Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Methotrexate (MTX)
is routinely used as the first-line drug for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). About 1
in 3 RA patients achieve excellent RA control with MTX monotherapy. Identifying
predictors of MTX response could allow treatment optimization, avoid drug
toxicities and treatment delays while saving costs.
Methods:
Potential baseline clinical
predictors were studied in two cohorts: Rheumatology & Arthritis
Investigational Network (RAIN) Early Predictors Study and Treatment of Early
Aggressive Rheumatoid Arthritis (TEAR) trial. RAIN is a 16-week, open-label
study where RA patients are started on weekly po MTX 15mg and escalated to 20
mg at 8 weeks if not in remission (DAS-28 ESR< 2.6). Clinical and laboratory
parameters are collected at baseline, 8, and 16 weeks. TEAR was a randomized, double-blind
study using 4 treatment arms: two arms with immediate combination therapy and
two step-up arms. We analyzed patients from TEAR step-up arms who initially were
on po MTX monotherapy. Primary outcome was absolute change in DAS-28 (baseline
to 16 weeks for RAIN and baseline to 12 weeks for TEAR) adjusted for the baseline.
Low disease activity (LDA; DAS28 <3.2) was a secondary outcome. Data were analyzed using ordinary least squares and
logistic regression.
Results:
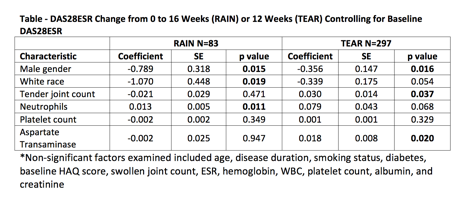
Eighty-three patients
(75% female, 89% white) completed the 16-week RAIN trial. Mean (SD) change in
DAS-28 from baseline to 16 weeks was -1.90 (1.50) with LDA achieved by 51%. Male
gender (p=0.015), white race (p=0.019) and lower baseline neutrophil (BNC) count
(p=0.011) were associated with significant improvement in DAS-28ESR (Table).
Male gender, higher hemoglobin and lower BNC were significantly associated with
achieving LDA (not shown).
Patients (n=297) who
received MTX monotherapy during TEAR were also analyzed (70% female, 81% white).
Mean (SD) change in DAS-28 from baseline to 12 weeks was -1.28 (1.19) with LDA achieved
by 20%. Male gender (p=0.016), lower baseline tender joint counts (p=0.037)
and lower baseline aspartate transaminase (p=0.020) were associated with
primary outcome (Table). Lower BNC showed a non-significant trend towards DAS28
improvement. Male gender, lower swollen joint count and higher hemoglobin were
associated with LDA (not shown).
Conclusion:
In both cohorts,
male gender and white race were associated with significant improvement in
DAS28ESR with MTX monotherapy; higher baseline hemoglobin was also associated
with achieving LDA. Lower BNC was associated with good response (absolute
change and LDA) to MTX in RAIN cohort, but only showed a trend in the TEAR
cohort. Larger studies with a focus on pharmaco-genetics may be required to
identify the RA patients who are ideal candidates for MTX monotherapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Danve A, Sayles H, Mikuls TR, O'Dell JR. Male Gender and Higher Hemoglobin Predict Response to Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/male-gender-and-higher-hemoglobin-predict-response-to-methotrexate-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/male-gender-and-higher-hemoglobin-predict-response-to-methotrexate-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/