Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster III: Biosimilars and New Compounds
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Sarilumab has shown efficacy in RA both as monotherapy and in combination with csDMARDs in Phase 3 trials. We assessed long-term safety from the sarilumab clinical development program in adult pts with RA who received sarilumab+csDMARD or sarilumab monotherapy from: MOBILITY (NCT01061736); TARGET (NCT01709578); ASCERTAIN (NCT01768572); MONARCH (NCT02332590); ACT11575 (NCT01217814); ONE (NCT02121210); COMPARE (NCT01764997); EASY (NCT02057250); and an ongoing open-label extension EXTEND (NCT01146652), which enrolled pts completing originator studies.
Methods:
Data (cut-off Jan 30, 2018) were pooled from pts on sarilumab+csDMARD (N=2887) or sarilumab monotherapy (N=471). Pts had received sarilumab 200 mg or 150 mg q2w SC, except 151 pts from MOBILITY Part A who received 100 mg qw, 150 mg qw, or 100 mg q2w. Treatment-emergent (TE) adverse events (AEs), AEs of special interest (AESI), and discontinuations were assessed.
Results:
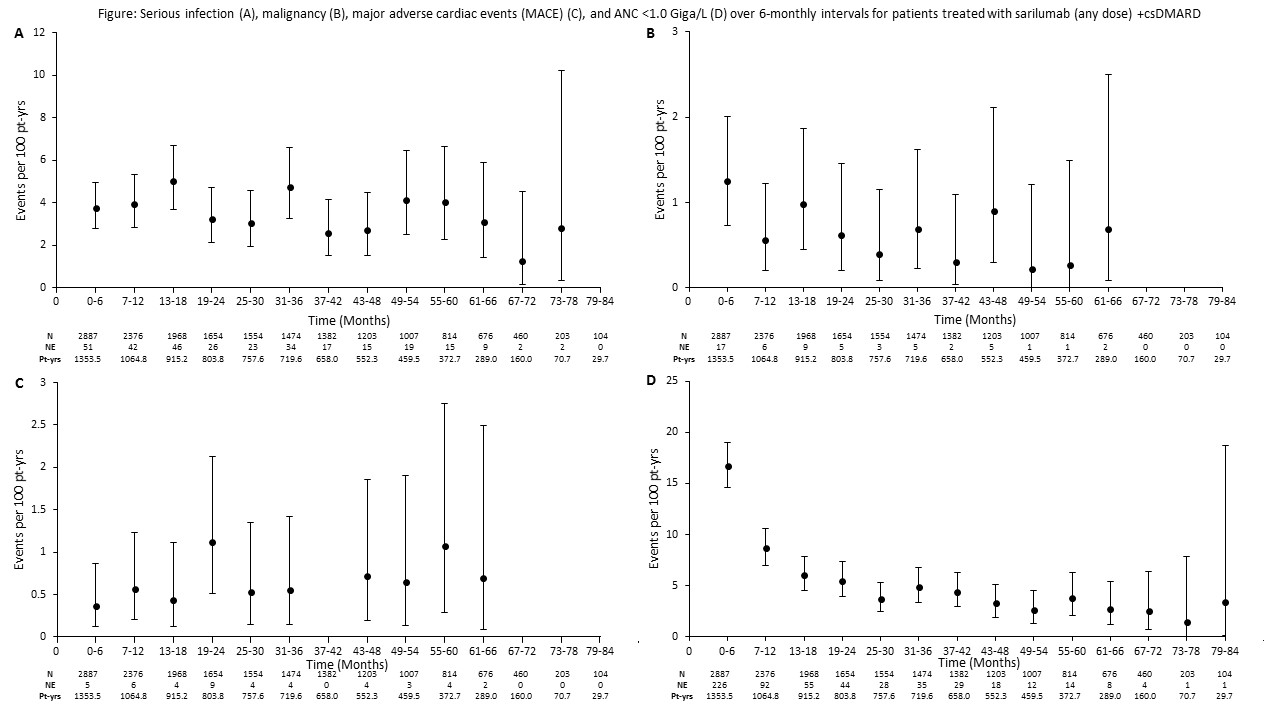
Baseline characteristics were similar between sarilumab+csDMARD and monotherapy pools (mean age 52 yrs; 81–83% female). At baseline, mean RA duration was 9.4 vs 8.3 yrs in combination and monotherapy pools, respectively, with 38.7% vs 8.5% of pts having received prior bDMARDs. Cumulative drug exposure was 7,985.5 vs 798.7 pt-yrs, with maximum duration 7.3 vs 3.5 yrs for sarilumab+csDMARD vs monotherapy, respectively. Exposure-adjusted rates of TEAEs, serious AEs, and TEAEs leading to discontinuations were similar between pools (Table). Infections were the most common AESI. Serious infection event rates were 3.7 vs 1.0/100 pt-yrs for combination vs monotherapy, respectively, and not associated with decreased absolute neutrophil counts (ANC). Incidences of ALT >3x upper limit of normal were 10.3% and 5.5% for sarilumab+csDMARD and monotherapy, and ANC <1.0 Giga/L were 12.7% and 14.9%, respectively. Rates of confirmed GI perforation for combination vs monotherapy were 0.1 vs 0/100 pt-yrs. Analyzing data by 6-month intervals showed no increase in rate over time for serious infections, malignancy, major adverse cardiac events, or ANC <1.0 Giga/L (Figure).
