Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
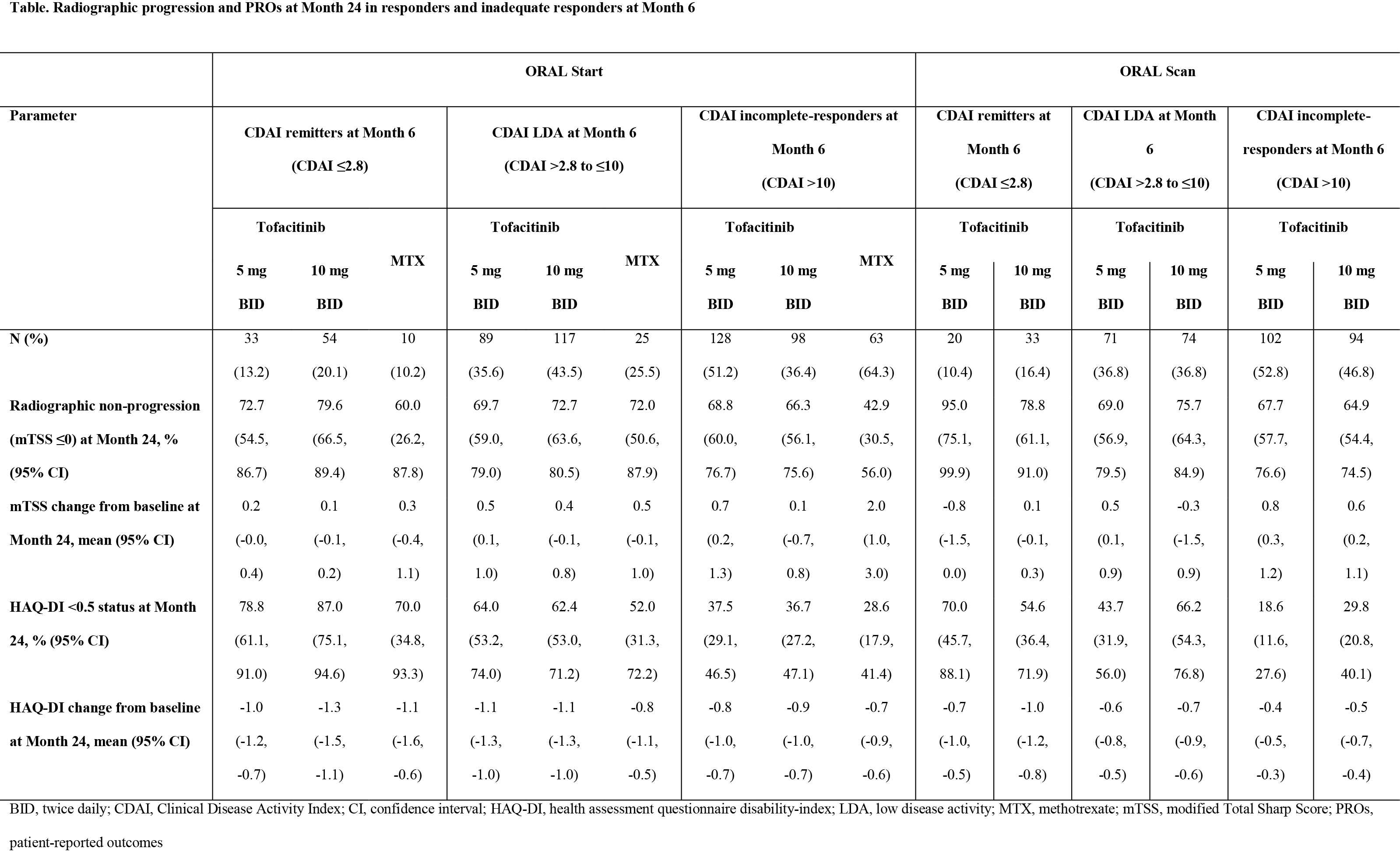
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. This analysis assessed if patients achieving Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) remission (REM) or low disease activity (LDA) at Month 6 had less radiographic progression and improved patient-reported outcomes (PROs) at Month 24 and compared results between tofacitinib and MTX.
Methods: ORAL Start (NCT01039688) and ORAL Scan (NCT00847613) were Phase 3 randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) in MTX therapeutically-naïve and MTX-inadequate response (IR) patients with RA, respectively, who received tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (BID) monotherapy vs MTX monotherapy or tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID + MTX vs placebo + MTX, respectively. This was an observed analysis of patients with radiographs at Months 6, 12, and 24, excluding placebo-treated patients in ORAL Scan. Patients were assigned to subpopulations according to CDAI responses at Month 6: REM (CDAI ≤2.8); LDA (CDAI >2.8 to ≤10); or incomplete-responders (CDAI ˃10). Outcomes included the proportion of patients with no radiographic progression (change in modified Total Sharp Score [mTSS] ≤0) and/or HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) <0.5 (defined as normative) at Month 24, and mean changes from baseline in mTSS and HAQ-DI.
Results: In ORAL Start, 250, 269, and 98 patients received tofacitinib 5 mg BID, tofacitinib 10 mg BID, and MTX, respectively. In ORAL Scan, 193 and 201 patients received tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID, respectively. Baseline demographics were generally similar between subpopulations within each RCT; however, incomplete-responders generally had higher baseline disease activity. In both ORAL Start and Scan, patients in REM or LDA with tofacitinib at Month 6 were more likely to be non-progressors and achieve normative HAQ-DI scores at Month 24 (Table). Tofacitinib-treated patients in REM at Month 6 generally had better HAQ-DI scores at Month 24 than LDA patients. In ORAL Start at Month 6, a higher proportion of tofacitinib- than MTX-treated patients were in REM or LDA (Table). CDAI incomplete-responders receiving tofacitinib had improved HAQ-DI scores and less radiographic progression compared with MTX. Overall, more patients receiving tofacitinib than MTX in REM or LDA were non-progressors and achieved HAQ-DI scores <0.5.
Conclusion: More MTX-naïve or MTX-IR tofacitinib-treated patients achieving CDAI REM or LDA at Month 6 were radiographic non-progressors with normative HAQ-DI scores at Month 24, compared to CDAI incomplete-responders. In ORAL Start, more tofacitinib than MTX-treated MTX-naïve patients achieved CDAI REM or LDA at Month 6 with better PROs and radiographic outcomes at Month 24.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Kavanaugh A, Kivitz AJ, van der Heijde D, Hoffmann E, Akylbekova E, Soonasra A, Snyder M, Soma K, Bananis E, Smolen JS. Long-Term Radiographic and Patient-Reported Outcomes Based on Clinical Disease Activity Index Responses with Tofacitinib at 6 Months [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-radiographic-and-patient-reported-outcomes-based-on-clinical-disease-activity-index-responses-with-tofacitinib-at-6-months/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-radiographic-and-patient-reported-outcomes-based-on-clinical-disease-activity-index-responses-with-tofacitinib-at-6-months/