Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: The objective of this analysis was to evaluate the proportion of patients switching from non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA) toradiographic axSpA (r-axSpA) after 10 years of follow-up and whether BME on MRI-SIJ at baseline is associated with the r-axSpA status over time.
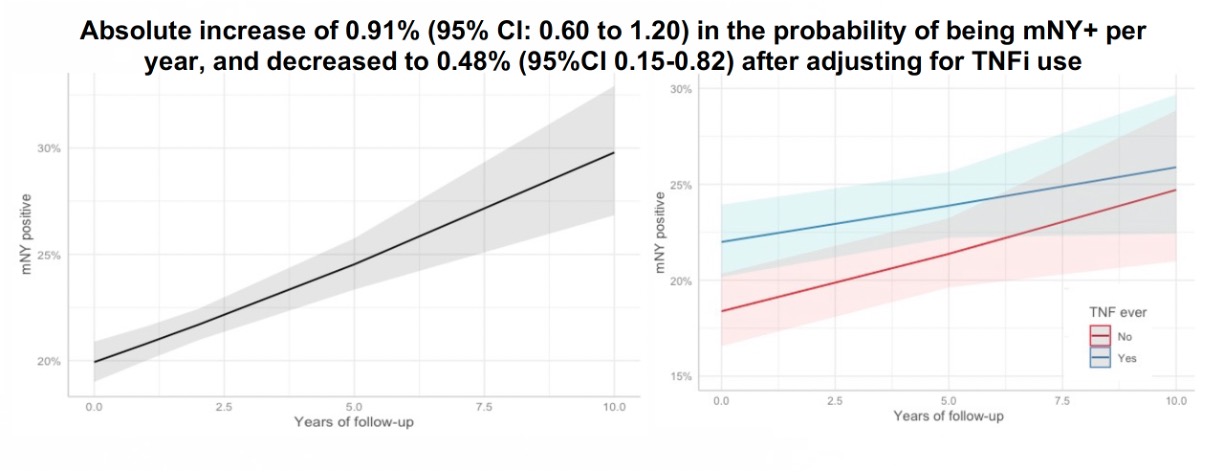
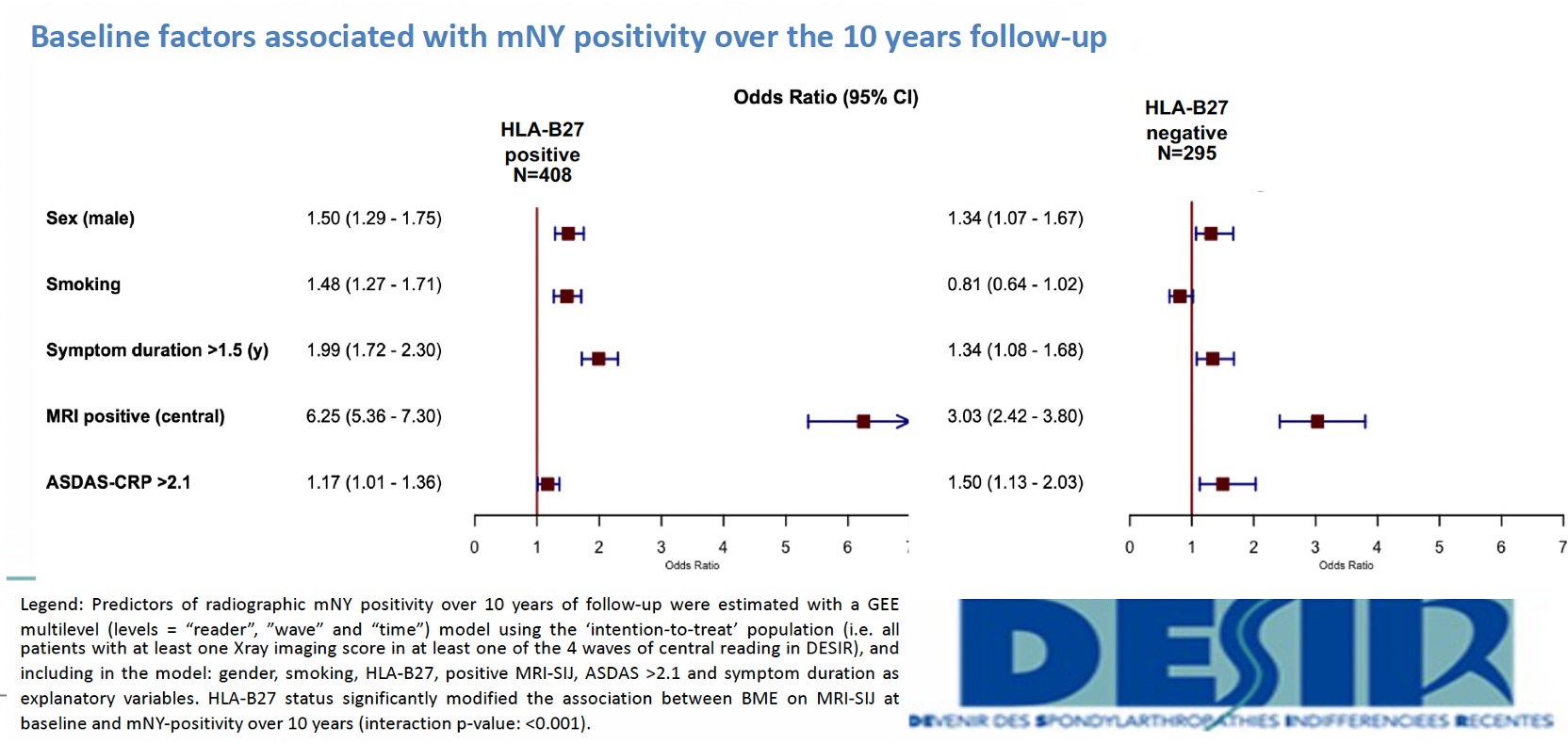
Methods: Patients with ≤3 years axSpA onset from the DESIR cohort were included. The radiographic status of the patients (r-axSpA versus nr-axSpA) was based on the mNY criteria (i.e. at least a bilateral grade 2 or a unilateral grade 3 on pelvic radiographs according to 2 out of 3 central readers). BME on MRI-SIJ was defined as positive ASAS definition according to 2 out 3 central readers at baseline. Information on mNY criteria was obtained in four reading waves (0 to 10y). Images were scored by 3 trained central readers, all of them unaware of the chronology of the images and the results of the other modality. A “progressor” was defined as a patient switching from nr-axSpA to r-axSpA. A “regressor” was defined as a patient switching from r-axSpA to nr-axSpA. The % of mNY net progressors (i.e. number of “progressors” minus number of “regressors” divided by the total number of patients) was assessed in “completers” (i.e., with pelvic radiographs available at BL and 10y in wave 4). A sensitivity analysis was conducted using a multilevel GEE model (‘integrated analysis’) that included all waves from all patients with at least one available mNY score from at least one reader available (“intention-to-follow” population). From this model, we estimated the absolute change per year in the percentage of mNY positive cases with and without adjusting for the use of anti-TNF drugs. Finally, the effect of BME on MRI-SIJ at baseline on mNY positivity over 10 years, adjusting for potential confounders (Figure) were evaluated in a multivariable GEE model in the “intention-to-follow” population.
