Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We examined associations of pain and physical function with Patient Global Assessment of disease activity (PtGA) in patients (pts) receiving tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID) or placebo (PBO) with background conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs).
Methods: This was a post-hoc analysis of pooled data from three Phase 3 randomized controlled trials (ORAL Sync [NCT00856544]; ORAL Standard [NCT00853385]; ORAL Scan [NCT00847613]) in pts with inadequate responses to biologic or csDMARDs (ORAL Sync) or methotrexate (MTX) (ORAL Standard/Scan). Patient Assessment of Arthritis Pain (Pain; visual analog scale [VAS] 0–100 mm), Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and PtGA (VAS 0–100 mm) scores were recorded at baseline (BL) and Month (M) 3. Associations between ‘low global assessment of disease’ (PtGA ≤20) and mild Pain (VAS score ≤30) or HAQ-DI response (score ≤0.5 or change from baseline ≥0.22) were independently evaluated. Relationships between PtGA and Pain or HAQ-DI were assessed using Spearman rank correlation coefficients at BL and M3 without adjustments for multiplicity.
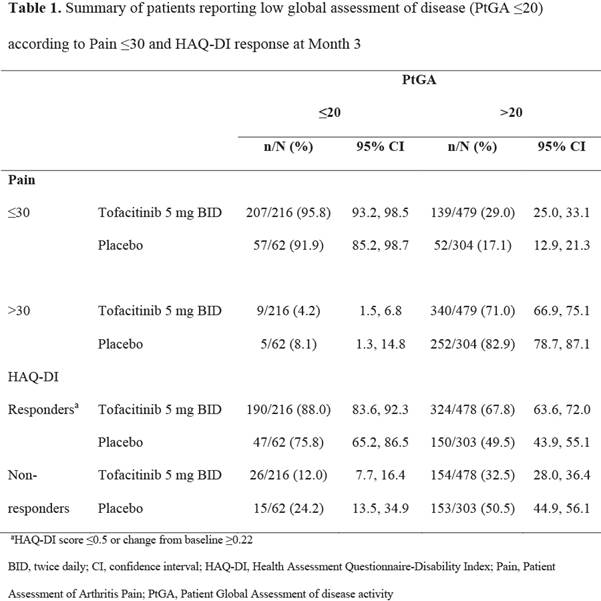
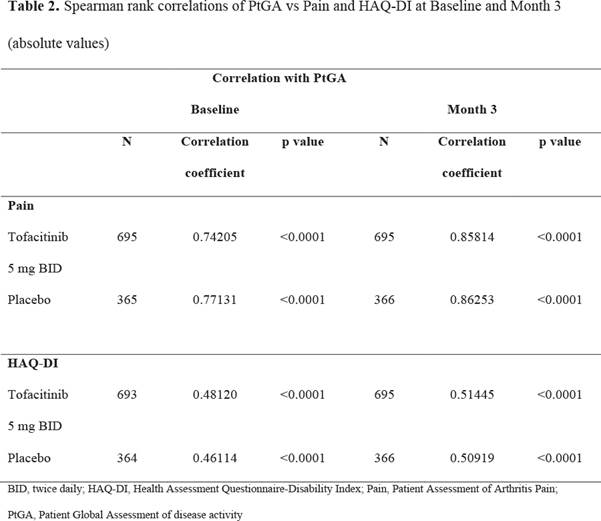
Results: At M3 216/695 (31.1%) pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID and 62/366 (16.9%) pts receiving PBO reported PtGA ≤20; 346/695 (49.8%) and 109/366 (29.8%) had Pain scores ≤30; 514/694 (74.1%) and 197/365 (54.0%) were HAQ-DI responders. Across treatment groups, of pts reporting PtGA ≤20 at M3, a larger proportion also reported Pain ≤30 vs Pain >30 (Table 1); of pts with PtGA >20, a high proportion had Pain scores >30. Of pts reporting PtGA ≤20 at M3, a larger proportion were HAQ-DI responders than HAQ-DI non-responders. Similar associations were noted between PtGA ≤20 and moderate or substantial improvements in Pain (data not shown). The proportions of pts reporting PtGA ≤20 and Pain ≤30 were numerically higher than those with PtGA ≤20 and HAQ-DI responses. Pain and HAQ-DI were significantly correlated with PtGA at BL and M3 (p<0.0001); correlation coefficients appeared numerically higher between PtGA and Pain than HAQ-DI (Table 2).
Conclusion: In this post-hoc analysis, reports of low PtGA scores were associated with low pain levels and improved physical function across treatment groups. Attainment of low PtGA levels appears more associated with improvements in pain than HAQ-DI responses.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Alten R, Kaine J, Soonasra A, Murray CW, Fan H, Mojcik CF, Wallenstein G. Low Patient Global Assessment Scores in Rheumatoid Arthritis Are Associated with Pain and Physical Function in Patients Treated with Tofacitinib: A Post-Hoc Analysis of Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-patient-global-assessment-scores-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-are-associated-with-pain-and-physical-function-in-patients-treated-with-tofacitinib-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-patient-global-assessment-scores-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-are-associated-with-pain-and-physical-function-in-patients-treated-with-tofacitinib-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-3-trials/