Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a common extra-articular manifestation of RA,1 and treatment-induced ILD is more common in Asia than the rest of the world.2
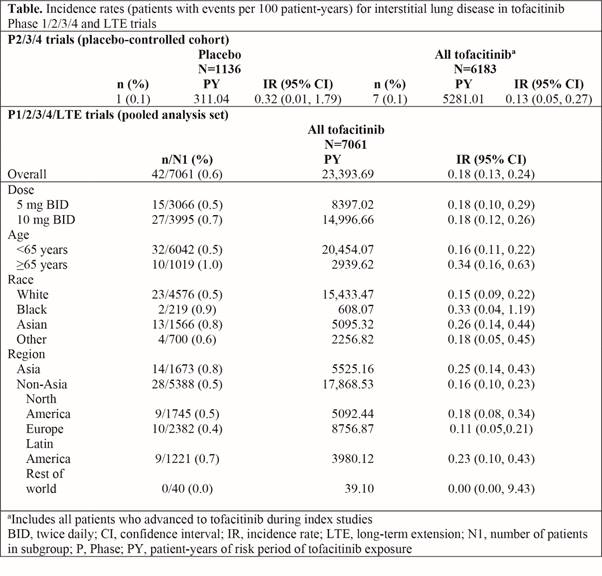
Methods: We aimed to investigate incidence rates (IR; patients [pts] with events per 100 pt-years [PY]) of ILD events in pts with active RA, receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily in a post hoc analysis of data pooled from 2 Phase (P)1, 10 P2, 7 P3/4, and 2 long-term extension (LTE) trials (ORAL Sequel LTE main study database locked at time of analysis: March 2017). No pts with pre-existing ILD were included. Potential ILD events were adjudicated by three independent pulmonologists as ‘probable’ (compatible adverse event [AE] with supportive clinical evidence) or ‘possible’ (compatible AE with no supportive clinical evidence). ILD IRs at 6-month intervals and by pt age and region are described. A descriptive case-matched control (ratio of pts with vs without ILD events 1:5, matched by age and gender) analysis identified potential ILD risk factors.
Results: Out of 7061 pts (PY of exposure = 23,394), 42 (0.6%) had an ILD event; median time to ILD event was 1144 days. The IR for ILD with both doses of tofacitinib treatment was 0.18 (Table; Figure). In a placebo-controlled cohort analysis in tofacitinib P2/3/4 studies, ILD event IRs were numerically lower with tofacitinib vs placebo (Table). IRs were numerically higher in pts aged ≥65 vs <65 years, and in Asian vs non-Asian countries; 95% confidence intervals were wide and overlapped. IRs generally remained stable over time, although the number of events was small in each interval (Figure). There were 17/42 (40.5%) serious AEs of ILD; 35/42 events (83.3%) were mild to moderate in severity. In the case-matched control analysis (case 42 vs control 210), the ILD group had a numerically higher proportion of pts who were Asian (31.0% vs 17.6%), smokers/ex-smokers (50.0% vs 39.5%), RF-positive (89.2% vs 71.0%), anti-CCP antibody positive (54.8% vs 46.7%), had received prior MTX (90.5% vs 79.5%), non-MTX csDMARDs (61.9% vs 55.2%), TNF inhibitors (26.2% vs 18.6%), and concomitant glucocorticoids (71.4% vs 52.9%), and had higher baseline mean ESR (57.0 vs 46.9 mm/hr) and CRP (25.4 vs 15.4 mg/L) vs controls.
Conclusion: Across P1/2/3/4/LTE studies, ILD events following tofacitinib treatment were low, and were associated with known risk factors.
1. Curtis J et al. Arthritis Res Ther 2015; 17: 319.
2. Furukawa H et al. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med 2015; 9 (Suppl 1): 1-7.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Citera G, Mysler E, Madariaga H, Cardiel MH, Castañeda O, Fischer A, Richette P, Chartrand S, Park JK, Strengholt S, Rivas JL, Thorat A, Girard T, Kwok K, Wang L, Ponce de Leon D. Low Interstitial Lung Disease Event Rate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pooled Post Hoc Analysis of Data from the Tofacitinib Clinical Development Program [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-interstitial-lung-disease-event-rate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-of-data-from-the-tofacitinib-clinical-development-program/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-interstitial-lung-disease-event-rate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-of-data-from-the-tofacitinib-clinical-development-program/