Results: Completers included 299 patients (mean age 34.5Y and 48.2% males), while the intention-to-follow population included 704 participants (mean age 33.7Y and 46.2% males). In the completers, the net % of progressors (switch from nr-axSpA to r-axSpA) was 5.7%. In the intention-to-follow population, there was a 0.91% (95%CI 0.60-1.20) increase per year in the probability of being mNY-positive (i.e. a progression of 9.1% after 10Y). After adjusting for anti-TNF use, this percentage decreased to 0.48% (95%CI 0.15-0.82) per year. The HLA-B27 status modified the association between BME on MRI-SIJ at baseline and mNY-positivity over 10 years (interaction pvalue: < 0.001). BME on MRI-SIJ was associated with being mNY positive over time in both HLA-B27 positive (OR 6.25 (95%CI 5.36-7.30)) and HLA-B27 negative patients (OR 3.03 (95%CI 2.42-3.80)), but the association was stronger in the former (Figure). In addition, male sex, symptom duration >1.5Y, ASDAS >2.1 (in HLA-B27 negatives) and smoking (in HLA-B27 positives) were also associated with being mNY-positive over 10 years.
Conclusion: Patients with early axSpA have a low likelihood of changing from nr-axSpA to r-axSpA over 10 years, especially when considering the use of anti-TNF. Local inflammation on MRI-SIJ is strongly associated damage accrual in the SIJ over time, in particular in patients who are HLA-B27 positive.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molto A, López Medina C, de Hooge M, Van Lunteren M, Sepriano A, Ramiro S, Dougados M. Low Rate of Switching from Nr-axSpA to r-axSpA After 10 Years of Follow up in Early Axialspondyloarthritis. Data from DESIR Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-rate-of-switching-from-nr-axspa-to-r-axspa-after-10-years-of-follow-up-in-early-axialspondyloarthritis-data-from-desir-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-rate-of-switching-from-nr-axspa-to-r-axspa-after-10-years-of-follow-up-in-early-axialspondyloarthritis-data-from-desir-cohort/