiplicity was adjusted for by testing both within and between transcripts.
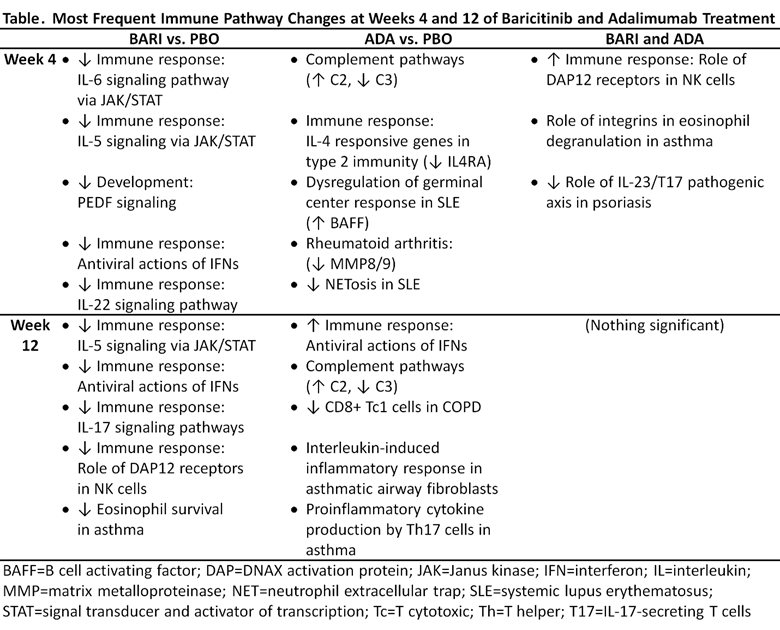
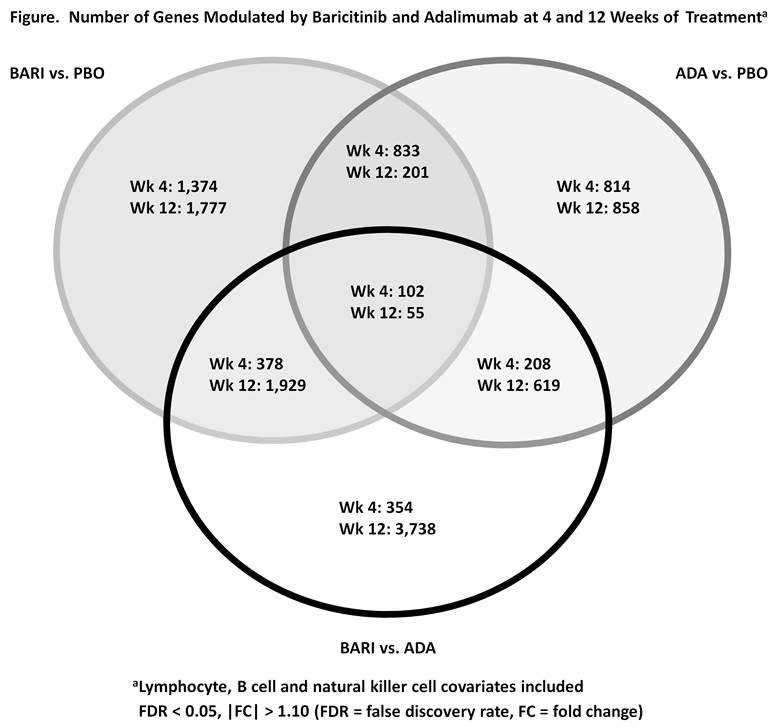
Results: Pathway analysis revealed that there was little overlap of the immune pathways modulated by both BARI and ADA at wk 4 with no significant overlap by wk 12 (Table). BARI downregulated JAK/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) signaling pathways, such as those induced by IFNs, IL-6, GM-CSF, IL-5, and IL-3. Expression of interferon responsive genes (IRGs) was downregulated by BARI and upregulated by ADA. BARI reduced IRGs by 75% at wk 4 in pts that had high IFN gene expression at BL. ADA modulated complement pathways. Of interest, STAT transcripts were reduced at wk 4 by BARI (STAT1, 2, 3, 5A, 5B, 6); by wk 12 several STATs (STAT 1, 2, 5A) did not differ from PBO. In addition to different pathways being modulated, there were additional differences noted in the number of genes modulated by each treatment (Figure). Using PBO as standard, BARI modulated more genes than ADA at wks 4 and 12; BARI resulted in more gene modulation at wk 12 than at wk 4, whereas ADA gene modulation was similar at wks 4 and 12. In addition, both the numbers and types of genes modulated by BARI diverged further from ADA at wk 12 than at wk 4.
Conclusion: While BARI and ADA both showed significant benefits compared to PBO in the RA-BEAM trial,1 gene expression profiling revealed significant differences between treatments. Notably, BARI and ADA modulated JAK/STAT or complement pathways, respectively, and the drugs had opposite effects on interferons. This analysis indicates that different, and possibly complementary mechanisms of action underlie each targeted therapy.
1Taylor et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376:652-62
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Emery P, Taylor PC, Weinblatt M, Tanaka Y, Keystone EC, Dow ER, Higgs R, Macias WL, Rocha G, Rooney TP, Schlichting DE, Zuckerman SH, McInnes IB. Microarray Pathway Analysis Comparing Baricitinib and Adalimumab in Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, from a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microarray-pathway-analysis-comparing-baricitinib-and-adalimumab-in-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-from-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microarray-pathway-analysis-comparing-baricitinib-and-adalimumab-in-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-from-a-phase-3-study/