Conclusion:
The long-term safety profile of sarilumab (a human IL-6R blocker recently approved for the treatment of RA), either as monotherapy (observed for >3.5 yrs) or with csDMARD, (observed for >7 yrs) remains stable and consistent with the anticipated profile of an IL-6Rα blocker.
Acknowledgements:
Study funding and medical writing support (Julie Gray, Adelphi Communications) provided by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
|
Table. Overview of safety analysis from the two pooled data sets sarilumab (any dose) +csDMARD and sarilumab monotherapy (any dose) |
||
|
|
Sarilumab+csDMARD |
Sarilumab monotherapy |
|
Safety overview: (patients/100 pt-yrs)a |
|
|
|
TEAEs |
2489/1726 (144.2) |
386/254.3 (151.8) |
|
Serious TEAEs |
685/7270 (9.4) |
52/770.4 (6.7) |
|
TEAEs leading to death |
31/8187 (0.4) |
5/812.3 (0.6) |
|
TEAEs leading to discontinuation |
705/8061 (8.7) |
53/804.9 (6.6) |
|
AESI: (events/100 pt-yrs)b |
Pt-yrs=8187.7 |
Pt-yrs =812.4 |
|
Infections |
4451 (54.4) |
446 (54.9) |
|
Serious Infections |
301 (3.7) |
8 (1.0) |
|
Opportunistic Infections |
76 (0.9) |
6 (0.7) |
|
Herpes zosterc |
60 (0.7) |
8 (1.0) |
|
Tuberculosisc |
4 (0.0) |
1 (0.1) |
|
Leukopeniad |
1482 (18.1) |
244 (30.0) |
|
Thrombocytopeniad |
147 (1.8) |
8 (1.0) |
|
Hepatic disorders |
726 (8.9) |
58 (7.1) |
|
Confirmed GI perforations |
9 (0.1) |
0 |
|
Elevation in lipidsd |
498 (6.1) |
18 (2.2) |
|
Major adverse cardiovascular eventse |
45 (0.5) |
2 (0.2) |
|
Hypersensitivity |
444 (5.4) |
48 (5.9) |
|
Anaphylaxis |
0 |
0 |
|
Injection site reactions |
1934 (23.6) |
279 (34.3) |
|
Malignancy |
56 (0.7) |
5 (0.6) |
|
Malignancy excluding NMSC |
38 (0.5) |
4 (0.5) |
|
Lupus-like syndrome |
5 (0.1) |
0 |
|
Demyelinating disorders |
0 |
1 (0.1) |
|
GI, gastrointestinal; NMSC, non-melanoma skin cancer; aexposure period is cumulative time at risk of first event; bAESI were investigator reported; exposure period is cumulative total TEAE period; call cases of herpes zoster reported to date were localized; herpes zoster and tuberculosis were reported as opportunistic infections per protocol (not per clinical judgment); dindividual events were reported and laboratory abnormalities were not necessarily persistent; eMACE includes cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for either unstable angina and/or transient ischemic attack. |
||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Lin Y, St. John G, van der Heijde D, Qiu C, Gómez-Reino JJ, Maldonado-Cocco JA, Stanislav M, Seriolo B, Burmester GR. Long-Term Safety with Sarilumab Plus Conventional Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (csDMARDs) and Sarilumab Monotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An Integrated Analysis with 9,000 Patient-Years (Pt-Yrs) of Follow-up [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-safety-with-sarilumab-plus-conventional-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-csdmards-and-sarilumab-monotherapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-an-integrated-analysis-with-9000-p/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-safety-with-sarilumab-plus-conventional-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-csdmards-and-sarilumab-monotherapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-an-integrated-analysis-with-9000-p/