Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. The efficacy and safety of tofacitinib have been demonstrated in patients (pts) with RA in global Phase (P)2, P3, and long-term extension (LTE) studies, and also in two P2 and one LTE study in Japanese pts. In this interim analysis (IA) of post-marketing surveillance (PMS) data, we report rates of serious adverse events (SAEs), malignancies, and deaths in Japanese pts with RA receiving tofacitinib.
Methods: All Japanese pts with RA receiving tofacitinib were prospectively registered in an ongoing three-year PMS study, and a 6-month IA of safety data was conducted (November 5, 2017 data-cut). All AEs were collected during tofacitinib treatment, and were coded using MedDRA ver.20.1. Follow-up surveillance after discontinuation of tofacitinib was conducted for serious infections, malignancy and death (up to 36 months). Incidences of malignancy or death were determined for the 6-month period. All-period (36‑month) data were used to calculate cumulative incidence rates (IRs; pts with events/100 pt-years [PY]) over time for malignancies.
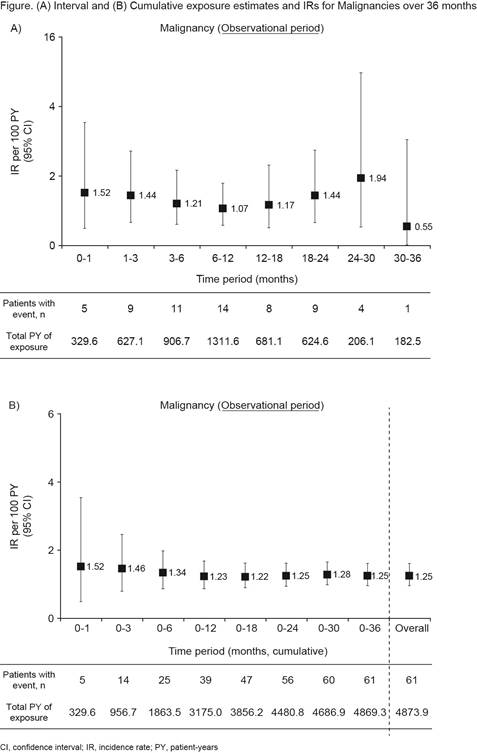
Results: Overall, 3929 pts received tofacitinib (1704.1 PY of exposure at six months). Mean age (standard deviation [SD] was 62.7 (12.6) years, 80.5% of pts were female, and mean duration of RA was 11.8 years. A total of 3037 pts (77.3%) completed six months of treatment; 892 pts (22.7%) discontinued treatment, mainly due to AEs (351 pts; 8.9%), or lack of efficacy (335 pts; 8.5%). At least one AE (all causality) was observed in 1313 pts (33.4%). The most frequent AE by system organ class was Infections and Infestations (12.5%), and SAEs (all causality) occurred in 287 pts (7.3%). Over the six‑month period, malignancy (all causality) was reported in 25 pts (0.6%); 12 cases were reported to be related to treatment. There were 21 deaths (0.5%) during the six‑month period. The most common cause of death (including pts with multiple causes listed) was infection (six cases); malignancy was the second most common cause of death (five cases). From all‑period (36-month) data, malignancies occurred in 61 pts (1.6%); gastric cancer occurred in eight pts (0.2%), lung neoplasm malignant in six pts (0.2%), breast cancer in five pts (0.1%), and diffuse large B‑cell lymphoma, ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, colon cancer, and pancreatic carcinoma in four pts each (0.1%). Over 36 months, the IR of malignancy was 1.25 (61 pts; 4874 PY). The IR of malignancy did not increase in the time intervals representative of longer tofacitinib treatment, suggesting no cumulative toxicity related to malignancy, though exposure time for intervals were limited (Figure).
Conclusion: In this IA of tofacitinib PMS in Japanese pts with RA, rates of malignancies and death were comparable with those in the tofacitinib RA clinical program; no new or unexpected safety risks were identified.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tamura N, Kuwana M, Atsumi T, Takei S, Harigai M, Fujii T, Matsuno H, Mimori T, Momohara S, Yamamoto K, Takasaki Y, Nomura K, Endo Y, Hirose T, Morishima Y, Sugiyama N, Yoshii N, Takagi M. Malignancy in Japanese Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Tofacitinib: Interim Analysis of All-Case Post-Marketing Surveillance [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/malignancy-in-japanese-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib-interim-analysis-of-all-case-post-marketing-surveillance/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/malignancy-in-japanese-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib-interim-analysis-of-all-case-post-marketing-surveillance/