Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Health Services Research Poster II: Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
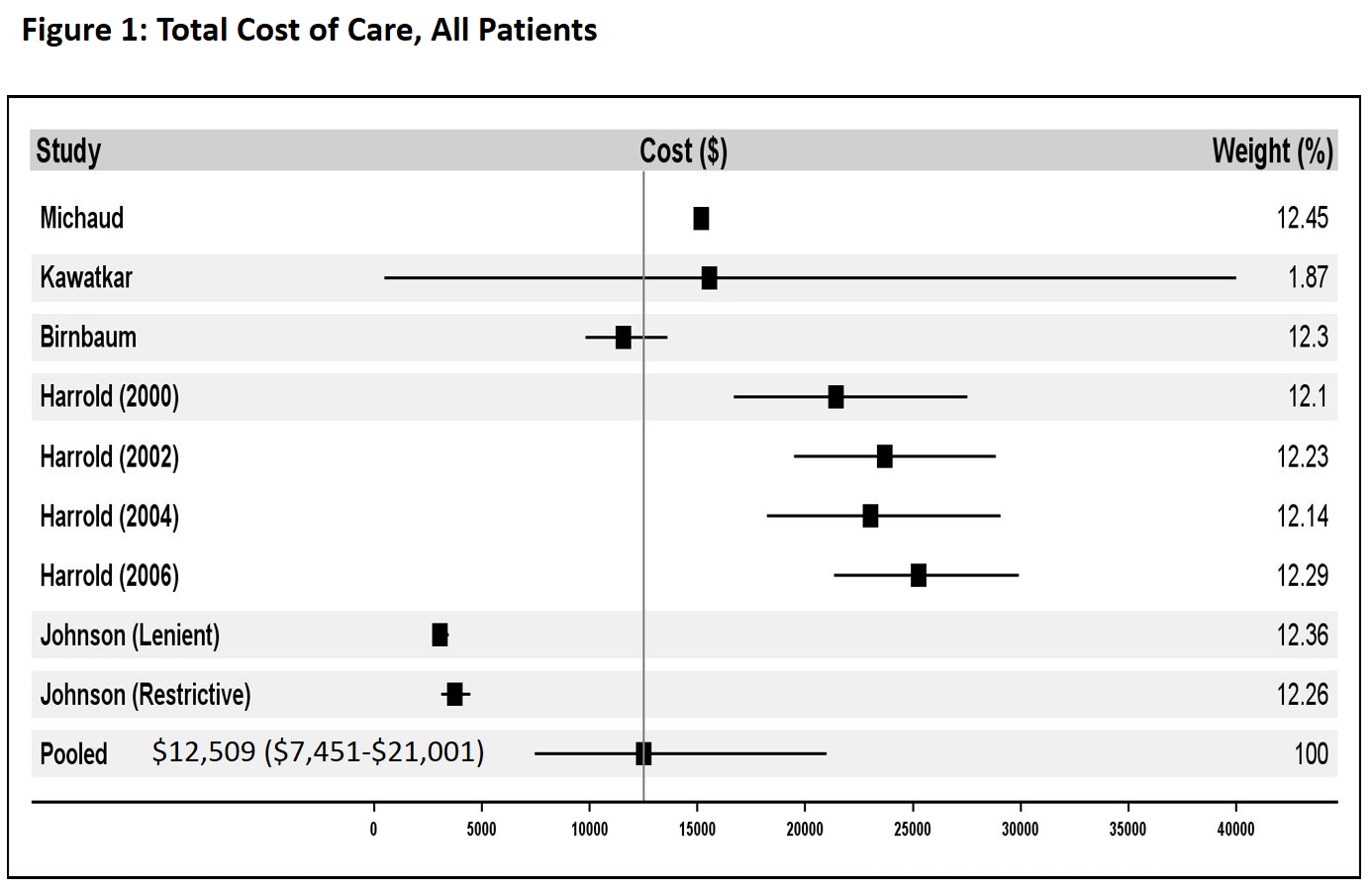
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature review and meta-analysis to assess direct annual medical cost for RA patients in the US receiving any treatment regimen for RA since the marketing of the first bDMARD in 1999. Studies were identified through a search of Medline using MeSH search terms related to cost of care and RA. Data were extracted independently by two reviewers (AH and DHS). Total direct medical costs as well as RA-specific costs were calculated using random effects meta-analysis. A subgroup analysis addressed costs for RA patients using bDMARDs.
Results: We found 541 potentially relevant studies and 11 papers met the selection criteria for meta-analysis. Total direct annual medical costs were estimated at $12,509 (95% CI $7,451-21,001) for all RA patients using any treatment regimen (see Figure 1) and $36,053 (95% CI $32,138-40,445) for bDMARD users (see Figure 2). RA-specific annual costs were $3,723 (95% CI $2,408-5,762) for all RA patients using any treatment regimen, representing 30% of total costs for all care. RA-specific annual costs were $20,262 (95% CI $17,480-23,487) for bDMARD users, representing 56% of total costs for all care.
Conclusion: The total and disease-specific direct annual medical cost of patients with RA is substantial. Among bDMARD users, cost of RA care is over half of all direct medical costs. These findings indicate that the burden of RA patients on the US health care system may become outsized compared to the disease’s relatively small prevalence as more patients use bDMARDs in the future. While patients that use bDMARD’s have increased annual cost over typical RA patients, the increment is below the total cost of bDMARDs themselves. This discrepancy suggests that either the use of bDMARD’s is associated with lower total non-drug direct medical costs or that there are crucial underlying demographic differences between bDMARD and traditional DMARD users.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hresko A, Lin TC, Solomon DH. Medical Care Costs Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis in the US: A Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/medical-care-costs-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-us-a-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/medical-care-costs-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-us-a-meta-analysis/