Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster III: Therapy
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Studies have shown that patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
have significantly compromised physical health and quality of life, and
negative effect on work productivity has been seen (Tillett W, et al. Rheumatology
[Oxford]. 2012;51:275-283). The Work Limitations Questionnaire (WLQ) is a reliable
tool for assessing limitations on work productivity in patients with chronic
health conditions and was used in the PALACE 1, 2, and 3 trials, which compared
the efficacy and safety of apremilast (APR), an oral phosphodiesterase 4
inhibitor, with placebo in patients with active PsA despite prior conventional
disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and/or biologics. Our objective
was to assess the effect of APR on work productivity and work limitations over
52 weeks in a pooled analysis of 802 patients in PALACE 1-3.
Methods:
Patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive placebo,
APR 30 mg BID (APR30), or APR 20 mg BID (APR20). Early
escape to active treatment was possible at Week 16 for placebo patients, and at Week 24, all patients remaining on placebo were
re-randomized to APR30 or APR20. The WLQ, a 25-item questionnaire
that assesses the impact of chronic health conditions on work performance and
productivity, was administered at baseline, Week 16, and Week 52. Work limitations
were categorized into 4 domains: physical demands (PDS), mental demands (MDS),
time management demands (TMS), and output demands (ODS). An
overall WLQ Productivity Score is calculated and expressed as the percentage
loss in productivity associated with illness
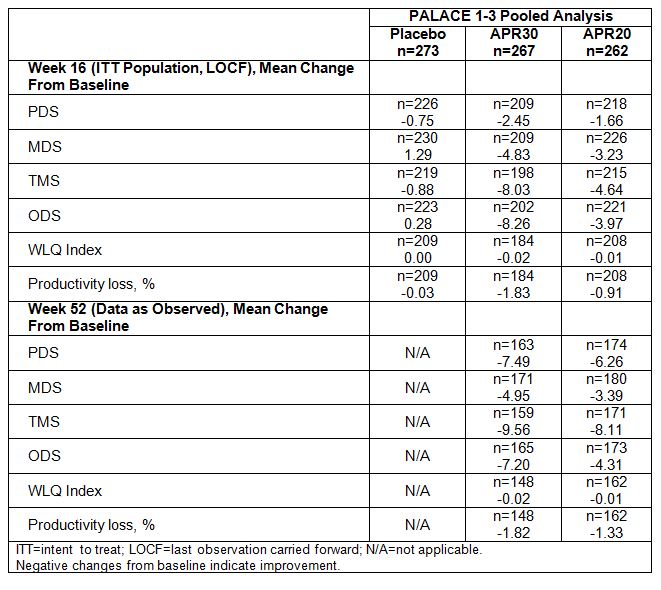
Results: Patient
demographics (age, sex, geographic region) were similar across treatment groups
for patients who completed at least 1 domain of the WLQ at baseline. At Week
16, both APR30 and APR20 were associated with a greater mean change from
baseline in PDS, MDS, TMS, and ODS vs. placebo, resulting in an improvement
from baseline in work productivity loss. Productivity improvements in PDS, MDS,
TMS, and ODS were also maintained among patients receiving APR30 and APR20 to Week
52 (Table).
Conclusion: APR30
and APR20 treatment increased work productivity and improved work limitations
among patients in the PALACE 1-3 studies. Improvements in productivity loss
were maintained through 52 Weeks of treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang F, Clancy Z, Li S. Long-Term Work Productivity Improvement Associated with Apremilast, an Oral Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor, in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Pooled Analysis of 3 Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-work-productivity-improvement-associated-with-apremilast-an-oral-phosphodiesterase-4-inhibitor-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-analysis-of-3-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-work-productivity-improvement-associated-with-apremilast-an-oral-phosphodiesterase-4-inhibitor-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-analysis-of-3-phase-3-studies/