Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
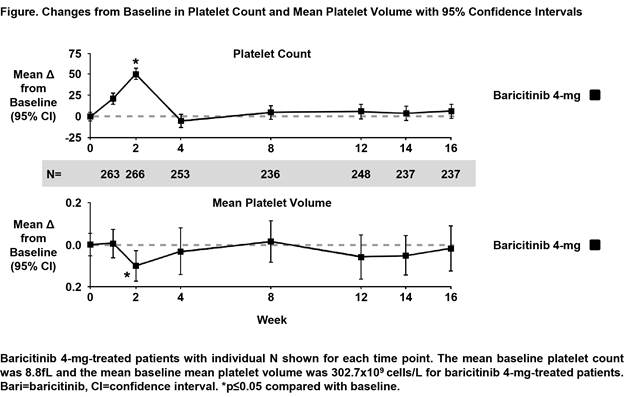
Background/Purpose: Transient increases in circulating platelets were observed in patients with RA treated with baricitinib, an oral selective Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor, approved for the treatment of RA in over 40 countries. We assessed mean platelet volume (MPV) in relation to platelet count to determine whether treatment-associated patterns of platelet change are indicative of altered platelet synthesis, release, and/or clearance.
Methods: MPV and platelet count were measured in a subset of patients with RA treated for up to 16 weeks (N=629), enrolled in the phase 3 RA-BEAM trial (NCT01710358), a 52-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled study of moderately-to-severely active methotrexate-inadequate responders. Adalimumab (40-mg every other week), a monoclonal antibody against TNF-alpha, was included as an active comparator to baricitinib (4-mg once daily).
Results: There was a significant increase in platelet count at Week 2 with baricitinib treatment, which then returned toward baseline and remained stable (though slightly above baseline) thereafter for the 16-week time-period (Figure). In contrast, adalimumab treatment resulted in a decrease in platelet count starting at 2 weeks that persisted over 16 weeks. The corresponding MPV changes with baricitinib treatment demonstrated a decrease in MPV at 2 weeks, which then returned to baseline, mirroring the platelet count change over time (Figure). By contrast, adalimumab treatment resulted in an increase in MPV at Week 2 and remained elevated through Week 16. Platelet count and MPV changes in the placebo arm were not significant throughout the 16-week time-period.
Conclusion: These analyses indicate that the increase in platelet count observed with baricitinib treatment at 2 weeks may be caused by a transient increase in circulating older, smaller platelets, accounting for the MPV decline; this finding is most consistent with a period of decreased platelet clearance rather than an increase in platelet production. By contrast, the prolonged platelet changes with adalimumab are consistent with increased platelet clearance and resultant increased platelet production. The association of changes in MPV with platelet function should be explored in future studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Giles JT, Nurmohamed MT, Rinder HM, Krishnan V, Crowe BJ, Saifan C, Dörner T. Mean Platelet Volume Changes with Baricitinib Indicate Reduced New Platelet Production in Baricitinib-Treated Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mean-platelet-volume-changes-with-baricitinib-indicate-reduced-new-platelet-production-in-baricitinib-treated-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mean-platelet-volume-changes-with-baricitinib-indicate-reduced-new-platelet-production-in-baricitinib-treated-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/