Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome is a heterogeneous chronic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology. Mandibular involvement appeared in approximately 10% of the SAPHO patients,(1) and the treatment for mandible lesions, including surgery and conservative treatment, has not reached consensus. However, these patients were rarely discussed, mainly in case reports. Here we first reported the patients with mandible involvement from the largest cohort of SAPHO syndrome(2) and explored their demographic, clinical, and scintigraphic characteristics and treatment.
Methods: From January 2004 to June 2019, 618 patients were recruited at Peking Union Medical College Hospital (PUMCH) in a previously established single-center dynamic cohort of SAPHO syndrome.(2) The demographic, clinical, scintigraphic, and laboratory data were collected at baseline. The mandibular involvement was confirmed by X-ray, scintigraphy, or biopsy. In May 2019, the prescription data was collected from the hospital information system, and the electronic questionnaire was distributed to all patients with mandibular involvement to ensure their medical compliance and to obtain their improvement in symptoms.
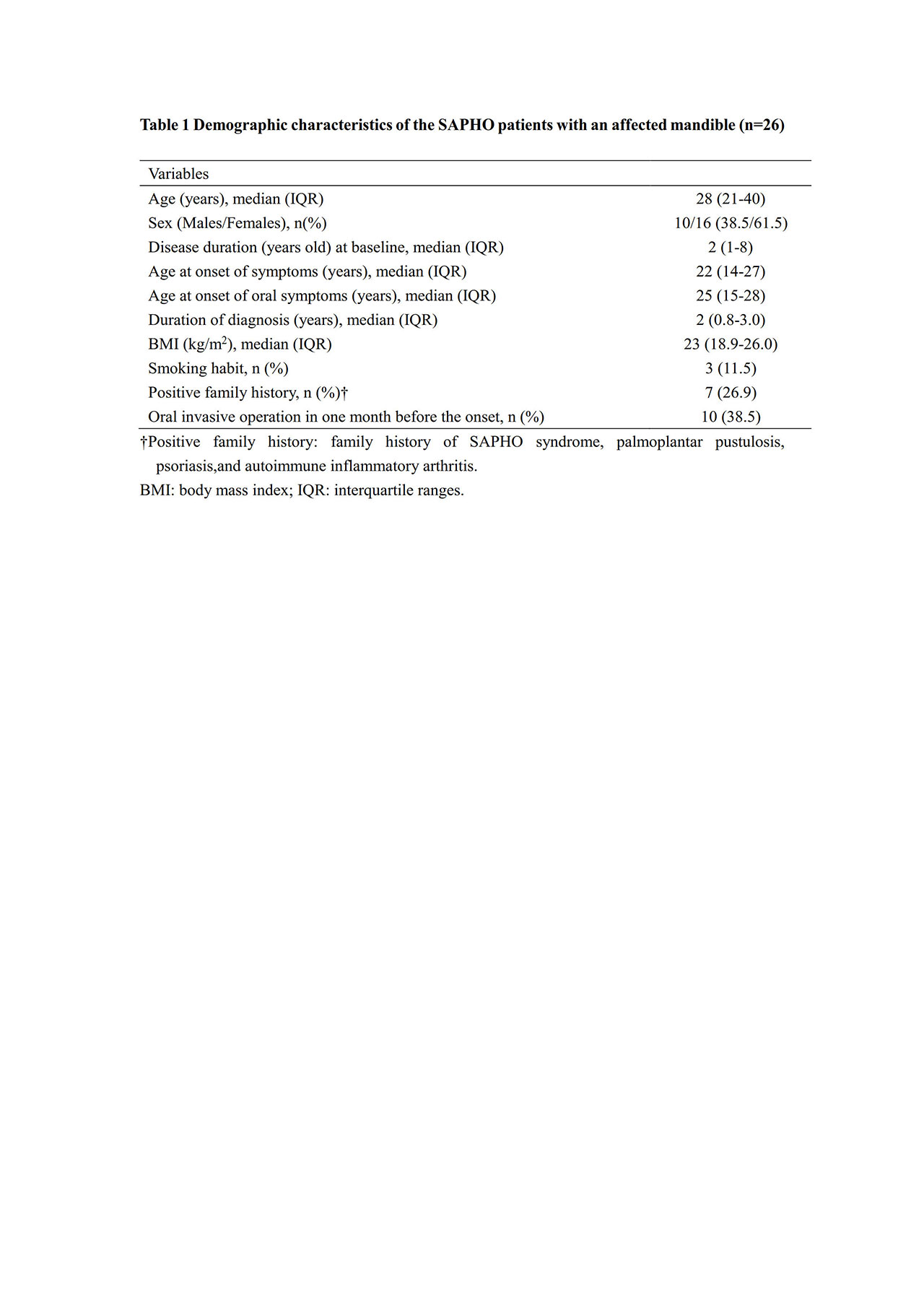
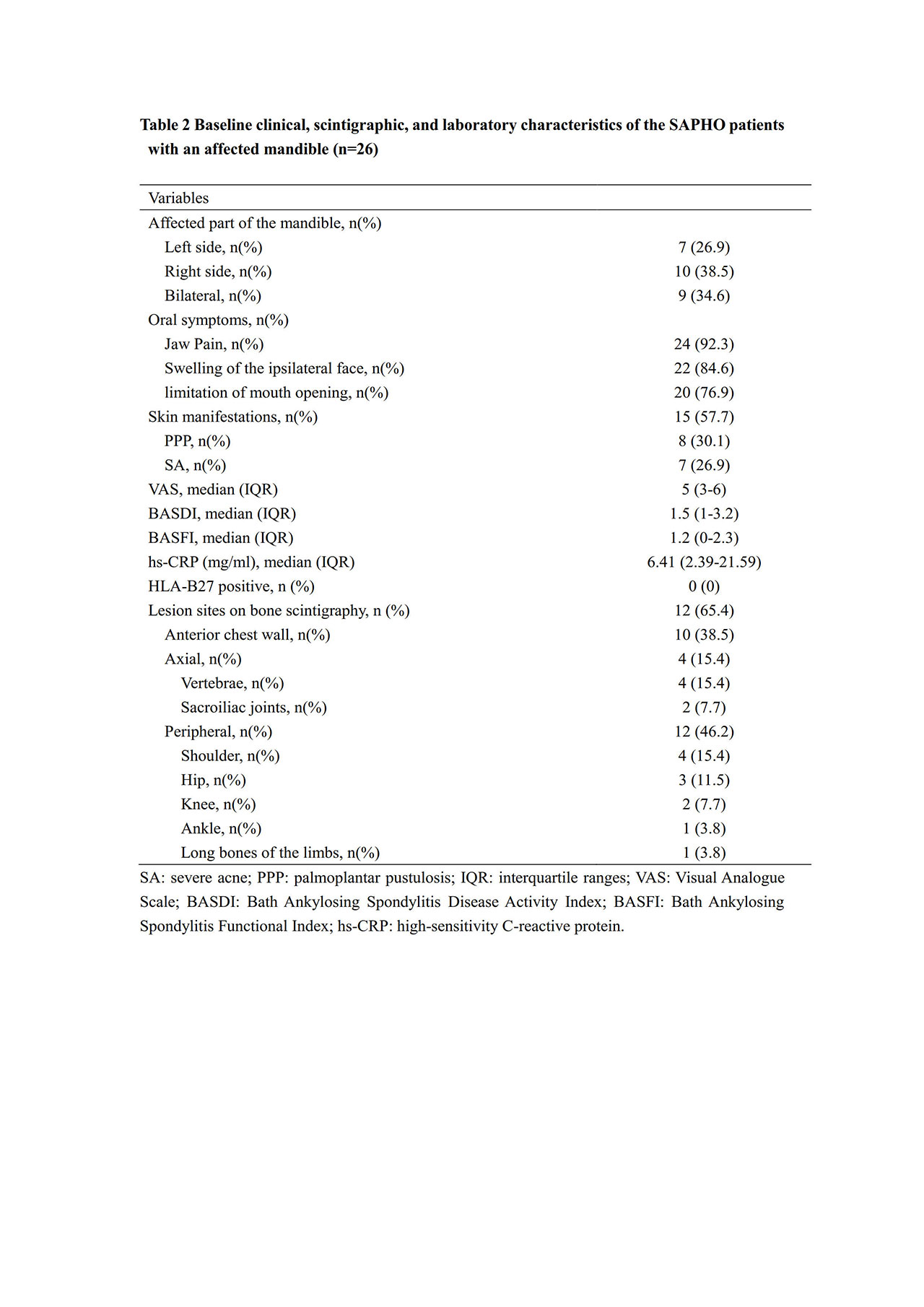
Results: A total of 26 SAPHO patients with mandibular involvement were identified, and all of them responded (38.5% male, median age 28 years old,and follow-up duration 2.1 years). Their median age at onset of symptoms was 22 years old (IQR 21-40 years old), younger than the median age of oral symptoms (25 years old, IQR 15-28 years old). Seven (26.9%) patients had a positive family history, and ten (38.5%) had received oral invasive operation in one month before the onset. Unilateral mandibular involvement was more common (65.4%). Skin lesions