Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Title: 6W021 ACR Abstract: Misc Rheumatic & Inflam DZ II (2970–2975)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose:
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is one of the most serious complications associated with rheumatic systemic diseases. Patients with ILD have increased mortality and limited treatment options. Lung transplant has been recognized as an option for patients with end-stage ILD associated with rheumatic systemic diseases (RSD-ILD). However, rheumatic diseases are still sometimes considered a contraindication for lung transplant because of concerns for worse outcomes.
Our aims were to: a) assess long-term post-transplant survival in patients with RSD-ILD and b) compare post post-transplant survival of patients with RSD-ILD to patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Methods:
Single center study in a referral center for lung transplant of all patients who underwent lung transplantation for RSD-ILD between 1998 and 2017. This cohort was compared with patients with IPF (group-matched for age, transplant year and basiliximab induction). Cumulative survival rates after transplantation were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared between groups using the log-rank test.
Results:
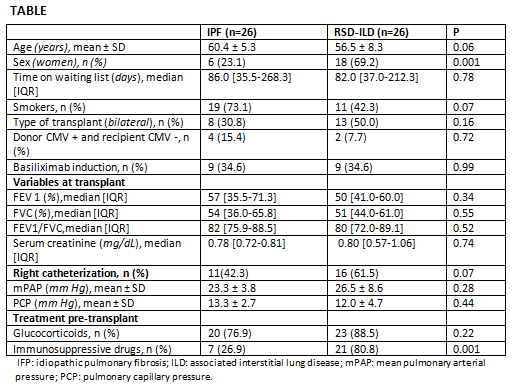
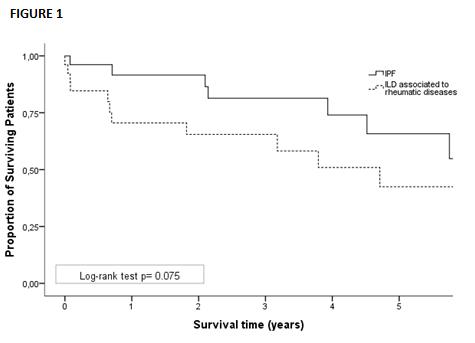
We studied 26 patients with RSD-ILD matched to 26 patients with IPF. The underlying diseases of patients with RSD-ILD were: Rheumatoid arthritis (n=8), Scleroderma (n=6), Sjögren syndrome (n=4), ANCA-vasculitis (n=3), Anti synthetase syndrome (n=2), Takayasu arteritis (n=1), Dermatomyositis (n=1), Systemic lupus erythematosus (n=1). The comparative study of baseline characteristics between both groups is shown in the TABLE. Cumulative survival rates at 5 years post-transplant did no differ significantly between RSD-ILD and IFP [42.4% vs 65.8% (p=0.075)] (FIGURE 1).
Conclusion:
Patients undergoing lung transplantation for RSD-ILD had similar long term post-transplant survival as those with IPF. These data support that lung transplantation should be considered in patients with end-stage ILD associated with rheumatic diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Prieto Peña D, Martinez Meñaca A, Calderón Goercke M, Martín-Varillas JL, Atienza-Mateo B, Mora Cuesta VM, Fernandez Rozas S, Iturbe Fernandez D, González-Vela C, Cifrian Martinez JM, González-Gay MA, Blanco R. Long-Term Survival in Lung Transplantation for Interstitial Lung Disease Due to Rheumatic Systemic Diseases. Study of 26 Cases of a Single Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-survival-in-lung-transplantation-for-interstitial-lung-disease-due-to-rheumatic-systemic-diseases-study-of-26-cases-of-a-single-center/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-survival-in-lung-transplantation-for-interstitial-lung-disease-due-to-rheumatic-systemic-diseases-study-of-26-cases-of-a-single-center/