Background/Purpose:
The OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis (RA) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scoring system (RAMRIS) is a validated scoring system for assessment of synovitis, bone edema and bone erosion. Previous studies have reported that TNF inhibitors improve RAMRIS scores, but it is not known how early this occurs. The rapid clinical efficacy of certolizumab pegol (CZP), a PEGylated Fc-free anti-TNF, in RA has been reported.1 This study aimed to identify the first time point of a MRI-verified response to CZP in RA patients.
Methods:
MARVELOUS (NCT01235598) is a Phase IIIb multicenter, randomized, double-blind (DB), placebo (PBO)-controlled (during initial 2 weeks) study. Eligible patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either CZP Q2W (400mg at Wks 0–4, then 200mg every 2 weeks to Wk16) or PBO at Day 0, then CZP Q2W (400mg Wks 2–6, then 200mg every 2 weeks to Wk16). Contrast enhanced MRI of one hand and wrist was acquired at Baseline (Wk0) and Wks 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16. Primary endpoint was change from Wk0 in OMERACT RAMRIS synovitis score in the CZP group. The first significance test was conducted at Wk16 and continued to earlier time points if prior test proved significant. All MRIs were analyzed by an experienced reader, blinded to subject identity, study treatment and time point; all six time points were read simultaneously. Change in bone edema, bone erosion and clinical parameters were secondary outcomes. LOCF imputation was used for synovitis and observed data for other outcomes. Safety variables were also assessed, including AEs, and laboratory parameters.
Results:
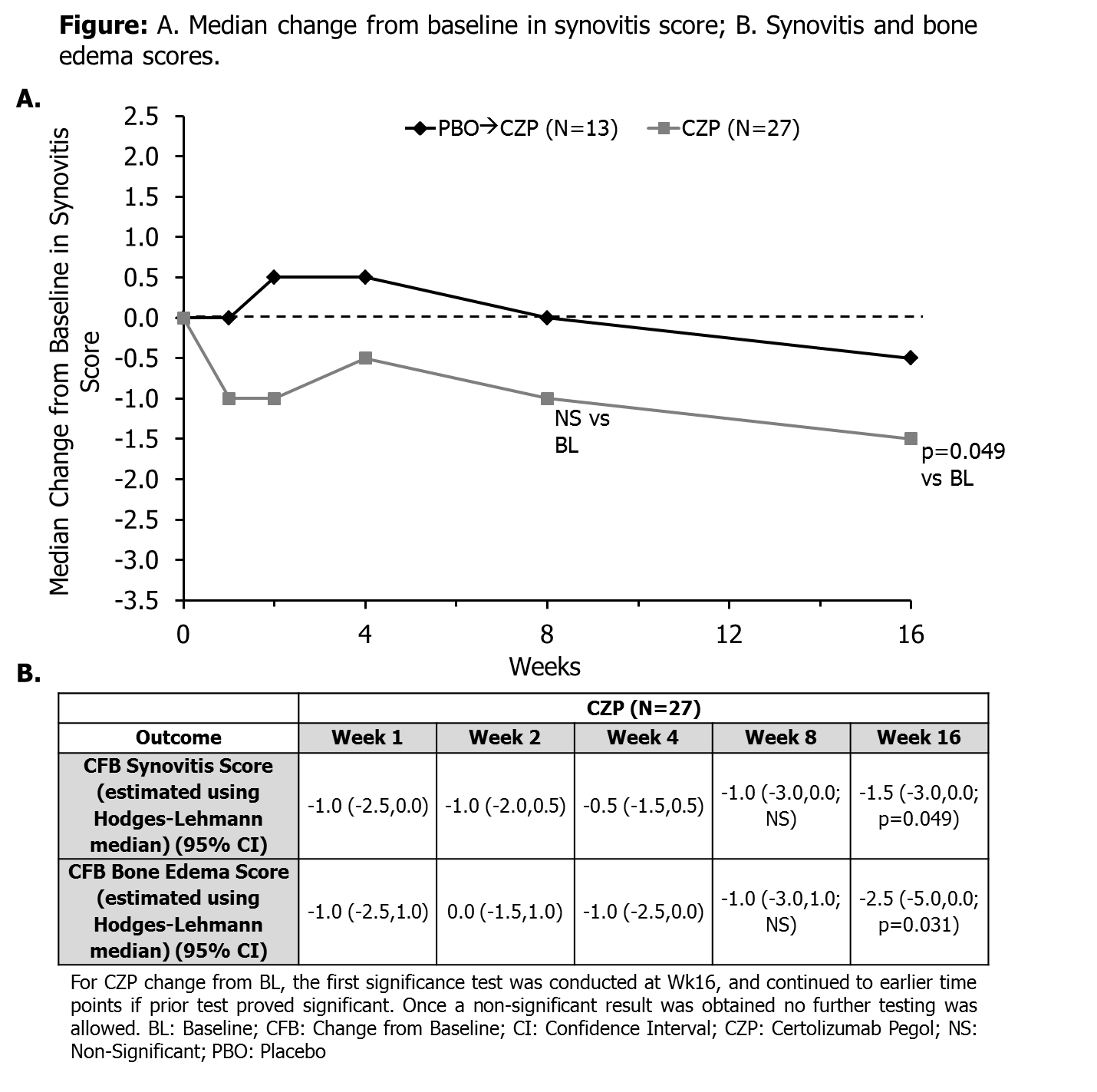
40 pts were randomized and treated: CZP group n=27 and PBO–CZP n=13. During the DB phase, 4 patients discontinued treatment (1 PBO, 3 CZP). In the CZP group a significant reduction from baseline in synovitis score was reported at Wk16 (median change= -1.5, p=0.049) (Figure A); reductions in synovitis score were not significant at Wk8, precluding further testing of earlier time points. In the CZP group, bone edema score was also significantly reduced at Wk16 (-2.5, p=0.031) (Figure B), whereas there was no significant change from Wk0 in bone erosion score. For all RAMRIS parameters (synovitis, bone edema, bone erosion), very good intra-reader reliability (intra-class correlations >0.90) was observed. Most AEs were mild or moderate, with low incidence of withdrawals due to AEs. There were no serious infections or deaths.
Conclusion:
In this first study with multiple MRIs following initiation of biological therapy, CZP successfully reduced the OMERACT RAMRIS synovitis and bone edema score as measured by MRI as early as Wk16, despite small sample size and the technical challenges of reading 6 time points simultaneously. This study documents the effect of CZP and provides essential information on the optimal timing of MRI and sample sizes for subsequent larger clinical trials.
References:
Disclosure:
M. Ostergaard,
Abbott, Pfizer and Centocor,
2,
Abbott, Pfizer, Merck, Roche, UCB Pharma,
5,
Abbott, Pfizer, Merck, BMS, UCB and Mundipharma,
8;
L. Jacobsson,
Pfizer,
2,
Abbvie, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, UCB,
9;
C. Schaufelberger,
None;
M. Sejer-Hansen,
UCB Pharma,
5;
J. Bijlsma,
UCB-NL,
2,
Nordic Countries symposium of UCB,
8;
A. Dudek,
None;
M. Rell-Bakalarska,
None;
F. Staelens,
UCB Pharma,
3;
R. Haake,
UCB Pharma,
3;
B. Sundman-Engberg,
UCB Pharma,
3;
H. Bliddal,
Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aventis, Axellus, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cambridge Nutritional Foods, Dansk Droge, Eurovita, Ferrosan, GlaxoSmithKline, Hoechst, LEO, Lundbeck, MSD, Mundipharma, Norpharma, NOVO, NutriCare, Nycomed, Pfizer, Pharmacia, Pierre-Fab,
5,
Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aventis, Axellus, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cambridge Nutritional Foods, Dansk Droge, Eurovita, Ferrosan, GlaxoSmithKline, Hoechst, LEO, Lundbeck, MSD, Mundipharma, Norpharma, NOVO, NutriCare, Nycomed, Pfizer, Pharmacia, Pierre-Fab,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/magnetic-resonance-imaging-assessment-of-early-response-to-certolizumab-pegol-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-phase-iiib-study-applying-magnetic-resonance-imagi/