appeared in 15 (57.7%) patients, among which seven (26.9%) were affected by severe acne. The whole body bone scintigraphy revealed more peripheral osteoarticular involvement (46.2%) than anterior chest wall involvement (38.5%) or axial skeleton involvement (14.2%). All of the 14 (53.8%) patients undergoing surgery intervention relapsed, while conservative treatment led to an improvement of oral symptoms in most patients (24, 92.3%). Less improvement was observed in dermatological (13.3%) and other osteoarticular symptoms (26.7%).
Conclusion: Mandibular involvement in SAPHO syndrome is predominant in young-aged women. Familial inheritance factors and oral invasive operation may be possibly correlated with its onset. Conservative treatment instead of surgery might be recommended, although their efficacy on non-oral involvement remains challenging.
1. Kahn MF, Hayem F, Hayem G, Grossin M. Is diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis of the mandible part of the synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome?: Analysis of seven cases. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology (1994) 78(5):594-8.
2. Cao Y, Li C, Xu W, Wu X, Sun X, Zhang W, et al. Spinal and sacroiliac involvement in SAPHO syndrome: A single center study of a cohort of 354 patients. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism (2019) 48(6):990-6.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li Y, Li C, Wang M, Cao Y, Xiang Y, Li Z, Zhang W, zhao J. Mandibular Involvement in SAPHO Syndrome: A Single-center Retrospective Study of 26 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mandibular-involvement-in-sapho-syndrome-a-single-center-retrospective-study-of-26-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mandibular-involvement-in-sapho-syndrome-a-single-center-retrospective-study-of-26-patients/